The Purpose Of Cycle Counting Is To
Holbox
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
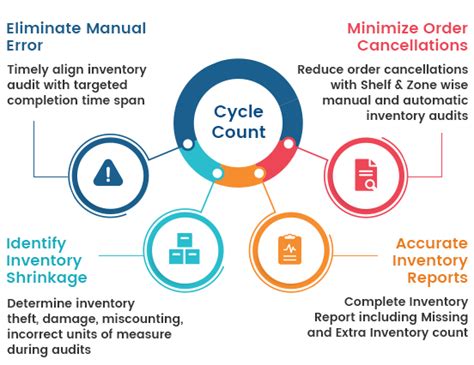
Table of Contents
- The Purpose Of Cycle Counting Is To
- Table of Contents
- The Purpose of Cycle Counting Is To... Maintain Inventory Accuracy and Much More
- Understanding the Core Purpose: Achieving Inventory Accuracy
- Going Beyond the Basics: The Broader Impact of Cycle Counting
- Implementing a Successful Cycle Counting Program: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 1. Define Objectives and Scope
- 2. Choose a Cycle Counting Method
- 3. Develop a Cycle Counting Schedule
- 4. Train Your Team
- 5. Utilize Technology
- 6. Implement and Monitor
- 7. Analyze and Improve
- The Synergy Between Cycle Counting and Other Inventory Management Techniques
- Addressing Common Challenges in Cycle Counting
- Conclusion: Cycle Counting – An Investment in Accuracy and Efficiency
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Purpose of Cycle Counting Is To... Maintain Inventory Accuracy and Much More
Cycle counting, a core inventory management technique, goes beyond simply verifying numbers. Its purpose extends to improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing overall supply chain visibility. While the primary goal is to maintain accurate inventory records, the benefits ripple across the entire organization. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the purpose of cycle counting, exploring its multifaceted advantages and how to implement a successful program.
Understanding the Core Purpose: Achieving Inventory Accuracy
At its heart, the purpose of cycle counting is to maintain accurate inventory records. This seemingly simple goal is crucial for numerous reasons:
-
Reduced Stockouts: Accurate counts prevent stockouts, ensuring that you always have the necessary items on hand to meet customer demand. Stockouts lead to lost sales, unhappy customers, and damaged reputation.
-
Minimized Overstocking: Conversely, accurate inventory data helps avoid overstocking, freeing up valuable storage space and reducing the risk of obsolescence, spoilage, or waste. Overstocked items tie up capital that could be invested elsewhere.
-
Improved Financial Reporting: Accurate inventory numbers are essential for reliable financial reporting. Incorrect inventory valuations can lead to inaccurate cost of goods sold (COGS) calculations, impacting profitability analysis and tax filings.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Accurate inventory data empowers better decision-making regarding purchasing, production planning, and resource allocation. You can make informed choices based on real-time data rather than estimations.
Going Beyond the Basics: The Broader Impact of Cycle Counting
While inventory accuracy is paramount, the purpose of cycle counting extends far beyond simply getting the numbers right. Consider these additional benefits:
-
Improved Operational Efficiency: Cycle counting streamlines inventory processes. By regularly counting smaller quantities of items, you avoid the disruptive impact of a large, annual physical inventory count. This minimizes downtime and maintains operational efficiency.
-
Reduced Costs: By preventing stockouts and overstocking, cycle counting directly reduces costs associated with lost sales, excess storage, and obsolescence. This leads to improved profitability and a healthier bottom line.
-
Increased Supply Chain Visibility: Cycle counting contributes to greater visibility throughout the supply chain. With accurate data, you can better anticipate future needs, manage lead times, and optimize your supply chain processes.
-
Better Inventory Control: Regularly counting items helps identify and address potential issues early on, such as discrepancies, damaged goods, or theft. This leads to tighter inventory control and minimized losses.
-
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Accurate inventory levels translate directly into improved customer satisfaction. By fulfilling orders promptly and avoiding stockouts, you foster stronger customer relationships and build loyalty.
Implementing a Successful Cycle Counting Program: A Step-by-Step Guide
The success of a cycle counting program hinges on careful planning and execution. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
1. Define Objectives and Scope
Before embarking on cycle counting, clearly define your objectives and scope. What are you hoping to achieve? Which areas of your inventory will be included? Establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure success. Examples of KPIs include:
- Inventory Accuracy Rate: The percentage of inventory items counted accurately.
- Cycle Count Frequency: How often items are counted.
- Time Spent on Cycle Counting: The amount of time dedicated to the process.
- Cost of Cycle Counting: The overall cost associated with the program.
2. Choose a Cycle Counting Method
Several cycle counting methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Consider the following:
-
ABC Analysis: Prioritize counting high-value ("A") items more frequently than low-value ("C") items. This method optimizes resources by focusing on the most critical inventory.
-
Random Sampling: Select items randomly for counting, providing a broad overview of inventory accuracy. This method is useful for large inventories where a complete count is impractical.
-
Frequency-Based Counting: Count items based on their turnover rate. Fast-moving items are counted more frequently than slow-moving items. This method ensures accurate tracking of high-demand items.
-
Zone Counting: Divide the warehouse or storage area into zones and assign each zone a counting schedule. This approach allows for focused counting efforts.
3. Develop a Cycle Counting Schedule
Once you've chosen a method, develop a realistic and achievable cycle counting schedule. Consider factors such as the number of items, storage location, and staff availability. The schedule should be integrated into the overall inventory management process.
4. Train Your Team
Proper training is essential for a successful cycle counting program. Ensure your team understands the chosen counting method, procedures, and the importance of accuracy. Provide clear instructions, and consider using training materials such as videos or manuals.
5. Utilize Technology
Technology can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of cycle counting. Consider using barcode scanners, RFID tags, or inventory management software to streamline the process and minimize errors. These tools automate data entry, reduce manual labor, and provide real-time inventory updates.
6. Implement and Monitor
Implement your cycle counting program and closely monitor its progress. Track your KPIs to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. Regularly review your procedures to ensure they remain effective and efficient.
7. Analyze and Improve
Regularly analyze your cycle counting data to identify trends and patterns. This information can be used to refine your counting methods, optimize your inventory management strategy, and improve overall efficiency.
The Synergy Between Cycle Counting and Other Inventory Management Techniques
Cycle counting works best in conjunction with other inventory management techniques. Consider the following:
-
Inventory Management Software: Integrating cycle counting data into inventory management software provides a holistic view of inventory levels, facilitating better decision-making.
-
Demand Forecasting: Accurate cycle count data provides input for demand forecasting, enabling more precise predictions of future needs.
-
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Cycle counting supports JIT inventory by ensuring that accurate inventory levels are maintained, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
-
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): In VMI arrangements, cycle counting provides transparency to vendors, allowing for better collaboration and optimized stock levels.
Addressing Common Challenges in Cycle Counting
Implementing a cycle counting program is not without its challenges. Addressing these proactively is key to success:
-
Resistance to Change: Some employees may resist adopting new procedures. Address this through clear communication, training, and emphasizing the benefits of cycle counting.
-
Time Constraints: Cycle counting can be time-consuming. Prioritize items based on their importance and utilize technology to streamline the process.
-
Inaccurate Counting: Human error is inevitable. Implement measures to minimize errors, such as double-checking counts and using scanning technology.
-
Lack of Resources: Insufficient staff or resources can hinder the effectiveness of cycle counting. Carefully plan resource allocation and seek management support.
Conclusion: Cycle Counting – An Investment in Accuracy and Efficiency
The purpose of cycle counting is multifaceted, extending far beyond simply verifying inventory numbers. It's an investment in accuracy, efficiency, and overall supply chain optimization. By implementing a well-planned and properly executed cycle counting program, businesses can significantly reduce costs, improve decision-making, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge. The key lies in understanding its multifaceted purposes, choosing the right methodology, and leveraging technology to maximize its impact. Remember, accurate inventory data is the bedrock of a successful and profitable business. Investing in cycle counting is investing in your future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Art Labeling Activity Anatomy Of The Urinary Tract
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Trees And Which Are Forests
Apr 04, 2025
-
Determine Which Of The Following Statements About Merchandise Is Correct
Apr 04, 2025
-
Kensie And Cal Are Both Great Students
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Products And Services Types Track Quantities
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Purpose Of Cycle Counting Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
