The Formation Of Lymph Increases As A Result Of
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
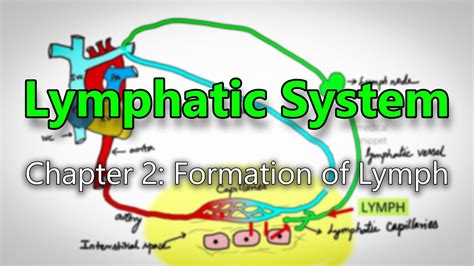
Table of Contents
- The Formation Of Lymph Increases As A Result Of
- Table of Contents
- The Formation of Lymph Increases as a Result of: A Deep Dive into Lymphatic Physiology
- Understanding Lymph Formation: The Basics
- Factors that Significantly Increase Lymph Formation
- 1. Increased Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure: The Driving Force
- 2. Decreased Capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure: Reduced Plasma Protein Retention
- 3. Increased Interstitial Fluid Colloid Osmotic Pressure: Protein Accumulation in Tissues
- 4. Increased Interstitial Fluid Hydrostatic Pressure: Obstruction and Blockages
- 5. Inflammation: A Complex interplay of Factors
- 6. Exercise and Muscle Contractions: The Lymphatic Pump
- 7. Changes in Body Position: Gravity's Influence
- Clinical Implications of Altered Lymph Formation
- Therapeutic Interventions and Maintaining Lymphatic Health
- Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Lymph Formation
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Formation of Lymph Increases as a Result of: A Deep Dive into Lymphatic Physiology
The lymphatic system, often overlooked in discussions of the circulatory system, plays a crucial role in maintaining bodily health and homeostasis. Its primary function is to maintain fluid balance, transport fats, and defend against infection. Understanding how lymph formation is influenced by various factors is key to comprehending its overall function and the implications for human health. This article delves deep into the mechanisms driving increased lymph formation, exploring the contributing factors and their physiological impact.
Understanding Lymph Formation: The Basics
Before examining the factors that increase lymph formation, a foundational understanding of the process itself is necessary. Lymph, a clear fluid, originates from interstitial fluid—the fluid surrounding cells within tissues. This interstitial fluid is formed by the process of filtration, where blood plasma, driven by hydrostatic pressure, leaks out of capillaries. The composition of interstitial fluid is remarkably similar to plasma, except for a lower protein concentration.
The lymphatic system collects this interstitial fluid via specialized lymphatic capillaries, which possess unique one-way valves that prevent fluid backflow. Once inside the lymphatic capillaries, the fluid is officially termed lymph. From here, lymph flows through progressively larger lymphatic vessels, ultimately returning to the bloodstream via the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic duct.
Factors that Significantly Increase Lymph Formation
Several physiological processes and external factors significantly influence lymph formation, causing its volume to increase. Let's examine these in detail:
1. Increased Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure: The Driving Force
The primary factor influencing lymph formation is capillary hydrostatic pressure. This pressure, representing the force of blood pushing against capillary walls, is directly proportional to blood pressure. An increase in blood pressure consequently leads to an increase in filtration and, therefore, an increase in interstitial fluid volume. This excess fluid is then picked up by the lymphatic system, leading to a rise in lymph formation. Conditions like hypertension can significantly increase lymph formation due to this mechanism.
2. Decreased Capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure: Reduced Plasma Protein Retention
Capillary colloid osmotic pressure, exerted by plasma proteins (primarily albumin), plays a vital role in drawing fluid back into the capillaries from the interstitial space. A decrease in plasma protein concentration, whether due to malnutrition, liver disease (leading to hypoalbuminemia), or kidney disease (leading to proteinuria), reduces this osmotic pressure. This imbalance results in less fluid reabsorption from the interstitial space, leading to increased interstitial fluid volume and consequently, increased lymph formation.
3. Increased Interstitial Fluid Colloid Osmotic Pressure: Protein Accumulation in Tissues
Conversely, an increase in interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure can also stimulate lymph formation. This occurs when the concentration of proteins in the interstitial fluid increases. This might happen due to inflammation, where increased capillary permeability allows proteins to leak into the interstitial space, or due to tissue damage, releasing proteins from damaged cells. The increased protein concentration draws more fluid into the interstitial space, increasing the load on the lymphatic system and causing a rise in lymph formation.
4. Increased Interstitial Fluid Hydrostatic Pressure: Obstruction and Blockages
Obstructions within the lymphatic system itself, such as those caused by tumors, infections (lymphangitis), or surgical removal of lymph nodes, can significantly increase interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure. The lymphatic system's inability to drain fluid effectively leads to a buildup of fluid in the interstitial space, resulting in lymphedema. This condition is characterized by swelling and significant increases in lymph formation in an attempt to compensate for the impaired drainage.
5. Inflammation: A Complex interplay of Factors
Inflammation, a complex physiological response to tissue injury or infection, significantly impacts lymph formation. Inflammation involves increased vascular permeability, allowing proteins and fluid to leak from capillaries. This leads to increased interstitial fluid volume, and subsequently, increased lymph formation. Furthermore, the inflammatory process stimulates lymphatic vessel growth and function (lymphangiogenesis), further enhancing lymph transport. The lymph formed during inflammation often carries inflammatory mediators, immune cells, and cellular debris, highlighting the lymphatic system's role in immune responses.
6. Exercise and Muscle Contractions: The Lymphatic Pump
Skeletal muscle contractions play a vital role in lymphatic drainage. The lymphatic system lacks a central pump like the heart; instead, it relies on external forces, including muscle contractions, to propel lymph through the lymphatic vessels. Increased physical activity, by increasing muscle contractions, enhances lymphatic drainage and thus increases the rate of lymph formation and its subsequent transport. This is why regular exercise is crucial for maintaining lymphatic health. The rhythmic contractions of smooth muscles within lymphatic vessels also contribute to lymph flow.
7. Changes in Body Position: Gravity's Influence
Changes in body position can also influence lymph formation. When standing upright, hydrostatic pressure in the lower extremities increases, leading to increased filtration and interstitial fluid accumulation. This results in greater lymph formation in the lower limbs. Conversely, when lying down, this pressure gradient is reduced, influencing the distribution of lymph formation.
Clinical Implications of Altered Lymph Formation
Understanding the factors that influence lymph formation has significant clinical implications. Conditions like lymphedema, caused by lymphatic obstruction, highlight the crucial role of lymphatic drainage in maintaining fluid balance. Similarly, understanding the lymphatic system's role in inflammation is vital in managing inflammatory diseases. Moreover, recognizing the impact of nutritional deficiencies and liver or kidney diseases on plasma protein levels can provide valuable insights into managing fluid imbalances and promoting overall health.
Therapeutic Interventions and Maintaining Lymphatic Health
Several therapeutic strategies focus on supporting lymphatic function and managing conditions associated with altered lymph formation. These include:
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): A gentle massage technique designed to stimulate lymphatic flow and reduce swelling.
- Compression Therapy: Using compression bandages or garments to reduce swelling and support lymphatic drainage.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances lymphatic drainage and overall lymphatic health.
- Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients supports plasma protein levels and overall lymphatic health.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Lymph Formation
Lymph formation is a dynamic process influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for appreciating the lymphatic system's crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, transporting lipids, and facilitating immune responses. Conditions such as hypertension, malnutrition, inflammation, and lymphatic obstructions can significantly alter lymph formation, highlighting the importance of maintaining overall health and addressing any potential disruptions to lymphatic function. Further research into the intricate mechanisms governing lymph formation will undoubtedly provide valuable insights into preventing and treating various health conditions. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and awareness of potential risk factors are crucial in supporting lymphatic health and maintaining overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Formation Of Lymph Increases As A Result Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.