The Total Manufacturing Cost Variance Is
Holbox
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
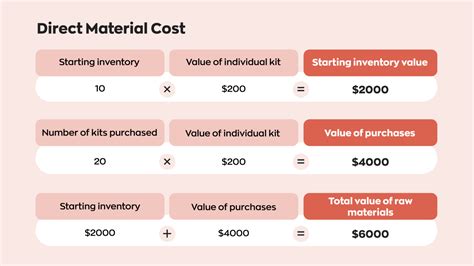
Table of Contents
The Total Manufacturing Cost Variance: A Deep Dive into Understanding and Analyzing Production Costs
Understanding and managing costs is crucial for any manufacturing business's success. A key metric in this process is the total manufacturing cost variance. This variance reveals the difference between the actual costs incurred in production and the budgeted or standard costs. Analyzing this variance allows businesses to identify areas of inefficiency, improve operational processes, and ultimately boost profitability. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the total manufacturing cost variance, exploring its components, calculation methods, and practical applications.
What is the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance?
The total manufacturing cost variance represents the overall difference between the actual manufacturing costs and the planned or standard manufacturing costs for a given period. It's a crucial indicator of the efficiency and effectiveness of the manufacturing process. A favorable variance means that actual costs are lower than budgeted costs, while an unfavorable variance indicates higher-than-expected costs.
This variance isn't just a single number; it's a composite of several individual variances, each highlighting different aspects of the manufacturing process. Understanding these individual components allows for more precise diagnosis and targeted improvements.
Key Significance: The total manufacturing cost variance is critical for:
- Performance Evaluation: It provides a clear picture of the manufacturing department's performance against budget.
- Cost Control: It helps identify areas of cost overruns and potential savings.
- Decision Making: It informs strategic decisions regarding pricing, production planning, and process improvements.
- Process Improvement: It highlights weaknesses in the production process, leading to efficiency gains.
Components of the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance
The total manufacturing cost variance is typically broken down into three main components:
-
Direct Materials Cost Variance: This variance reflects the difference between the actual cost of direct materials used and the standard cost of materials for the actual production volume. It's further divided into:
- Direct Materials Price Variance: This measures the difference between the actual price paid for materials and the standard price, multiplied by the actual quantity used.
- Direct Materials Quantity Variance: This measures the difference between the actual quantity of materials used and the standard quantity allowed for the actual output, multiplied by the standard price.
-
Direct Labor Cost Variance: This variance represents the difference between the actual direct labor cost and the standard direct labor cost for the actual production volume. It's similarly broken down into:
- Direct Labor Rate Variance: This measures the difference between the actual labor rate and the standard labor rate, multiplied by the actual hours worked.
- Direct Labor Efficiency Variance: This measures the difference between the actual labor hours worked and the standard labor hours allowed for the actual output, multiplied by the standard labor rate.
-
Manufacturing Overhead Cost Variance: This variance represents the difference between the actual manufacturing overhead costs and the standard manufacturing overhead costs applied to production. This component is more complex, often further categorized into:
- Variable Overhead Spending Variance: Compares actual variable overhead costs to the budgeted variable overhead costs based on actual activity levels.
- Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance: Measures the difference between actual and standard activity levels, multiplied by the standard variable overhead rate.
- Fixed Overhead Spending Variance: Compares actual fixed overhead costs to the budgeted fixed overhead costs.
- Fixed Overhead Volume Variance: Measures the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead costs and the fixed overhead costs applied based on standard production levels.
Calculating the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance
Calculating the total manufacturing cost variance involves several steps, starting with the calculation of each individual component variance outlined above. Here's a generalized approach:
1. Determine Standard Costs: Establish standard costs for direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead based on historical data, industry benchmarks, and engineering estimates. This includes defining standard quantities, prices, and rates.
2. Collect Actual Costs: Accurately record actual costs incurred during the production period. This includes the actual cost of materials purchased and used, actual labor hours and rates, and actual manufacturing overhead costs.
3. Calculate Individual Variances: Using the standard and actual cost data, calculate each of the individual variance components (direct materials price and quantity, direct labor rate and efficiency, and manufacturing overhead variances). Remember to clearly identify whether each variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
4. Calculate the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance: Finally, sum up all the individual variances to arrive at the total manufacturing cost variance. A positive value indicates a favorable variance, while a negative value indicates an unfavorable variance. The formula is:
Total Manufacturing Cost Variance = Direct Materials Cost Variance + Direct Labor Cost Variance + Manufacturing Overhead Cost Variance
Analyzing and Interpreting the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance
Simply calculating the total variance isn't enough; understanding its underlying causes is crucial. A large unfavorable variance requires a detailed investigation to pinpoint the root causes. This might involve analyzing:
- Material Usage: Were more materials used than expected? Was there waste or spoilage? Were substandard materials used?
- Labor Efficiency: Were more labor hours required than anticipated? Were there skill deficiencies among workers? Were there production bottlenecks?
- Overhead Costs: Were utilities, rent, or maintenance costs higher than budgeted? Were there unexpected repairs or downtime?
Using the Total Manufacturing Cost Variance for Improvement
The analysis of the total manufacturing cost variance should lead to actionable steps to improve efficiency and reduce costs. These actions might include:
- Improving Material Procurement: Negotiating better prices with suppliers, improving inventory management, or implementing stricter quality control measures.
- Enhancing Labor Productivity: Providing employee training, improving production processes, or investing in new technology to streamline operations.
- Optimizing Overhead Costs: Negotiating better deals with utility providers, improving maintenance schedules, or finding ways to reduce waste and energy consumption.
- Implementing Cost Control Systems: Strengthening internal controls to prevent cost overruns and ensure efficient resource allocation.
Advanced Considerations and Challenges
While calculating and analyzing the total manufacturing cost variance provides valuable insights, several factors need consideration:
- Complexity: The calculation and analysis can be complex, especially in large manufacturing operations with many product lines and diverse cost drivers.
- Data Accuracy: Accurate cost data is essential. Inaccurate data will lead to misleading results and ineffective decision-making.
- External Factors: External factors such as economic fluctuations, changes in raw material prices, and unexpected disruptions can significantly impact the variance. These should be considered when interpreting the results.
- Integration with Other Metrics: The total manufacturing cost variance should be analyzed in conjunction with other key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production volume, sales revenue, and profit margin for a holistic view of business performance.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Manufacturing Success
The total manufacturing cost variance is a powerful tool for analyzing production costs, identifying areas for improvement, and ultimately boosting profitability in the manufacturing industry. By thoroughly understanding its components, calculation methods, and interpretation, manufacturing businesses can leverage this metric to enhance operational efficiency and achieve greater success. The process of analyzing this variance should be continuous and iterative, leading to ongoing refinements in manufacturing practices and a stronger bottom line. Remember, the goal isn't just to identify variances but to understand their underlying causes and implement effective solutions. Through diligent analysis and proactive improvements, businesses can turn unfavorable variances into opportunities for growth and increased profitability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Question Plum Select All The True Statements That Are True
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Processes Can Viruses Carry Out
Mar 22, 2025
-
Find F In Terms Of G
Mar 22, 2025
-
Performance Evaluations Are Best Done Using
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Presidents Power Has Largely Depended On
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Total Manufacturing Cost Variance Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
