The Term Meaning Above Or Outside The Ribs Is
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
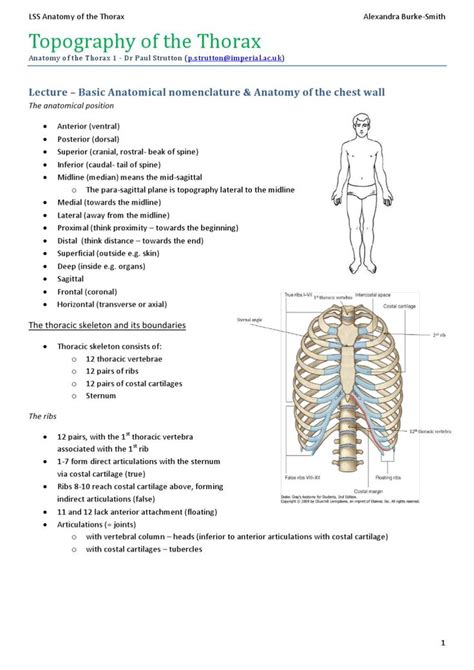
Table of Contents
- The Term Meaning Above Or Outside The Ribs Is
- Table of Contents
- The Term Meaning Above or Outside the Ribs Is: A Comprehensive Guide to Supracostal Anatomy and Clinical Significance
- I. Defining the Supracostal Region: Anatomy and Boundaries
- II. Clinical Significance of the Supracostal Region: Conditions and Procedures
- III. Imaging Techniques and Diagnostic Approaches
- IV. Supracostal Access in Various Medical Procedures
- V. Understanding the Supracostal Region: Implications for Patients
- VI. Conclusion: A Multifaceted Anatomical Area
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Term Meaning Above or Outside the Ribs Is: A Comprehensive Guide to Supracostal Anatomy and Clinical Significance
The term "supracostal" literally translates to "above the ribs" or "above the costal margin." Understanding this seemingly simple anatomical term unlocks a wealth of information regarding various structures, clinical conditions, and surgical procedures. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the supracostal region, exploring its anatomy, clinical relevance, and the implications for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
I. Defining the Supracostal Region: Anatomy and Boundaries
The supracostal region is situated superior (above) to the costal margin, the inferior border of the rib cage formed by the articulation of the seventh to tenth ribs with their costal cartilages. Precisely defining its boundaries can be nuanced, as it depends on the context. Generally, it encompasses the area extending from the inferior border of the rib cage to the superior structures within the thorax, neck, and upper abdomen.
Key anatomical structures within or adjacent to the supracostal region include:
-
Muscles: The diaphragm, a crucial muscle for respiration, forms the inferior boundary. Superiorly, the supracostal region houses parts of the pectoralis major and minor, serratus anterior, and other shoulder and neck muscles. These muscles play significant roles in movement and respiration.
-
Nerves: Several important nerves traverse or are located near the supracostal region. These include intercostal nerves, which emerge from the spinal cord and innervate the intercostal spaces, as well as branches of the brachial plexus, which supply the upper limbs. Damage to these nerves can result in sensory loss or motor weakness.
-
Vessels: The region contains portions of the subclavian arteries and veins, along with intercostal arteries and veins that supply blood to the thoracic wall. These vessels are vital for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues.
-
Organs: While the major organs of the thorax and abdomen are generally inferior to the ribs, portions of the lungs, particularly the superior lobes, and the upper portion of the liver can extend to the supracostal region, though technically this area does not contain fully encompassed organs.
-
Lymphatics: The supracostal area has a rich network of lymphatic vessels and nodes, which play a crucial role in immune function. Infection or malignancy in this region can affect the lymphatic system.
II. Clinical Significance of the Supracostal Region: Conditions and Procedures
The supracostal region is a critical area for various clinical conditions and procedures. Its location necessitates careful consideration by healthcare professionals across diverse specialties.
A. Pain and Trauma:
-
Rib Fractures: Fractures to the ribs can cause significant pain in the supracostal region. Pain can radiate to the back, and the severity depends on the number and location of fractures.
-
Intercostal Neuralgia: This condition involves inflammation or compression of the intercostal nerves, resulting in sharp, stabbing pain along the rib cage. The supracostal region is a frequent site of this pain.
-
Blunt Chest Trauma: Severe trauma to the chest can cause injuries to the underlying organs and blood vessels in the supracostal region. This can lead to life-threatening complications such as pneumothorax (collapsed lung) or hemothorax (blood in the pleural space).
B. Surgical Procedures:
-
Thoracotomy: This major surgical procedure involves an incision through the chest wall to access the thoracic cavity. The incision may be located in the supracostal region depending on the targeted organ or pathology.
-
Lung Biopsy: A small incision in the supracostal region may be made to obtain a sample of lung tissue for diagnostic purposes.
-
Supraclavicular Lymph Node Biopsy: Lymph nodes in the supraclavicular fossa (above the clavicle) can be assessed through an incision in the adjacent supracostal region, particularly if there is concern for malignancy.
-
Central Venous Catheter Placement: A catheter may be inserted into a subclavian vein, which is located near the supracostal region, to administer intravenous medications or fluids, or to monitor central venous pressure.
C. Other Clinical Conditions:
-
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleura (the membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity) can cause sharp pain that is often felt in the supracostal region.
-
Tumors: The supracostal region can be the site of both benign and malignant tumors, such as those originating from the ribs, muscles, nerves, or lymphatic structures.
-
Hernias: While less common, hernias can occur in the supracostal region. These can involve protrusion of abdominal contents through weaknesses in the diaphragm or abdominal wall.
III. Imaging Techniques and Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis of conditions affecting the supracostal region often requires advanced imaging techniques. Several modalities are utilized:
-
Chest X-ray: A standard chest X-ray is often the initial imaging study, providing a general overview of the thoracic structures and identifying potential abnormalities.
-
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images, allowing for better visualization of bones, soft tissues, and organs. This is particularly useful in evaluating rib fractures, pleural effusions, or tumors.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI excels at imaging soft tissues, making it useful in evaluating muscle injuries, nerve compression, or soft tissue tumors.
-
Ultrasound: Ultrasound is a non-invasive technique that can be used to assess the pleural space, evaluate blood flow, or guide needle biopsies.
Correlation of clinical findings with imaging results is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
IV. Supracostal Access in Various Medical Procedures
The supracostal space offers a valuable anatomical pathway for various minimally invasive procedures. These approaches often provide advantages over traditional open surgeries, including:
-
Reduced trauma: Minimally invasive approaches often result in less tissue damage and pain compared to open surgery.
-
Faster recovery: Patients typically experience quicker recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
-
Lower risk of infection: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of postoperative infections.
-
Improved cosmesis: Smaller incisions result in less visible scarring.
However, supracostal access also has limitations. Certain procedures require a wider access, negating the benefits of a minimally invasive approach. The surgeon's expertise and the patient's individual anatomy play crucial roles in determining the feasibility and safety of a supracostal approach.
V. Understanding the Supracostal Region: Implications for Patients
Understanding the supracostal region and its potential clinical implications is important for patients to advocate for their own health. Patients should:
-
Communicate clearly with their healthcare provider: Precisely describe the location and nature of any pain or discomfort experienced.
-
Ask questions: Don't hesitate to ask your physician about the location, nature, and possible causes of your symptoms.
-
Seek appropriate medical attention: Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for optimizing outcomes.
-
Understand treatment options: Educate yourself about the advantages and disadvantages of different treatment modalities.
-
Follow post-operative instructions: Adhering to your healthcare provider's instructions is essential for a successful recovery.
VI. Conclusion: A Multifaceted Anatomical Area
The supracostal region, though seemingly a simple anatomical area, represents a complex interplay of various structures and functions. Its importance in clinical practice is vast, extending across numerous specialties and encompassing a wide range of conditions and surgical procedures. From the diagnostic challenges presented by chest pain to the meticulous planning required for minimally invasive procedures, understanding the anatomy and clinical implications of this region is paramount for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Continued research and technological advancements will undoubtedly further refine our understanding of the supracostal region and enhance the management of associated conditions. The information presented in this comprehensive guide aims to provide a foundational knowledge base for those seeking a deeper appreciation of this crucial anatomical region.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Based On The Above Income Statement Data And The Formula
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Largest Expense For Most Airlines Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
Formal Education As An Approach To Employee Development Includes
Mar 29, 2025
-
Vail Company Recorded The Following Transactions During November
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Coversheet Is Attached To Help Protect A Secret Document
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Term Meaning Above Or Outside The Ribs Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
