The Stated Purposed Of Nafta And Usmca Is To
Holbox
Mar 28, 2025 · 7 min read
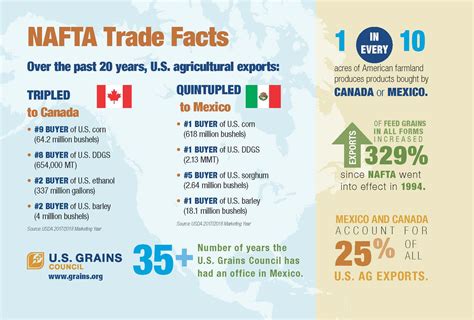
Table of Contents
- The Stated Purposed Of Nafta And Usmca Is To
- Table of Contents
- The Stated Purposes of NAFTA and USMCA: A Comparative Analysis
- NAFTA's Stated Purposes: A Foundation for Trilateral Trade
- 1. Eliminating Tariffs and Non-Tariff Barriers:
- 2. Promoting Fair Competition:
- 3. Increasing Investment Opportunities:
- 4. Expanding Intellectual Property Rights:
- 5. Strengthening Cooperation:
- USMCA's Stated Purposes: Addressing NAFTA's Shortcomings
- 1. Enhanced Labor and Environmental Standards:
- 2. Protecting Digital Trade:
- 3. Strengthening Rules of Origin:
- 4. Addressing Agricultural Trade:
- 5. Dispute Resolution Mechanisms:
- Comparing and Contrasting NAFTA and USMCA: Key Differences and Similarities
- The Impact of NAFTA and USMCA: An Ongoing Evaluation
- Conclusion: A Work in Progress
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Stated Purposes of NAFTA and USMCA: A Comparative Analysis
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its successor, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), were both ambitious trade pacts designed to foster economic growth and integration among Canada, Mexico, and the United States. While sharing a common goal of promoting free trade, the stated purposes, as outlined in their respective agreements, reveal subtle yet significant differences reflecting evolving economic priorities and geopolitical realities. This comprehensive analysis will delve deep into the stated purposes of both agreements, comparing and contrasting their approaches and assessing their impact on the participating nations.
NAFTA's Stated Purposes: A Foundation for Trilateral Trade
NAFTA, implemented in 1994, aimed to create a trilateral free trade area amongst its member nations. Its stated purposes, broadly interpreted, centered around these core principles:
1. Eliminating Tariffs and Non-Tariff Barriers:
NAFTA's primary objective was the gradual elimination of tariffs and other non-tariff barriers to trade. This involved phasing out duties on a wide range of goods and services, facilitating the smoother flow of commerce across borders. The agreement sought to create a more predictable and transparent trading environment, reducing the administrative hurdles and associated costs for businesses. This, in theory, would stimulate economic activity and increase competitiveness.
2. Promoting Fair Competition:
Beyond tariff reduction, NAFTA sought to establish a framework for fair competition. This involved provisions aimed at preventing anti-competitive practices, such as dumping (selling goods below cost) and subsidies. The agreement included mechanisms for dispute resolution, allowing member countries to address unfair trade practices and ensure a level playing field for businesses. The focus on fair competition was crucial for ensuring that the benefits of free trade were broadly shared across the participating economies.
3. Increasing Investment Opportunities:
NAFTA aimed to enhance investment opportunities within the trilateral region. This involved provisions that protected the rights of investors, reducing risks and encouraging cross-border capital flows. By guaranteeing investor protections, NAFTA intended to attract foreign investment, boosting economic growth and creating jobs in all three countries. This focus on investment was crucial for modernization and infrastructure development.
4. Expanding Intellectual Property Rights:
The protection of intellectual property rights (IPR) was another key objective of NAFTA. The agreement established strong provisions for protecting patents, copyrights, and trademarks, incentivizing innovation and creativity. The stronger IPR provisions aimed to safeguard the interests of businesses engaged in research and development, fostering technological advancement and competitiveness.
5. Strengthening Cooperation:
Beyond economic objectives, NAFTA also sought to strengthen cooperation amongst the three countries on a range of issues. This included collaboration on environmental protection, labor standards, and other matters of mutual concern. While these provisions were often criticized for lacking teeth, they signaled a commitment to sustainable and equitable development alongside economic growth.
USMCA's Stated Purposes: Addressing NAFTA's Shortcomings
The USMCA, ratified in 2020, replaced NAFTA, reflecting a shift in the economic and political landscape. While building on the foundations laid by NAFTA, the USMCA sought to address perceived shortcomings and incorporate new priorities:
1. Enhanced Labor and Environmental Standards:
A significant difference between NAFTA and USMCA lies in the heightened emphasis on labor and environmental standards. The USMCA includes stronger provisions to ensure that member countries uphold minimum labor standards, including protections for workers' rights, and to promote environmental sustainability. This shift reflects a growing awareness of the social and environmental consequences of trade and a desire to ensure that economic development is not achieved at the expense of human rights or environmental protection. These provisions are more enforceable than under NAFTA, and this was a crucial point of negotiation.
2. Protecting Digital Trade:
The USMCA reflects the growing importance of digital trade. It includes specific provisions to facilitate the cross-border flow of digital data and services, addressing the challenges posed by the digital economy. This acknowledges the transformative role of technology in modern trade and aims to create a regulatory environment conducive to digital commerce.
3. Strengthening Rules of Origin:
The USMCA contains stronger rules of origin than NAFTA. This aims to increase the percentage of goods manufactured in North America to qualify for preferential tariff treatment. This measure seeks to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on goods from other countries. This was a key objective for the US administration, aimed at boosting domestic production and employment.
4. Addressing Agricultural Trade:
The USMCA also incorporates specific provisions to address agricultural trade, including measures to improve market access for agricultural products and to resolve trade disputes in this crucial sector. This underscores the importance of agriculture to the economies of all three countries and aims to create a more balanced and equitable trading environment for agricultural producers.
5. Dispute Resolution Mechanisms:
While NAFTA included dispute resolution mechanisms, the USMCA introduces modifications to these processes, aiming for quicker and more efficient resolution of trade disputes. The changes are designed to reduce the potential for lengthy and costly legal battles, contributing to a more predictable and stable trading environment. This addresses concerns about the previous system being too favorable to corporations and less favorable to nations.
Comparing and Contrasting NAFTA and USMCA: Key Differences and Similarities
While both agreements share the overarching goal of promoting free trade among Canada, Mexico, and the United States, several key differences distinguish them:
| Feature | NAFTA | USMCA |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Standards | Relatively weak | Significantly strengthened, with enforceable provisions |
| Environmental Standards | Relatively weak | Significantly strengthened, with enforceable provisions |
| Digital Trade | Limited coverage | Comprehensive provisions addressing the digital economy |
| Rules of Origin | Less stringent | More stringent, promoting North American manufacturing |
| Dispute Resolution | Subject to criticism for being lengthy and complex | Revised for quicker and more efficient dispute resolution |
| State-Owned Enterprises | Less specific regulations | More explicit guidelines to prevent unfair competition from state-owned enterprises |
| Intellectual Property | Strong protections | Further strengthened protections for intellectual property rights |
| Sunset Clause | None | 16-year review period, with automatic termination if not renewed |
Both agreements share common ground in their aims to reduce tariffs, promote fair competition, and increase investment. However, the USMCA demonstrates a greater emphasis on labor and environmental protections, digital trade, and stronger rules of origin, reflecting evolving concerns about the social and environmental impacts of trade, globalization, and the rise of the digital economy.
The Impact of NAFTA and USMCA: An Ongoing Evaluation
The full impact of NAFTA and now the USMCA is still unfolding. While NAFTA led to increased trade and investment among the three countries, it also faced criticism for contributing to job losses in certain sectors and widening income inequality. The USMCA seeks to mitigate some of these criticisms through its stronger labor and environmental provisions, but its ultimate success remains to be seen.
Empirical research on the economic impacts is varied and complex, often dependent on the specific methodology and assumptions used. Some studies point to significant positive effects on GDP growth and overall trade, while others highlight negative consequences in specific sectors and for particular groups within the population. A nuanced approach is required, acknowledging both the benefits and drawbacks for different stakeholders.
The long-term implications of the USMCA, particularly its stricter rules of origin and emphasis on regional value content, will significantly impact the structure of North American supply chains and manufacturing industries. This will require ongoing adjustment and adaptation for businesses involved in cross-border trade and investment.
Furthermore, geopolitical shifts and global economic uncertainty can significantly influence the success of both agreements. Changes in trade relationships with other countries and developments in global technology could reshape the landscape of North American trade in unforeseen ways.
Conclusion: A Work in Progress
The stated purposes of NAFTA and USMCA reflect a continual evolution in the understanding of international trade and its broader societal implications. While both agreements aimed to foster free trade and economic growth, the USMCA represents a more nuanced approach, incorporating stronger protections for workers, the environment, and the digital economy. The long-term effectiveness of these agreements in achieving their stated purposes depends on various factors, including the political environment, global economic conditions, and the ongoing efforts of the three member nations to effectively implement and enforce its provisions. Continuous evaluation and adaptation are necessary to ensure the enduring benefits of this crucial North American trade partnership. The ongoing discussion and research surrounding both NAFTA and USMCA's impact highlight the complex and multifaceted nature of international trade agreements and their lasting influence on national and regional economies.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Should You Stock Brightly Colored Bandages
Apr 01, 2025
-
Database File Maintenance Typically Involves Select All That Apply
Apr 01, 2025
-
Henry Is Working At The Hospital Information Desk
Apr 01, 2025
-
When It Comes To Management Issues Small Businesses
Apr 01, 2025
-
This Type Of Industry Is Classified As
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Stated Purposed Of Nafta And Usmca Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
