Select All That Apply To Calcitonin
Holbox
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
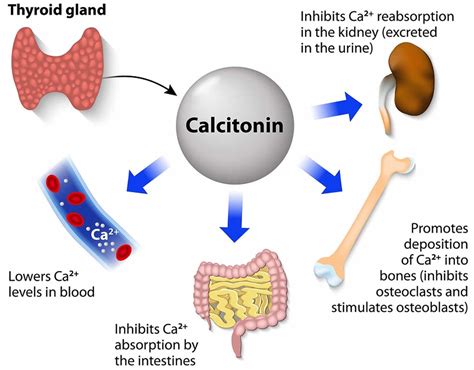
Table of Contents
- Select All That Apply To Calcitonin
- Table of Contents
- Calcitonin: A Deep Dive into its Functions, Mechanisms, and Clinical Significance
- Calcitonin Production and Regulation
- Mechanisms of Action: How Calcitonin Lowers Calcium Levels
- Detailed Molecular Mechanisms
- Physiological Effects and Significance of Calcitonin
- Calcitonin's Clinical Applications: When is it used?
- Disorders Related to Calcitonin Dysfunction
- Calcitonin: Future Directions and Research
- Conclusion: Calcitonin – A Vital Player in Calcium Homeostasis
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Calcitonin: A Deep Dive into its Functions, Mechanisms, and Clinical Significance
Calcitonin, a 32-amino acid polypeptide hormone, plays a crucial role in calcium homeostasis. While less prominent than parathyroid hormone (PTH) in maintaining calcium balance, its actions are vital, particularly in regulating bone metabolism and calcium excretion. This article will explore the multifaceted nature of calcitonin, delving into its production, mechanisms of action, physiological effects, clinical applications, and associated disorders.
Calcitonin Production and Regulation
Where is it produced? Primarily, calcitonin is synthesized and secreted by the parafollicular cells (also known as C-cells) of the thyroid gland. These cells are distinct from the follicular cells responsible for producing thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). A smaller amount of calcitonin is also produced by other tissues, such as the thymus and the brain.
What triggers its release? The primary trigger for calcitonin release is a rise in plasma calcium levels (hypercalcemia). This elevation is detected by the C-cells, leading to an increase in calcitonin secretion. Other factors influencing calcitonin release include:
- Gastrin: This gastrointestinal hormone can stimulate calcitonin secretion.
- Pentagastrin: Similar to gastrin, pentagastrin also acts as a potent stimulator.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK): This hormone, involved in digestion, has been shown to affect calcitonin levels.
- Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR): The CaSR located on C-cells acts as the primary sensor for extracellular calcium, initiating the release mechanism.
Mechanisms of Action: How Calcitonin Lowers Calcium Levels
Calcitonin exerts its hypocalcemic effects primarily through two mechanisms:
1. Inhibiting Bone Resorption: This is the most significant mechanism of calcitonin action. Calcitonin acts on osteoclasts, the bone cells responsible for bone resorption (breakdown). It binds to specific receptors on osteoclasts, inhibiting their activity and reducing the release of calcium and phosphate from the bone matrix. This slows down the rate at which calcium enters the bloodstream.
2. Increasing Renal Calcium Excretion: Calcitonin also promotes the excretion of calcium by the kidneys. It does this by increasing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and reducing the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules. This further contributes to lowering calcium levels in the blood.
Detailed Molecular Mechanisms
The precise molecular mechanisms by which calcitonin inhibits osteoclast activity are complex and still under investigation. However, several pathways are believed to be involved:
- Adenylate cyclase pathway: Calcitonin binding to its receptor activates adenylate cyclase, leading to an increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP). Increased cAMP levels then trigger intracellular signaling cascades that inhibit osteoclast activity.
- Protein kinase A (PKA) pathway: PKA, activated by cAMP, phosphorylates various proteins within the osteoclasts, leading to changes in their cytoskeleton and ultimately, reduced bone resorption.
- Other signaling pathways: Other pathways, such as those involving phospholipase C and calcium channels, are also believed to contribute to calcitonin's inhibitory effects.
Physiological Effects and Significance of Calcitonin
Calcitonin's primary physiological role is to counteract the effects of PTH, helping to fine-tune calcium homeostasis. While its effects are less dramatic than those of PTH, calcitonin plays a crucial role in preventing hypercalcemia and maintaining bone health.
1. Maintaining Calcium Homeostasis: Calcitonin's contribution to calcium balance is more pronounced in situations of hypercalcemia, effectively buffering against excessive increases in plasma calcium levels.
2. Protecting Bone Mass: By inhibiting bone resorption, calcitonin helps protect bone mass, especially in conditions like osteoporosis, where excessive bone loss occurs. Although not a primary treatment, it can play a supporting role.
3. Potential Effects on Other Systems: Emerging research suggests that calcitonin might have effects beyond calcium regulation. Studies are exploring its potential roles in other physiological processes, including inflammation, cardiovascular function, and even certain cancers. However, these potential effects are not yet fully understood and require further investigation.
Calcitonin's Clinical Applications: When is it used?
While not a first-line treatment for most calcium disorders, calcitonin finds applications in specific clinical settings:
-
Paget's Disease of Bone: This condition involves excessive bone turnover and remodeling. Calcitonin is used to reduce bone resorption and alleviate pain associated with Paget's disease.
-
Hypercalcemia of Malignancy: In cases of severe hypercalcemia caused by cancer, calcitonin can provide temporary relief by lowering calcium levels. It is usually used in conjunction with other treatments.
-
Osteoporosis: While not a standard treatment, calcitonin is sometimes used in conjunction with other medications to manage osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women. Its effectiveness in this context is debated, and other therapies are often preferred.
-
Bone Pain Management: Calcitonin's analgesic effects can be beneficial in reducing bone pain associated with various conditions, including fractures and metastatic bone disease.
Disorders Related to Calcitonin Dysfunction
Disorders related to calcitonin dysfunction are relatively rare compared to conditions involving PTH or vitamin D. However, abnormalities can occur:
-
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC): This rare type of thyroid cancer originates from the C-cells, which produce calcitonin. Measuring calcitonin levels is a crucial diagnostic and monitoring tool for MTC. Elevated calcitonin levels often indicate the presence of MTC.
-
Hypocalcitonemia: A deficiency of calcitonin is less commonly studied and characterized, but it's possible that it might contribute to an increased susceptibility to hypercalcemia or bone loss.
Calcitonin: Future Directions and Research
Research into calcitonin continues to explore its various aspects, including:
-
Exploring its broader physiological roles: Understanding calcitonin's potential effects beyond calcium regulation, such as its anti-inflammatory or cardiovascular properties.
-
Developing new delivery methods: Improving the delivery methods of calcitonin to enhance its effectiveness and reduce side effects.
-
Investigating its potential in cancer therapy: Exploring calcitonin's role in cancer progression and its possible therapeutic applications.
-
Unraveling the intricate details of its molecular mechanisms: Further elucidating the specific signaling pathways and cellular interactions involved in calcitonin's actions.
Conclusion: Calcitonin – A Vital Player in Calcium Homeostasis
Calcitonin, although not as prominently featured as PTH in the regulation of calcium balance, plays a critical role in maintaining calcium homeostasis and bone health. Its action in inhibiting bone resorption and promoting calcium excretion contributes to the overall fine-tuning of calcium levels in the bloodstream. While not a first-line treatment for many calcium-related conditions, calcitonin remains a valuable therapeutic tool in specific clinical settings and an active area of ongoing research. Its role extends beyond simple calcium regulation, suggesting future potential in various therapeutic areas. Further research will undoubtedly expand our understanding of this important hormone and its multifaceted functions within the body.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 Meters In Inches
May 21, 2025
-
82 90 Kg In Stone And Pounds
May 21, 2025
-
What Is 81 Cm In Inches
May 21, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 10
May 21, 2025
-
200 Kilos Is How Many Pounds
May 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Select All That Apply To Calcitonin . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.