The Following Name Is Incorrect. Select The Correct Iupac Name.
Holbox
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
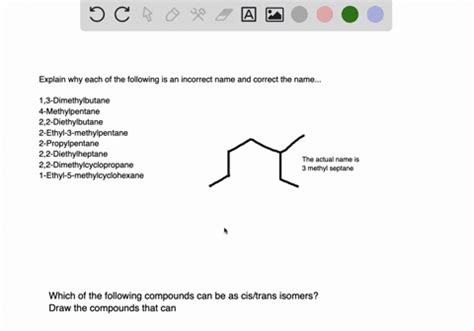
Table of Contents
- The Following Name Is Incorrect. Select The Correct Iupac Name.
- Table of Contents
- The Following Name is Incorrect. Select the Correct IUPAC Name: A Deep Dive into Organic Nomenclature
- Understanding the Fundamentals of IUPAC Nomenclature
- Key Steps in IUPAC Naming:
- Common Errors and Their Corrections:
- Error 1: Incorrect Parent Chain Selection
- Error 2: Incorrect Numbering of the Parent Chain
- Error 3: Incorrect Alphabetization of Substituents
- Error 4: Ignoring Substituent Priority (In complex molecules with multiple functional groups)
- Error 5: Failure to Include All Substituents
- Advanced Cases and Subtleties in IUPAC Nomenclature:
- Handling Multiple Substituents of the Same Type:
- Dealing with Complex Substituents:
- Handling Multiple Functional Groups:
- Cyclic Compounds:
- Stereoisomerism and IUPAC Nomenclature:
- Practical Exercises and Case Studies:
- Conclusion:
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
The Following Name is Incorrect. Select the Correct IUPAC Name: A Deep Dive into Organic Nomenclature
Organic chemistry can be a daunting subject, especially when it comes to naming compounds. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a systematic nomenclature system to avoid ambiguity and ensure global understanding. However, even experienced chemists can sometimes stumble. This article will delve into the complexities of IUPAC nomenclature, exploring common errors and offering a step-by-step guide to selecting the correct IUPAC name for a given organic molecule. We will tackle various functional groups, complexities in branching, and subtle nuances often missed.
Understanding the Fundamentals of IUPAC Nomenclature
Before we tackle incorrect names and their corrections, let's establish a solid foundation. The IUPAC system is built on a series of rules and priorities. The core principle is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain (parent chain) and then consider any substituents attached to it. The parent chain dictates the base name (e.g., methane, ethane, propane, etc.), while substituents are named and numbered according to their position on the chain.
Key Steps in IUPAC Naming:
-
Identify the Parent Chain: Find the longest continuous carbon chain within the molecule. This chain forms the basis of the name.
-
Identify Substituents: Identify any atoms or groups of atoms attached to the parent chain. These are the substituents. Common substituents include alkyl groups (methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc.), halogens (fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo), and functional groups (hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, etc.).
-
Number the Parent Chain: Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain, starting from the end closest to the first substituent. If multiple substituents are present, prioritize the one with the highest priority according to the IUPAC rules (explained further below). The goal is to give substituents the lowest possible numbers.
-
Name the Substituents: Name each substituent. For alkyl groups, use the prefixes (methyl, ethyl, propyl, etc.). For halogens, use the prefixes (fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo). More complex substituents have their own naming conventions.
-
Arrange Substituents Alphabetically: List the substituents alphabetically, ignoring prefixes like di-, tri-, tetra-, etc. (Numbers are considered before alphabetization). Note that prefixes like iso- and tert- are alphabetized.
-
Combine the Information: Combine the information to create the complete IUPAC name. The format generally follows: (Substituent Position)-(Substituent Name)-(Parent Chain Name). If multiple substituents are present, list them alphabetically with their respective positions separated by commas, before the parent chain name.
Common Errors and Their Corrections:
Let's explore common mistakes encountered when assigning IUPAC names. These examples highlight the importance of meticulous application of the rules.
Error 1: Incorrect Parent Chain Selection
Incorrect Name: 2-Methylbutane
Correct Name: Pentane
Explanation: The longest carbon chain in this molecule actually contains five carbon atoms. The seemingly "2-methylbutane" name incorrectly identifies a four-carbon chain as the parent. Always ensure you've found the longest continuous chain.
Error 2: Incorrect Numbering of the Parent Chain
Incorrect Name: 4-Methylpentane
Correct Name: 2-Methylpentane
Explanation: The molecule should be numbered from the end closest to the methyl group to give the substituent the lowest possible number. Numbering from the opposite end would give the substituent a higher number (4 instead of 2), making the name incorrect.
Error 3: Incorrect Alphabetization of Substituents
Incorrect Name: 2-Ethyl-3-methylpentane
Correct Name: 3-Ethyl-2-methylpentane
Explanation: The alphabetization should consider the substituents (ethyl and methyl) before considering any prefixes. "Ethyl" comes before "methyl" alphabetically. Therefore, "3-Ethyl-2-methylpentane" is the correct IUPAC name.
Error 4: Ignoring Substituent Priority (In complex molecules with multiple functional groups)
Incorrect Name (Illustrative Example): 3-oxo-4-methylpentanoic acid
Correct Name (Illustrative Example): 4-Methyl-3-oxopentanoic acid
Explanation: In molecules with multiple functional groups, the highest priority functional group determines the parent chain and suffix. In this example, carboxylic acid (-COOH) has higher priority than ketone (=O), therefore, the suffix "-oic acid" will be used.
Error 5: Failure to Include All Substituents
Incorrect Name (Illustrative Example): 2-methylhexane
Correct Name (Illustrative Example): 2,5-dimethylhexane
Explanation: The molecule contains two methyl substituents, which both must be included in the IUPAC name and their positions indicated. Failure to incorporate all substituents results in an incomplete and incorrect name.
Advanced Cases and Subtleties in IUPAC Nomenclature:
The examples above represent simpler cases. Let's delve into situations that demand a more profound understanding of IUPAC rules.
Handling Multiple Substituents of the Same Type:
When multiple substituents of the same type are present, prefixes such as di-, tri-, tetra-, etc., are used. The positions of the identical substituents are separated by commas and listed together before the substituent name.
Example: 2,3-dimethylbutane (two methyl groups at positions 2 and 3).
Dealing with Complex Substituents:
Complex substituents, such as branched alkyl groups, require their own names before being incorporated into the main chain's name. These substituents are often named as alkyl groups with further branching indicated by additional substituents. The nomenclature process then follows the same steps as before, assigning numbers to locate substituents on the main chain and the branched alkyl groups.
Handling Multiple Functional Groups:
When a molecule contains multiple functional groups, a hierarchy of priority determines which group determines the suffix and which ones are designated as prefixes. IUPAC has a clearly defined order of priority for functional groups. The highest priority functional group determines the parent chain and suffix; the others become prefixes.
Cyclic Compounds:
Cyclic compounds are named using the prefix "cyclo-" before the parent chain name. The numbering of the ring begins at the substituent with the highest priority and proceeds in the direction that gives the other substituents the lowest possible numbers.
Stereoisomerism and IUPAC Nomenclature:
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms. IUPAC nomenclature incorporates prefixes and descriptors to denote stereochemistry, such as cis-, trans-, R-, S-, E-, and Z-.
Practical Exercises and Case Studies:
To solidify your understanding, let's analyze some case studies.
Case Study 1:
Consider a molecule with the structure: CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH(C2H5)-CH3.
Incorrect Name: 3-Ethyl-2-methylpentane (Common mistake: Incorrect prioritization of substituents)
Correct Name: 3-Methyl-4-ethylhexane (Longest chain is 6 carbons. Numbering starts from right to left)
Case Study 2:
Consider a cyclic molecule with the structure: A cyclohexane ring with a methyl group at position 1 and an ethyl group at position 3.
Incorrect Name: 1-Methyl-3-ethylcyclohexane (Potential mistake: incorrect numbering)
Correct Name: 1-Methyl-3-ethylcyclohexane (Correct in this case, but emphasize the numbering rule)
Case Study 3: A molecule with a double bond and an alcohol group. (Illustrates functional group priority)
(Structure needs to be provided to solve this) This would require a specific structure. The correct name would depend on which functional group (alkene or alcohol) has precedence.
Conclusion:
Mastering IUPAC nomenclature is crucial for any aspiring chemist. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the rules, emphasizing common pitfalls and offering a structured approach to naming organic compounds accurately. Remember to always systematically follow the rules, prioritizing the longest carbon chain, numbering correctly, alphabetizing substituents appropriately, and handling complex situations using the IUPAC guidelines for priority. Consistent practice with diverse examples is essential for building confidence and accuracy in this fundamental aspect of organic chemistry. Regularly reviewing the IUPAC rules and practicing with various examples will improve your proficiency in this critical area. The more you practice, the more intuitive the process will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 39 Inches
May 19, 2025
-
32 Kg Is How Many Lbs
May 19, 2025
-
77 Kg Is How Many Pounds
May 19, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Is 2000 Seconds
May 19, 2025
-
How Many Minutes In 9 Hrs
May 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Following Name Is Incorrect. Select The Correct Iupac Name. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.