The Infraspinatus Muscle Is Included In The __________ Muscles.
Holbox
May 12, 2025 · 6 min read
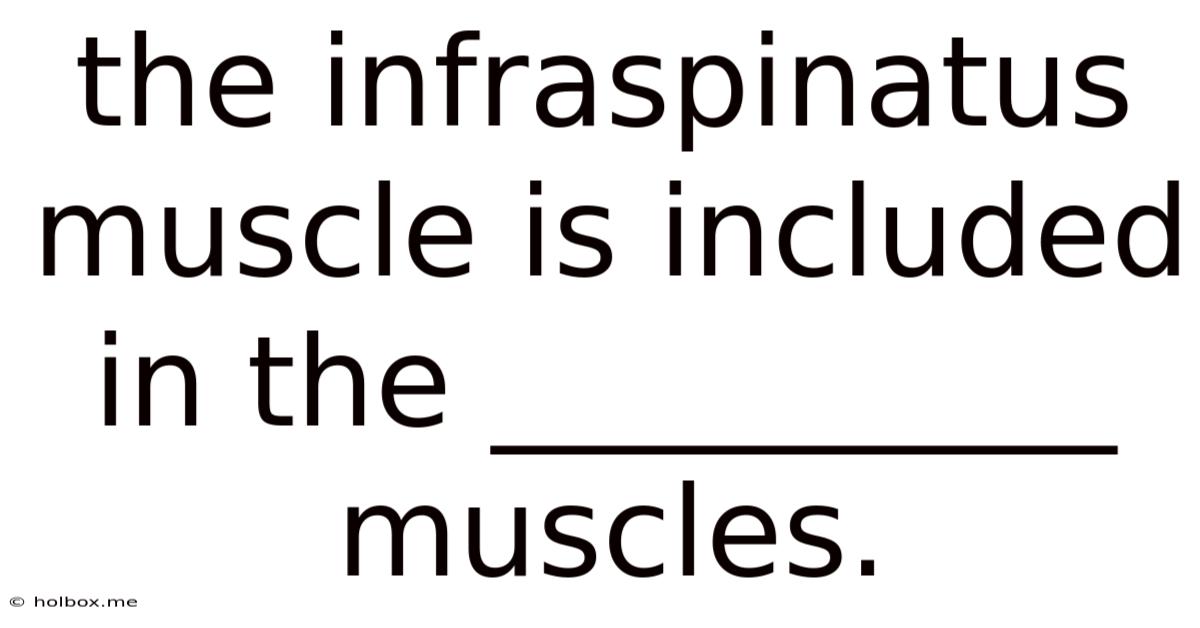
Table of Contents
- The Infraspinatus Muscle Is Included In The __________ Muscles.
- Table of Contents
- The Infraspinatus Muscle is Included in the Rotator Cuff Muscles
- Anatomy of the Infraspinatus Muscle
- Key Anatomical Features:
- The Rotator Cuff: A Team Effort
- Function of the Infraspinatus Muscle
- Common Infraspinatus Injuries
- Risk Factors for Infraspinatus Injuries:
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Infraspinatus Injuries
- Strengthening the Infraspinatus Muscle
- The Infraspinatus and Overall Shoulder Health
- Conclusion: The Infraspinatus' Vital Role
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Infraspinatus Muscle is Included in the Rotator Cuff Muscles
The infraspinatus muscle is a crucial component of the rotator cuff, a group of four muscles and their tendons that surround the shoulder joint. Understanding its role within this vital muscle group is key to comprehending shoulder function, common injuries, and effective rehabilitation strategies. This comprehensive article delves into the infraspinatus muscle's anatomy, function, common injuries, and how it interacts with other rotator cuff muscles to maintain shoulder stability and mobility.
Anatomy of the Infraspinatus Muscle
The infraspinatus muscle resides on the posterior (back) aspect of the scapula (shoulder blade). Its name, "infraspinatus," literally translates to "below the spine," accurately reflecting its location below the spine of the scapula. Originating from the infraspinous fossa (a large, slightly depressed area on the posterior scapula), its fibers converge to form a tendon that inserts into the greater tubercle of the humerus (upper arm bone). This insertion point is just inferior to the supraspinatus tendon, another critical rotator cuff muscle.
Key Anatomical Features:
- Origin: Infraspinous fossa of the scapula.
- Insertion: Greater tubercle of the humerus.
- Innervation: Suprascapular nerve (C5-C6). Damage to this nerve can significantly impair infraspinatus function.
- Blood Supply: Primarily supplied by branches of the suprascapular artery.
- Action: Primarily responsible for external rotation of the humerus. It also contributes to shoulder joint stabilization and horizontal abduction.
The Rotator Cuff: A Team Effort
The infraspinatus muscle doesn't work in isolation. It's a critical member of the rotator cuff, a dynamic team of four muscles working in concert to ensure the shoulder joint's stability and mobility. The other three rotator cuff muscles are:
- Supraspinatus: Located above the spine of the scapula, primarily responsible for initiating abduction (lifting the arm away from the body).
- Teres Minor: Situated inferior to the infraspinatus, assists with external rotation and adduction (moving the arm towards the body).
- Subscapularis: Located on the anterior (front) aspect of the scapula, responsible for internal rotation and contributes significantly to shoulder joint stability.
This synergistic interplay between the four muscles allows for a wide range of controlled movements and protects the shoulder joint from dislocation and injury. Think of the rotator cuff as a dynamic sling, meticulously controlling the humeral head within the glenoid cavity (the shallow socket of the shoulder blade).
Function of the Infraspinatus Muscle
The primary function of the infraspinatus is external rotation of the humerus. This movement is essential for a multitude of everyday activities, from reaching behind your back to throwing a ball. However, its role extends beyond simple external rotation:
- Shoulder Stability: The infraspinatus plays a crucial role in stabilizing the shoulder joint, particularly during movements involving the arm. It helps to compress the humeral head against the glenoid cavity, preventing unwanted movement and reducing the risk of dislocation.
- Fine Motor Control: Its involvement in fine motor control allows for precise movements and dexterity, which are necessary for tasks such as writing and buttoning clothes.
- Synergistic Action with Other Muscles: The infraspinatus works in coordination with other rotator cuff muscles and larger muscles of the shoulder girdle to generate a fluid and controlled range of motion. Its actions are rarely isolated; rather, it participates in a complex interplay of muscle actions.
Common Infraspinatus Injuries
Given its crucial role in shoulder stability and function, the infraspinatus is susceptible to various injuries, including:
- Infraspinatus Tendinitis: Inflammation of the infraspinatus tendon, often caused by overuse, repetitive movements, or poor posture. Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and limited range of motion.
- Infraspinatus Tear: A partial or complete tear of the infraspinatus tendon, which can result from acute trauma (e.g., a fall) or chronic overuse. Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the tear, ranging from mild pain to significant weakness and loss of function.
- Rotator Cuff Tear (Involving Infraspinatus): The infraspinatus is frequently involved in rotator cuff tears, often in conjunction with other rotator cuff muscles, especially the supraspinatus. This can lead to significant pain, weakness, and instability.
Risk Factors for Infraspinatus Injuries:
- Overuse: Repetitive overhead activities (e.g., throwing, swimming, weightlifting) can place significant stress on the infraspinatus tendon, increasing the risk of injury.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or poor posture can put excessive strain on the shoulder muscles, including the infraspinatus, leading to pain and inflammation.
- Age: The risk of infraspinatus tears increases with age due to natural degeneration of the tendons.
- Sudden Trauma: Falls or direct blows to the shoulder can cause acute injuries to the infraspinatus tendon.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Infraspinatus Injuries
Diagnosis of infraspinatus injuries typically involves a thorough physical examination, including assessment of range of motion, strength, and palpation of the affected area. Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasound, may be used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the injury.
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury and may include:
- Conservative Treatment: This typically involves rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), pain medication (e.g., NSAIDs), physical therapy, and targeted exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles.
- Surgical Treatment: Surgical repair may be necessary for significant tears of the infraspinatus tendon that don't respond to conservative treatment. Arthroscopic surgery is often preferred as it is minimally invasive.
Strengthening the Infraspinatus Muscle
Strengthening the infraspinatus muscle, along with the other rotator cuff muscles, is crucial for maintaining shoulder health and preventing injuries. Here are some exercises that target the infraspinatus:
- External Rotation with Theraband: Holding a theraband in both hands, anchor one end securely. With your elbow bent at 90 degrees, rotate your arm outward against the resistance of the band.
- Lying External Rotation: Lie on your side with your elbow bent at 90 degrees. Keeping your elbow close to your body, externally rotate your arm, lifting a light weight or using a theraband.
- Scapular Retractions: These exercises help strengthen the muscles that stabilize the shoulder blade, which indirectly supports the infraspinatus. Squeeze your shoulder blades together and hold, then release.
Important Note: It's crucial to consult with a physical therapist or other qualified healthcare professional to develop a safe and effective exercise program tailored to your individual needs and condition. Improper exercises can worsen existing injuries or lead to new ones.
The Infraspinatus and Overall Shoulder Health
The infraspinatus muscle's contribution to shoulder health extends beyond its own functionality. Its role within the rotator cuff significantly impacts the overall health and functionality of the shoulder joint. By understanding its anatomy, function, and potential injuries, we can better appreciate the importance of maintaining its health through preventative measures such as proper posture, regular exercise, and appropriate treatment when injuries occur. Neglecting infraspinatus health can significantly compromise shoulder function, leading to pain, weakness, and instability that can impact daily life.
Conclusion: The Infraspinatus' Vital Role
The infraspinatus muscle, a key member of the rotator cuff muscles, plays a pivotal role in shoulder stability, mobility, and overall upper body function. Its involvement in external rotation, along with its synergistic action with other rotator cuff muscles, is essential for a wide range of movements. Awareness of its anatomy, function, and susceptibility to injury is paramount for maintaining shoulder health and preventing debilitating conditions. Regular exercise focusing on rotator cuff strength, alongside maintaining good posture and avoiding overuse, are key strategies for protecting this vital muscle and ensuring optimal shoulder performance. When injuries do occur, prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, often in conjunction with physical therapy, are vital for successful recovery and a return to normal function.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Infraspinatus Muscle Is Included In The __________ Muscles. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.