The Law Of Conservation Of Energy States That
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
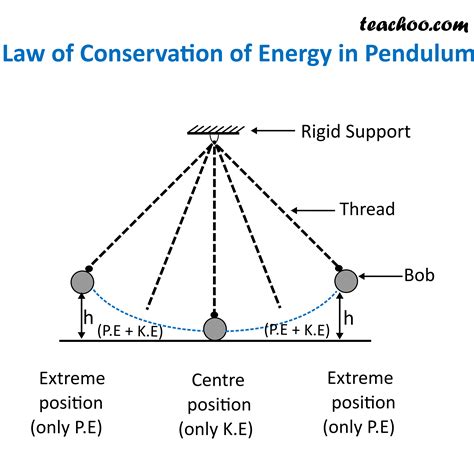
Table of Contents
- The Law Of Conservation Of Energy States That
- Table of Contents
- The Law of Conservation of Energy: A Comprehensive Exploration
- Understanding the Core Principle
- Different Forms of Energy
- Applications of the Law of Conservation of Energy
- Engineering and Technology
- Everyday Life
- Limitations and Nuances
- Non-Isolated Systems
- Frictional Losses
- Einstein's Mass-Energy Equivalence
- The Law and Other Conservation Laws
- Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Energy Conservation
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Law of Conservation of Energy: A Comprehensive Exploration
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in physics, stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This seemingly simple statement has profound implications across all areas of science and engineering, shaping our understanding of the universe from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest galaxies. This article delves deep into the law, exploring its various facets, applications, and subtle nuances.
Understanding the Core Principle
At its heart, the law of conservation of energy asserts that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time. An isolated system is one that doesn't exchange energy with its surroundings. This means that within such a system, energy might change forms – from kinetic energy (energy of motion) to potential energy (stored energy), from chemical energy to thermal energy (heat), or from electrical energy to light – but the sum total of all these forms of energy remains the same.
Think of a pendulum swinging. At its highest point, the pendulum possesses maximum potential energy (due to its position in the Earth's gravitational field). As it swings downwards, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, reaching its maximum at the bottom of its arc. As it swings back upwards, the process reverses, kinetic energy transforming back into potential energy. Ignoring frictional losses (which we'll address later), the total energy (potential + kinetic) remains constant throughout the pendulum's motion.
Different Forms of Energy
The law encompasses a vast array of energy forms, including:
-
Kinetic Energy: The energy an object possesses due to its motion. This is directly proportional to its mass and the square of its velocity.
-
Potential Energy: Stored energy due to an object's position or configuration. Gravitational potential energy depends on an object's height above a reference point, while elastic potential energy is stored in a stretched or compressed spring or other elastic material. Chemical potential energy is stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules.
-
Thermal Energy (Heat): The internal energy of a substance due to the random motion of its atoms and molecules. Heat transfer occurs when there's a temperature difference between two objects.
-
Radiant Energy (Light): Energy that travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, including visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet radiation.
-
Electrical Energy: Energy associated with the flow of electric charge.
-
Nuclear Energy: Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom, released through nuclear fission or fusion.
-
Sound Energy: Energy transmitted through vibrations in a medium.
Applications of the Law of Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy is not merely a theoretical concept; it's a cornerstone of numerous practical applications and technological advancements.
Engineering and Technology
Engineers rely heavily on this principle in designing and analyzing systems. For example:
-
Power Generation: Power plants, whether they utilize fossil fuels, nuclear reactions, or renewable sources like solar or wind, all operate based on the conversion of one form of energy into another, ultimately generating electricity. The efficiency of these systems is determined by how effectively they convert the initial energy source into electrical energy.
-
Automotive Engineering: Internal combustion engines transform chemical energy (from fuel) into mechanical energy to power vehicles. The design of engines focuses on maximizing the efficiency of this energy conversion. Hybrid and electric vehicles utilize different energy conversion pathways, but the fundamental principle remains the same.
-
Aerospace Engineering: Aircraft design involves careful consideration of energy transformations, from the chemical energy of fuel to the kinetic energy of flight, accounting for lift, drag, and thrust. Rocket propulsion relies on the conversion of chemical energy into kinetic energy to achieve launch and orbital maneuvers.
Everyday Life
The law's influence extends far beyond large-scale engineering projects. It governs many everyday phenomena:
-
Cooking: Cooking involves transferring thermal energy to food, changing its chemical structure and temperature.
-
Sports: The motion of athletes, from running to jumping, involves the conversion of chemical energy (from food) into kinetic energy.
-
Heating and Cooling: Heating systems convert electrical or chemical energy into thermal energy to warm buildings, while cooling systems move thermal energy from inside to outside.
Limitations and Nuances
While the law of conservation of energy is remarkably robust, it's important to acknowledge certain nuances and limitations:
Non-Isolated Systems
The law strictly applies only to isolated systems. In systems that exchange energy with their surroundings, the total energy of the system might change. For instance, a car engine is not an isolated system; it takes in chemical energy (fuel) and releases thermal energy (heat) and mechanical energy (motion) to the environment. The total energy of the engine alone does not remain constant.
Frictional Losses
In real-world scenarios, energy is often "lost" due to friction. This isn't a violation of the law, but rather a conversion of mechanical energy into thermal energy (heat). The heat energy is often dissipated into the surroundings, making it difficult to account for in a closed system analysis. This highlights the importance of considering energy efficiency in practical applications.
Einstein's Mass-Energy Equivalence
Einstein's famous equation, E=mc², reveals another crucial aspect. This equation demonstrates the equivalence of mass and energy, showing that mass itself is a form of energy. In nuclear reactions, a small amount of mass is converted into a significant amount of energy. While this doesn't invalidate the law, it extends our understanding, showing that energy conservation must account for changes in mass.
The Law and Other Conservation Laws
The law of conservation of energy is closely related to other fundamental conservation laws in physics:
-
Conservation of Momentum: The total momentum of a closed system remains constant unless acted upon by an external force.
-
Conservation of Mass (in classical mechanics): In classical mechanics, mass is considered to be conserved. This is a good approximation for many everyday processes, but Einstein's work showed that it's not universally true.
-
Conservation of Charge: The total electric charge in an isolated system remains constant.
These laws, along with the law of conservation of energy, form the foundation of classical physics and are crucial for understanding the behavior of physical systems.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Energy Conservation
The law of conservation of energy stands as a powerful and enduring principle, underpinning our comprehension of the physical world. Its implications extend across diverse scientific disciplines and technological applications. While acknowledging its limitations and nuances, the law remains an essential tool for understanding energy transformations and designing efficient systems. As we strive towards a sustainable future, a deep understanding of energy conservation and its implications is more crucial than ever, guiding us towards responsible energy usage and the development of renewable energy sources. The law serves not only as a description of physical reality but also as a guiding principle for innovation and responsible resource management. It encourages us to look for ways to optimize energy usage, minimize waste, and build a more efficient and sustainable world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Law Of Conservation Of Energy States That . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.