The Goal Of The Human Rights Code Is To
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
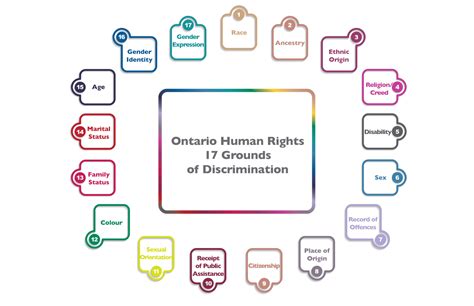
Table of Contents
The Goal of the Human Rights Code Is To… Achieve a Just and Equitable World
The goal of any human rights code, whether it's a national constitution, an international treaty, or a local ordinance, boils down to one fundamental aim: to create a just and equitable world for all. This seemingly simple statement encompasses a vast and complex network of principles, protections, and processes designed to ensure the dignity, worth, and fundamental freedoms of every individual, regardless of their background, beliefs, or circumstances. Let's delve deeper into the multifaceted goals underlying these codes.
Protecting Fundamental Rights and Freedoms
At its core, a human rights code aims to protect fundamental rights and freedoms. These rights are often categorized into civil and political rights and economic, social, and cultural rights.
Civil and Political Rights: The Cornerstones of Freedom
Civil and political rights are essential for individual autonomy and participation in society. They include:
- The right to life: Protection from arbitrary killing and unlawful violence.
- Freedom from torture and cruel, inhuman, or degrading treatment or punishment: A cornerstone of humane treatment and the prohibition of state-sanctioned violence.
- The right to liberty and security of person: Protection against arbitrary arrest, detention, and exile.
- The right to a fair trial: Guaranteeing due process and the right to legal representation.
- Freedom of expression: The ability to communicate freely, including speech, press, and assembly.
- Freedom of religion or belief: The right to practice one's faith, or lack thereof, without coercion or discrimination.
- The right to participate in government: The right to vote, run for office, and participate in political processes.
These rights establish a framework for individual liberty and participation in a democratic society. They ensure individuals are free from arbitrary state power and can actively shape their own lives and the society in which they live.
Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights: Building Blocks of a Just Society
Economic, social, and cultural rights are equally crucial for a fulfilling and dignified life. These rights recognize that mere freedom from oppression is not enough; individuals need the resources and opportunities to thrive. Key examples include:
- The right to an adequate standard of living: Access to food, clothing, shelter, and other essential resources.
- The right to health: Access to quality healthcare services and preventative measures.
- The right to education: Access to free and compulsory primary education, and opportunities for further education.
- The right to work: The right to choose one's employment and receive fair wages and working conditions.
- The right to social security: Protection against unemployment, sickness, disability, and old age.
- The right to participate in cultural life: The freedom to express one's culture and participate in cultural activities.
These rights ensure that individuals have the basic necessities for a life with dignity and the opportunity to participate fully in society. They emphasize the importance of government's role in creating social and economic conditions conducive to well-being.
Promoting Equality and Non-discrimination
A central goal of any human rights code is to promote equality and non-discrimination. This means ensuring that all individuals are treated with equal respect and dignity, regardless of their:
- Race: Preventing racial discrimination and promoting racial equality.
- Color: Protecting individuals from discrimination based on their skin color.
- Sex: Ensuring gender equality and combating gender-based discrimination.
- Language: Protecting linguistic diversity and preventing discrimination based on language.
- Religion: Guaranteeing freedom of religion and preventing religious discrimination.
- Political or other opinion: Protecting freedom of expression and opinion, regardless of political affiliation.
- National or social origin: Protecting against discrimination based on ethnicity or social background.
- Property: Preventing discrimination based on socioeconomic status.
- Birth: Preventing discrimination based on one's family background or social standing.
- Other status: A broad category encompassing other grounds for potential discrimination, such as disability, sexual orientation, and marital status.
These provisions aim to create a society where individuals are judged on their merits and not on arbitrary characteristics. They recognize that prejudice and discrimination can severely limit opportunities and undermine the well-being of individuals and communities.
Ensuring Accountability and Enforcement
The effectiveness of a human rights code depends on ensuring accountability and enforcement. This includes:
- Establishing independent mechanisms for redress: Providing avenues for individuals to seek justice when their rights are violated.
- Creating effective monitoring and reporting systems: Regularly assessing compliance with human rights standards and identifying areas for improvement.
- Empowering civil society organizations: Supporting organizations that work to monitor and protect human rights.
- Promoting international cooperation: Collaborating with other countries to uphold human rights standards.
- Holding perpetrators accountable: Investigating and prosecuting those who violate human rights.
These mechanisms are vital for ensuring that the promises enshrined in human rights codes are translated into tangible improvements in people's lives. They create a system of checks and balances that prevents abuses and promotes a culture of respect for human rights.
Fostering Inclusive Participation and Development
Beyond protecting individual rights, a human rights code seeks to foster inclusive participation and development. This means creating a society where all individuals can contribute their talents and perspectives, and where development benefits all members of society. This involves:
- Promoting inclusive governance: Ensuring that decision-making processes are participatory and representative.
- Empowering marginalized groups: Addressing the specific challenges faced by vulnerable and marginalized groups, such as women, children, people with disabilities, and indigenous peoples.
- Promoting sustainable development: Ensuring that economic and social development is environmentally sustainable and benefits all members of society.
- Protecting the environment: Recognizing the link between human rights and environmental protection.
These elements recognize that human rights are not just individual concerns but also essential for the well-being of communities and the environment. A just and equitable society requires the active participation of all its members and sustainable practices that benefit current and future generations.
Addressing Systemic Inequalities and injustices
Human rights codes aim to address systemic inequalities and injustices that prevent individuals from enjoying their rights. This means challenging discriminatory laws, policies, and practices and tackling deep-rooted social, economic, and political structures that perpetuate inequality. This includes:
- Combatting poverty and inequality: Addressing the root causes of poverty and promoting equitable distribution of resources.
- Promoting access to justice: Ensuring that individuals have equal access to legal systems and remedies.
- Tackling discrimination in all its forms: Actively combatting discrimination on all grounds, including through affirmative action and anti-discrimination legislation.
- Promoting inclusive education: Providing quality education for all, regardless of background or ability.
- Strengthening the rule of law: Ensuring that laws and institutions are fair, effective, and accountable.
By acknowledging and actively addressing systemic inequalities, human rights codes strive to build societies where all individuals have the opportunity to reach their full potential. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves tackling social injustices at their roots and creating an environment conducive to inclusive growth.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Pursuit of Justice
The goal of the human rights code is not a static achievement but a continuous pursuit. It demands constant vigilance, commitment, and action to protect and promote human dignity and well-being for all. The work requires ongoing efforts by governments, civil society organizations, international bodies, and individuals to ensure the realization of a just and equitable world for everyone, everywhere. It's a journey that demands perseverance, collaboration, and an unwavering commitment to the principles of human rights. The ultimate objective remains to build a future where every individual can live a life free from fear, discrimination, and oppression, with the opportunity to fully participate in and contribute to a vibrant and flourishing society.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Correct Order Of Elements In The Whmis Classification System
Mar 10, 2025
-
The Traffic Light System Is A Helpful Way To
Mar 10, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Grocery Stores Allowed To Do
Mar 10, 2025
-
Under Ctpat Your Carrier Is Required To Follow
Mar 10, 2025
-
Select The True Statements About Hydrocarbons
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Goal Of The Human Rights Code Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
