The Wrist Is Blank To The Elbow
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
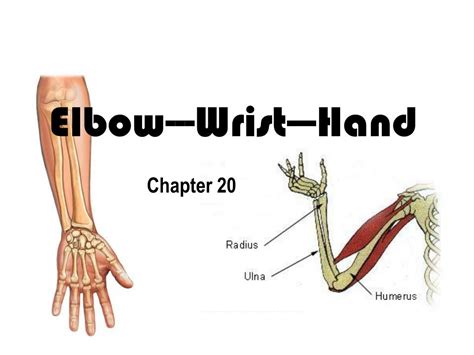
Table of Contents
- The Wrist Is Blank To The Elbow
- Table of Contents
- The Wrist is Blank to the Elbow: Exploring the Enigma of Congenital Deficiency
- Understanding the Anatomy of a Normal Forearm
- The Spectrum of "Wrist is Blank to the Elbow"
- 1. Mild Deficiency:
- 2. Moderate Deficiency:
- 3. Severe Deficiency:
- Causes and Risk Factors: The Genetic Puzzle
- Impact on Daily Life: Challenges and Adaptations
- Treatment and Management Options: Restoring Function and Improving Quality of Life
- 1. Prosthetic Devices:
- 2. Orthotics:
- 3. Surgery:
- 4. Occupational Therapy:
- 5. Physical Therapy:
- 6. Psychological Support:
- The Role of Technology and Advancements
- Conclusion: Embracing Diversity and Supporting Individuals
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Wrist is Blank to the Elbow: Exploring the Enigma of Congenital Deficiency
The phrase "the wrist is blank to the elbow" describes a severe form of congenital limb deficiency, specifically a longitudinal deficiency of the forearm. This condition, also known as terminal transverse deficiency or radial longitudinal deficiency, affects the bones and soft tissues of the forearm, resulting in a shortened or absent forearm, leaving the hand seemingly attached directly to the elbow. The severity varies greatly, ranging from minor shortening of the radius or ulna to a complete absence of both bones. Understanding this complex condition requires exploring its causes, impact, and the various treatment options available.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Normal Forearm
Before delving into the specifics of the condition, it's crucial to understand the normal anatomy of the forearm. The forearm is composed of two long bones: the radius (on the thumb side) and the ulna (on the pinky finger side). These bones articulate with the humerus (upper arm bone) at the elbow joint and with the carpal bones (wrist bones) at the wrist joint. Numerous muscles, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels run along the length of the forearm, controlling hand movements, providing sensation, and nourishing the tissues. The intricate interplay of these structures allows for a wide range of hand and wrist motions, essential for daily activities.
The Spectrum of "Wrist is Blank to the Elbow"
The term "wrist is blank to the elbow" is a lay description, highlighting the striking absence of the visible forearm. Clinically, this condition falls under the broader umbrella of limb reduction defects, specifically focusing on longitudinal deficiencies of the radius and/or ulna. The spectrum of severity is vast:
1. Mild Deficiency:
This may involve a slight shortening of the radius or ulna, resulting in a subtly deformed forearm. Hand function might be relatively normal, although there might be some limitations in range of motion.
2. Moderate Deficiency:
A more significant shortening or partial absence of one or both forearm bones is characteristic of this level of severity. The hand may be smaller, and the range of motion significantly restricted. This can significantly impact the individual's ability to perform fine motor skills.
3. Severe Deficiency:
In severe cases, both the radius and ulna are severely shortened or absent altogether, leading to the appearance of the hand directly attached to the elbow. Hand function is dramatically compromised, and specialized assistive devices are often necessary for even basic tasks.
Causes and Risk Factors: The Genetic Puzzle
The precise cause of congenital forearm deficiencies, including the "wrist is blank to the elbow" presentation, remains largely unknown. While genetic factors are strongly implicated, the exact genes responsible have not been definitively identified in most cases. However, researchers have identified several possibilities:
-
Genetic Mutations: Several studies suggest a connection between specific genetic mutations and limb development disorders. These mutations can disrupt the complex signaling pathways crucial for proper bone and tissue formation during embryonic development.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain teratogens (substances that cause birth defects) during pregnancy, such as certain medications or infections, may increase the risk of limb malformations.
-
Multifactorial Inheritance: The most likely scenario is a complex interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental influences. A combination of genetic vulnerability and exposure to teratogens might trigger the development of this condition.
Impact on Daily Life: Challenges and Adaptations
The implications of "the wrist is blank to the elbow" extend far beyond the purely physical. The functional limitations imposed by this condition can significantly affect various aspects of daily life:
-
Fine Motor Skills: Tasks requiring dexterity, such as writing, buttoning clothes, or using utensils, can be incredibly challenging, if not impossible without adaptive devices.
-
Gross Motor Skills: Depending on the severity, even simple activities like carrying objects or reaching for things may be difficult.
-
Psychological Well-being: The visible difference and functional limitations can lead to emotional and psychological challenges, including body image issues, low self-esteem, and social isolation.
Treatment and Management Options: Restoring Function and Improving Quality of Life
Treatment for "wrist is blank to the elbow" is highly individualized and depends on the severity of the deficiency, the child's age, and the family's preferences. The primary goals are to optimize hand function, improve independence, and enhance the child's overall quality of life. Common approaches include:
1. Prosthetic Devices:
Prosthetic limbs can significantly enhance functionality, enabling individuals to perform tasks that would otherwise be impossible. Modern prosthetics are sophisticated, lightweight, and adaptable, offering improved control and aesthetics.
2. Orthotics:
Orthotic devices provide support and improve hand function. Custom-made splints can help stabilize the hand, improve grip strength, and reduce fatigue.
3. Surgery:
In some cases, surgery may be considered to improve bone alignment, enhance muscle function, or address associated deformities. However, surgical options are often limited due to the complexity of the condition.
4. Occupational Therapy:
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in adapting daily activities to the individual's limitations and maximizing functional independence. Therapists work with individuals to develop compensatory strategies, learn adaptive techniques, and use assistive devices effectively.
5. Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy focuses on improving range of motion, strengthening muscles, and enhancing overall physical fitness. This can improve dexterity, reduce pain, and enhance the individual's overall well-being.
6. Psychological Support:
Addressing the emotional and psychological consequences of the condition is vital. Counseling and support groups can help individuals cope with body image issues, build self-esteem, and develop effective coping mechanisms.
The Role of Technology and Advancements
Technological advancements continually expand the treatment options available for individuals with congenital limb deficiencies. Innovations in prosthetic design, including advanced materials and myoelectric control, offer greater functionality and comfort. 3D printing is revolutionizing the creation of customized prosthetic devices and orthotic splints, ensuring a better fit and enhanced performance. Further research into genetics and developmental biology holds the promise of eventually leading to better preventative strategies and more effective treatments.
Conclusion: Embracing Diversity and Supporting Individuals
"The wrist is blank to the elbow" represents a significant challenge, but it doesn't define an individual's potential. With appropriate medical care, therapeutic interventions, and ongoing support, individuals with this condition can lead fulfilling lives, achieving their personal and professional goals. Raising awareness, fostering inclusive environments, and supporting research efforts are crucial for improving the lives of individuals affected by this condition and many others like it. The focus should always be on celebrating individual strengths, embracing diversity, and promoting a society that values inclusion and accessibility for everyone. The journey may be complex, but with the right support and resources, the possibilities are limitless.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Wrist Is Blank To The Elbow . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.