The Threat Of New Entrants Is High When There Are
Holbox
Mar 18, 2025 · 7 min read
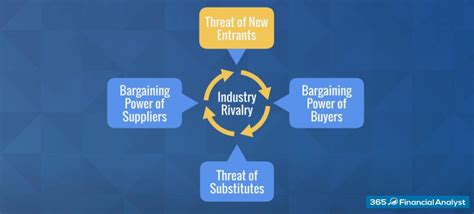
Table of Contents
- The Threat Of New Entrants Is High When There Are
- Table of Contents
- The Threat of New Entrants is High When There Are… Low Barriers to Entry!
- Low Barriers to Entry: The Core Issue
- 1. Low Capital Requirements: A Welcoming Mat for New Businesses
- 2. Easy Access to Distribution Channels: Opening the Doors to Market
- 3. Lack of Product Differentiation: A Sea of Sameness
- 4. Absence of Government Regulations and Legal Barriers: A Clear Path Forward
- 5. Low Switching Costs for Customers: Easy to Change Sides
- 6. Lack of Economies of Scale: Small Can Compete with Big
- 7. Limited Access to Proprietary Technology or Know-How: No Secret Sauce
- Mitigating the Threat of New Entrants: Strategies for Existing Businesses
- Conclusion: A Constant Vigilance
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Threat of New Entrants is High When There Are… Low Barriers to Entry!
The threat of new entrants is a crucial element of Porter's Five Forces, a framework for analyzing the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry. A high threat of new entrants signifies a less attractive industry, as it indicates increased competition, price pressure, and reduced profitability for existing players. This threat isn't just about if new companies will enter, but how easily they can. This article delves deep into the factors contributing to a high threat of new entrants, exploring each element with detailed examples.
Low Barriers to Entry: The Core Issue
The fundamental reason the threat of new entrants is high is the presence of low barriers to entry. These barriers are obstacles that make it difficult and costly for new companies to enter a market. When these barriers are low, it's significantly easier for new competitors to jump in, disrupting the existing market dynamics.
1. Low Capital Requirements: A Welcoming Mat for New Businesses
One of the most significant barriers to entry is the amount of capital required to start a business. Industries with low capital requirements are particularly vulnerable to new entrants. Think about it: if you can start a small online business with minimal investment, the hurdle to entry is substantially lower than trying to establish a car manufacturing plant.
Examples:
- Online retail: Setting up an e-commerce store through platforms like Shopify or Etsy requires relatively low capital investment compared to opening a physical retail store. This explains the booming number of online businesses.
- Blogging and content creation: The low barrier to entry in blogging and content creation has led to a highly competitive landscape. While monetization can be challenging, starting a blog only requires a domain name and hosting, making it easily accessible.
- Food trucks and mobile businesses: Compared to opening a traditional restaurant, food trucks require significantly less capital for setup, rent, and infrastructure, facilitating rapid growth in this sector.
2. Easy Access to Distribution Channels: Opening the Doors to Market
Distribution channels are the pathways a company uses to reach its customers. If access to these channels is easy, it lowers the barrier to entry. Conversely, if established companies control distribution channels, it creates a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Examples:
- Online marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy provide readily available distribution channels for new businesses, reducing the need for extensive marketing and logistics investments. This has democratized commerce, but simultaneously increased competition.
- Social media marketing: The rise of social media has opened new and relatively inexpensive distribution channels for businesses of all sizes. While organic reach can be challenging, paid advertising offers a relatively low-cost pathway to potential customers.
- Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands: The ability to bypass traditional retail channels by selling directly to consumers online reduces reliance on established distributors, lowering the barrier to entry for many new businesses.
3. Lack of Product Differentiation: A Sea of Sameness
In industries where products or services are largely undifferentiated, new entrants can easily compete on price. The absence of unique features or strong brand loyalty makes it easier for newcomers to attract customers simply by offering lower prices.
Examples:
- Commodity markets: Markets for agricultural products or raw materials often have low product differentiation. New players can enter by simply offering a competitive price.
- Generic pharmaceuticals: Once a drug patent expires, generic drug manufacturers can enter the market with essentially identical products, leading to intense price competition.
- Basic services: Simple services like cleaning, lawn care, or basic consulting often lack significant product differentiation, making entry easier for new providers.
4. Absence of Government Regulations and Legal Barriers: A Clear Path Forward
Strict government regulations, licensing requirements, or intellectual property protection can significantly deter new entrants. Industries with minimal regulatory hurdles face a higher threat of new competitors.
Examples:
- Some craft industries: While some craft industries have guilds or associations, many lack stringent regulatory bodies, leading to a relatively easy entry for new artisans.
- Small-scale service businesses: Many service-based businesses, such as freelance writing or consulting, operate with minimal government oversight, reducing regulatory barriers.
- Countries with lax regulations: Countries with less stringent business registration and operational regulations tend to attract a higher number of new businesses, increasing competition.
5. Low Switching Costs for Customers: Easy to Change Sides
If customers can easily switch between different providers without incurring significant costs or inconvenience, it reduces the loyalty to existing companies and makes it easier for new entrants to gain market share.
Examples:
- Online services: Switching from one email provider, streaming service, or cloud storage provider to another often involves minimal effort and no financial penalty.
- Commodity purchases: Customers are highly likely to switch providers for basic commodities like gasoline or groceries if a cheaper option is available nearby.
- Simple products with low brand loyalty: Products lacking a strong brand identity are easy to switch between, as customers primarily focus on price or availability.
6. Lack of Economies of Scale: Small Can Compete with Big
Economies of scale refer to cost advantages enjoyed by large companies due to their production volume. If economies of scale are not significant, smaller companies can compete effectively against established players, increasing the threat of new entrants.
Examples:
- Small-batch production: Businesses focusing on handcrafted items or bespoke services often don't experience significant economies of scale, allowing smaller businesses to compete effectively.
- Localized businesses: Businesses targeting a niche market or specific geographic area might not need large-scale production to be successful, minimizing the advantage enjoyed by larger companies.
- Digital businesses: Many online businesses can leverage digital infrastructure to scale their operations without significant increases in costs, reducing the need for large-scale production.
7. Limited Access to Proprietary Technology or Know-How: No Secret Sauce
If a company's competitive advantage doesn't rely on proprietary technology or specialized knowledge that's difficult to replicate, it's easier for new entrants to enter the market.
Examples:
- Industries based on readily available technology: Industries using publicly accessible technologies or open-source software are vulnerable to new entrants who can easily leverage these resources.
- Businesses with easily replicable processes: If a company’s success depends on easily duplicated processes or business models, the threat of new entrants increases.
- Service-based industries: Some service-based industries rely less on exclusive technological advantages compared to those in manufacturing or pharmaceuticals.
Mitigating the Threat of New Entrants: Strategies for Existing Businesses
While the factors listed above can be hard to alter, existing businesses can implement strategies to mitigate the threat of new entrants:
-
Product Differentiation and Brand Building: Creating strong brand loyalty and developing unique product features are essential for reducing price sensitivity and attracting customers. Focus on providing superior value, creating a strong brand identity, and cultivating customer loyalty.
-
Economies of Scale and Scope: Companies can achieve cost advantages by expanding their production volume, diversifying their product offerings, or streamlining their operations. This creates a barrier to entry for new entrants who cannot achieve the same cost efficiencies.
-
Strategic Alliances and Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses can help companies secure access to distribution channels, technology, or other resources, making it more difficult for new entrants to compete.
-
Lobbying for Government Regulation: While this may seem counterintuitive, supportive regulations can create a more level playing field, preventing excessive competition or ensuring standards.
-
Aggressive Pricing and Marketing Strategies: Responding to new entrants with competitive pricing or targeted marketing campaigns can effectively deter newcomers. This requires careful analysis of market dynamics and competitor actions.
-
Innovation and Continuous Improvement: Constantly innovating and improving products or services keeps the company ahead of the competition and creates a barrier to entry for imitators.
-
Focus on Customer Retention: Building strong customer relationships and providing excellent customer service can increase customer loyalty, making it harder for new entrants to attract customers.
Conclusion: A Constant Vigilance
The threat of new entrants is a dynamic force in any industry. While some industries are inherently more vulnerable due to inherent characteristics, companies can implement proactive strategies to reduce their vulnerability. Constant monitoring of market trends, competitor activities, and technological advancements is critical for staying ahead of the curve and mitigating the risks associated with new entrants. Understanding the factors that lead to low barriers to entry is the first step in developing effective strategies to ensure long-term success in a competitive landscape.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Threat Of New Entrants Is High When There Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.