Seminspinalis Blank Extends And Rotates The Head.
Holbox
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
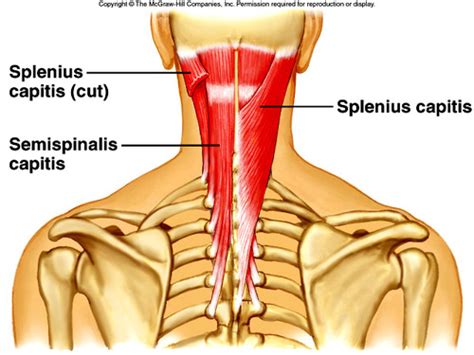
Table of Contents
- Seminspinalis Blank Extends And Rotates The Head.
- Table of Contents
- Semispinalis Capitis: The Extensor and Rotator of the Head
- Anatomy of the Semispinalis Capitis: A Deep Dive
- Origin and Insertion: The Anchors of Movement
- Innervation: The Neural Control Center
- Relationship with Other Muscles: A Synergistic Dance
- Function of the Semispinalis Capitis: Extension and Rotation
- Clinical Significance: When Things Go Wrong
- Muscle Strain and Sprain: A Common Issue
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Persistent Problem
- Posture and Alignment Issues: The Root Cause
- Other Conditions
- Rehabilitation and Treatment: Restoring Function
- Rest and Ice: Initial Management
- Physical Therapy: A Holistic Approach
- Medications: Pain Relief
- Prevention: Proactive Strategies
- Maintaining Good Posture: The Foundation of Health
- Regular Exercise: Strength and Flexibility
- Ergonomics: Optimizing Your Workspace
- Stress Management: A Holistic Approach
- Conclusion: Understanding the Semispinalis Capitis for Optimal Health
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Semispinalis Capitis: The Extensor and Rotator of the Head
The human head, a marvel of biological engineering, boasts a complex network of muscles responsible for its intricate movements. Among these crucial muscles, the semispinalis capitis plays a pivotal role, contributing significantly to head extension and rotation. Understanding its function, anatomy, and clinical implications is crucial for healthcare professionals, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in the intricacies of human biomechanics. This comprehensive article delves into the multifaceted nature of the semispinalis capitis muscle, exploring its actions, relationships with other muscles, potential injuries, and relevant rehabilitation strategies.
Anatomy of the Semispinalis Capitis: A Deep Dive
The semispinalis capitis, a deep muscle residing in the posterior neck, belongs to the transversospinalis group of intrinsic back muscles. This group is characterized by its muscles' oblique orientation, spanning multiple vertebrae. Unlike the superficial muscles responsible for gross movements, the transversospinalis muscles, including the semispinalis capitis, allow for fine motor control and precise movements of the head and neck.
Origin and Insertion: The Anchors of Movement
The semispinalis capitis originates from the transverse processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae (typically T1-T6) and the articular processes of the lower cervical vertebrae (C4-C7). From these origins, its muscle fibers ascend obliquely, converging to insert into the occipital bone, specifically the area between the superior and inferior nuchal lines. This strategic insertion point allows for significant influence on head movements.
Innervation: The Neural Control Center
The semispinalis capitis receives its neural input from the posterior rami of the upper cervical and lower thoracic spinal nerves (C1-C3 and T1-T6). This complex innervation pattern reflects its involvement in multiple head and neck movements.
Relationship with Other Muscles: A Synergistic Dance
The semispinalis capitis doesn't work in isolation. It collaborates closely with other muscles in the neck and upper back to execute various head and neck movements efficiently and gracefully. These synergistic relationships are crucial for maintaining posture and stability. Key muscles working in conjunction with the semispinalis capitis include:
- Splenius capitis: This superficial muscle also extends and rotates the head, often acting in concert with the semispinalis capitis.
- Rectus capitis posterior major and minor: These small, deep muscles contribute to head extension and rotation, providing finer control of movement.
- Suboccipital muscles (rectus capitis posterior major, rectus capitis posterior minor, obliquus capitis inferior, obliquus capitis superior): This group plays a vital role in proprioception (awareness of head position in space) and fine head movements.
Function of the Semispinalis Capitis: Extension and Rotation
The primary functions of the semispinalis capitis are:
-
Head Extension: By contracting bilaterally (both sides simultaneously), the semispinalis capitis extends the head, pulling it backward. This action is crucial for maintaining upright posture and counteracting the forward pull of gravity.
-
Head Rotation: When the semispinalis capitis contracts unilaterally (one side only), it rotates the head towards the opposite side. For instance, contraction of the right semispinalis capitis will rotate the head to the left. This rotation is vital for various everyday activities, such as looking over your shoulder.
-
Lateral Flexion (Side Bending): While not its primary function, unilateral contraction of the semispinalis capitis can contribute slightly to lateral flexion of the head towards the same side.
Clinical Significance: When Things Go Wrong
Problems affecting the semispinalis capitis can result in various symptoms and conditions.
Muscle Strain and Sprain: A Common Issue
Strain or sprain of the semispinalis capitis, often caused by sudden or forceful movements of the head or neck, is relatively common. This can lead to:
- Neck pain: Localized pain in the upper neck, often radiating to the head or shoulders.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion in the neck.
- Headaches: Pain may be felt in the back of the head, often described as tension headaches.
- Muscle spasms: Involuntary contractions of the muscle can exacerbate pain and stiffness.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Persistent Problem
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) can involve the semispinalis capitis, resulting in persistent pain and tenderness in the upper neck and head. Trigger points (hypersensitive areas within the muscle) can develop, leading to referred pain in other areas.
Posture and Alignment Issues: The Root Cause
Poor posture, prolonged sitting, or repetitive movements can overstress the semispinalis capitis and other neck muscles, potentially contributing to muscle imbalances, pain, and chronic headaches.
Other Conditions
Rarely, tumors or other pathologies can affect the semispinalis capitis, but these instances are significantly less common than muscle strains or myofascial pain.
Rehabilitation and Treatment: Restoring Function
Treatment and rehabilitation for semispinalis capitis issues focus on reducing pain, improving muscle flexibility, and restoring normal function. Common strategies include:
Rest and Ice: Initial Management
Initially, rest is crucial to allow the muscle to heal. Applying ice packs can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Physical Therapy: A Holistic Approach
Physical therapy is often a cornerstone of treatment. A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program focusing on:
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle stretches and movements to improve neck flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: Exercises to strengthen the semispinalis capitis and supporting neck muscles.
- Postural correction: Education and exercises to improve posture and reduce strain on the neck muscles.
- Manual therapy: Techniques such as massage and mobilization may be used to address muscle tightness and trigger points.
Medications: Pain Relief
Over-the-counter pain relievers (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation. In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication or muscle relaxants.
Prevention: Proactive Strategies
Preventing semispinalis capitis problems involves adopting proactive measures:
Maintaining Good Posture: The Foundation of Health
Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping is crucial. Regular posture checks and adjustments can help prevent muscle strain.
Regular Exercise: Strength and Flexibility
Regular exercise, including strength training and flexibility exercises, is beneficial for overall health and can help prevent muscle imbalances and injuries.
Ergonomics: Optimizing Your Workspace
Ergonomic workstation setups, including proper chair height, monitor placement, and keyboard positioning, can minimize strain on the neck and back.
Stress Management: A Holistic Approach
Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and pain. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce muscle tension.
Conclusion: Understanding the Semispinalis Capitis for Optimal Health
The semispinalis capitis, a crucial muscle in the neck, plays a vital role in head extension and rotation. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical implications is crucial for maintaining neck health and preventing injury. By adopting good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, individuals can protect this important muscle and maintain optimal head and neck function. This multifaceted muscle deserves attention, not only from healthcare professionals but from anyone seeking to understand and improve their own physical well-being. The information provided here serves as a comprehensive guide, highlighting the importance of this often-overlooked muscle in maintaining the health and functionality of the head and neck. Remember, proactive measures and early intervention are key to preventing and managing issues related to the semispinalis capitis.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Seminspinalis Blank Extends And Rotates The Head. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.