Sieve Analysis - Percent Finer Chegg
Holbox
Mar 12, 2025 · 6 min read
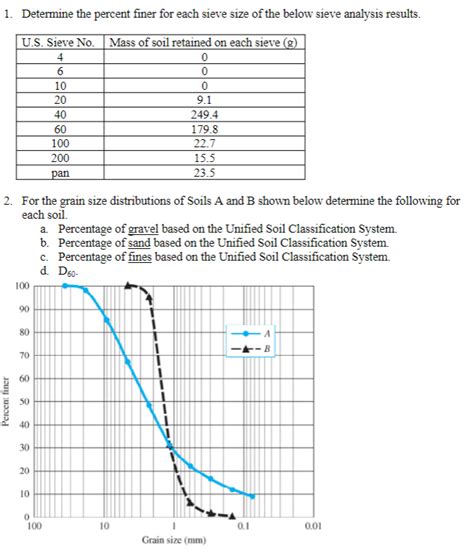
Table of Contents
- Sieve Analysis - Percent Finer Chegg
- Table of Contents
- Sieve Analysis: Understanding Percent Finer and its Applications
- What is Sieve Analysis?
- Understanding Percent Finer
- Calculating Percent Finer
- Interpreting the Percent Finer Curve
- Applications of Sieve Analysis and Percent Finer Data
- 1. Civil Engineering:
- 2. Mining and Metallurgy:
- 3. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- 4. Other Industries:
- Advanced Techniques and Considerations
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Sieve Analysis: Understanding Percent Finer and its Applications
Sieve analysis, also known as particle size analysis or gradation analysis, is a crucial technique in various industries, including civil engineering, geology, and materials science. This method determines the particle size distribution of a granular material, providing valuable insights into its properties and behavior. Understanding the "percent finer" data derived from sieve analysis is key to interpreting the results and making informed decisions about material selection and application. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of sieve analysis, focusing on the significance of percent finer data and its practical applications.
What is Sieve Analysis?
Sieve analysis involves passing a sample of granular material through a series of sieves with progressively smaller openings. Each sieve retains particles larger than its aperture size. By weighing the material retained on each sieve, we can determine the mass fraction of particles within specific size ranges. This process yields a particle size distribution curve, essential for characterizing the material's properties. The process is straightforward but requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure accurate results. Factors like sample preparation, sieve shaking duration, and the cleanliness of the sieves directly impact the reliability of the analysis.
Understanding Percent Finer
The "percent finer" data is a critical output of sieve analysis. It represents the cumulative percentage of the total sample mass that is finer than a given sieve size. For example, if the "percent finer" at a 2mm sieve size is 70%, it means that 70% of the sample material passes through a 2mm sieve (i.e., is smaller than 2mm). This cumulative data is crucial because it facilitates a clear understanding of the overall size distribution, not just the material retained on individual sieves.
Calculating Percent Finer
The calculation is straightforward. Once the mass retained on each sieve is determined, the cumulative mass retained up to a particular sieve size is calculated. Then, the percent finer is calculated using the following formula:
Percent Finer = (Total Mass - Cumulative Mass Retained) / Total Mass * 100%
Where:
- Total Mass is the initial mass of the sample.
- Cumulative Mass Retained is the sum of the masses retained on all sieves larger than the sieve size in question.
This percentage is then plotted against the corresponding sieve size to create a particle size distribution curve, often presented on a semi-logarithmic graph.
Interpreting the Percent Finer Curve
The percent finer curve provides valuable insights into the material's characteristics:
-
Well-graded material: A well-graded material shows a smooth, relatively steep curve. It has a wide range of particle sizes, leading to good compaction and stability.
-
Uniformly graded material: A uniformly graded material exhibits a sharp curve, indicating a narrow range of particle sizes. While this might simplify some aspects of material handling, it often leads to poor compaction and potentially lower strength compared to well-graded materials.
-
Gap-graded material: A gap-graded material shows significant gaps in the particle size distribution, potentially indicating a lack of certain particle sizes. This often results in poor compaction and increased void space within the material.
Applications of Sieve Analysis and Percent Finer Data
The applications of sieve analysis are numerous and span across various industries:
1. Civil Engineering:
-
Concrete Mix Design: Sieve analysis of aggregates (sand, gravel) is critical in determining the optimal mix proportions for concrete. The percent finer data ensures a good balance of particle sizes, leading to higher strength, durability, and workability. Understanding the grading curve helps engineers select the right aggregate mix for different applications, considering factors like compressive strength, freeze-thaw resistance, and permeability.
-
Soil Classification: In geotechnical engineering, sieve analysis plays a vital role in classifying soils based on their particle size distribution. This classification is crucial for determining the soil's engineering properties, such as its bearing capacity, permeability, and shear strength. The percent finer curve helps categorize the soil as gravel, sand, silt, or clay, guiding the design of foundations, earthworks, and other geotechnical structures.
-
Road Construction: The grading of aggregates used in asphalt and base courses is determined using sieve analysis. Optimal grading ensures proper compaction, stability, and durability of the pavement structure. Understanding the percent finer curve allows engineers to tailor the aggregate blend to meet specific traffic loads and environmental conditions.
2. Mining and Metallurgy:
-
Ore Processing: Sieve analysis is essential in characterizing the size distribution of ore particles. This information is crucial for optimizing crushing, grinding, and separation processes during ore processing. Understanding particle size allows for efficient extraction of valuable minerals and reduces waste.
-
Powder Metallurgy: In powder metallurgy, sieve analysis helps control the particle size distribution of metal powders used in manufacturing processes. Consistent particle size is vital for achieving uniform density, strength, and other desired properties in the final product.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry:
-
Drug Formulation: Sieve analysis is employed to ensure the uniformity of particle size in drug formulations. Consistent particle size contributes to consistent drug delivery and bioavailability.
-
Quality Control: Sieve analysis is a critical quality control tool in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that the final product meets predetermined specifications.
4. Other Industries:
-
Food Industry: Sieve analysis is used in food processing to classify food particles based on size. This is crucial for controlling the texture and consistency of various food products.
-
Agricultural Industry: Sieve analysis can be used to determine soil particle size distribution to optimize irrigation and fertilization techniques.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While standard sieve analysis provides valuable information, more advanced techniques can offer greater precision and detail:
-
Laser Diffraction: This technique uses laser light scattering to determine particle size distribution. It's particularly useful for finer particles that are difficult to analyze using sieves.
-
Image Analysis: This method uses digital image processing to analyze the size and shape of individual particles. This provides more comprehensive information than traditional sieve analysis alone.
-
Sedimentation Methods: These techniques utilize the settling behavior of particles in a liquid to determine their size distribution.
Conclusion
Sieve analysis, coupled with the interpretation of percent finer data, is an indispensable tool for characterizing granular materials. Its applications span a wide range of industries, playing a crucial role in quality control, material selection, and process optimization. By understanding the principles of sieve analysis and interpreting the percent finer curve accurately, engineers, scientists, and technicians can make informed decisions that lead to improved product quality, enhanced process efficiency, and enhanced structural integrity in various applications. The combination of traditional sieve analysis with advanced techniques provides a comprehensive understanding of particle size distribution, ensuring optimal material performance and reliability. Accurate data analysis and careful consideration of the specific application are crucial for leveraging the full potential of sieve analysis in various industries.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sieve Analysis - Percent Finer Chegg . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.