Select All Of The Events That Happen In Anaphase.
Holbox
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
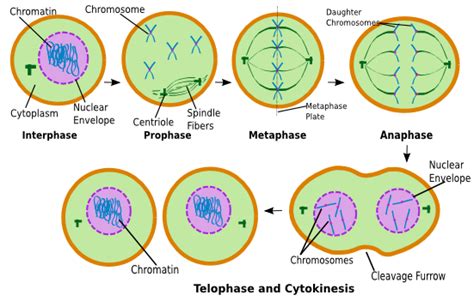
Table of Contents
- Select All Of The Events That Happen In Anaphase.
- Table of Contents
- Anaphase: A Deep Dive into the Events of Chromosome Separation
- Anaphase: Setting the Stage
- Anaphase A: The Journey to the Poles
- 1. Microtubule Depolymerization:
- 2. Motor Proteins:
- 3. The Role of Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC):
- Anaphase B: Spindle Pole Separation
- 1. Kinesin-5: Sliding Microtubules:
- 2. Kinesin-4 and Kinesin-10: Microtubule Depolymerization at the Plus-ends:
- 3. Dynein at the Cortex:
- 4. The Role of the Cell Cortex:
- The Checkpoint Mechanisms: Ensuring Accuracy
- Consequences of Anaphase Errors:
- Anaphase in Meiosis: Key Differences
- Concluding Remarks: The Intricate Dance of Chromosomes
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Anaphase: A Deep Dive into the Events of Chromosome Separation
Anaphase, a pivotal stage in cell division, is characterized by the precise separation of duplicated chromosomes and their movement towards opposite poles of the cell. This meticulously orchestrated process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete and identical set of genetic material. Understanding the intricacies of anaphase is crucial for comprehending the fundamental mechanisms of cell division and the potential consequences of errors during this critical phase. This article will delve deep into the events that transpire during anaphase, exploring both anaphase A and anaphase B, and discussing the regulatory mechanisms and potential implications of errors.
Anaphase: Setting the Stage
Before diving into the specifics of anaphase, it's important to briefly review the preceding stages of mitosis and meiosis, which set the stage for chromosome segregation. During prophase and prometaphase, chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle assembles. The spindle, a complex network of microtubules, plays a crucial role in chromosome movement during anaphase. Kinetochores, protein complexes assembled on the centromeres of each chromosome, serve as attachment points for the spindle microtubules. By the end of metaphase, chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate, equidistant from the two spindle poles, ensuring equal distribution during the subsequent anaphase separation.
Anaphase A: The Journey to the Poles
Anaphase A is primarily defined by the movement of chromosomes towards the spindle poles. This movement is driven by the shortening of kinetochore microtubules. Several mechanisms contribute to this shortening:
1. Microtubule Depolymerization:
The prevailing model suggests that kinetochore microtubules depolymerize at their kinetochore ends. This depolymerization, a carefully regulated process involving several motor proteins and associated enzymes, pulls the chromosomes towards the poles. Think of it like a rope being pulled in from one end – the chromosome is attached to that end and is dragged along as the rope shortens.
2. Motor Proteins:
Motor proteins, specifically cytoplasmic dynein, play a crucial role in the movement of chromosomes during anaphase A. Dynein, located at the poles of the cell, interacts with the kinetochore microtubules and actively “walks” along them, pulling the chromosomes towards the poles. This motor protein activity contributes significantly to the overall force generated for chromosome movement. The precise interaction and coordination between depolymerization and motor protein activity remain areas of active research.
3. The Role of Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC):
The CPC, a crucial regulator of mitosis, plays a significant role in ensuring accurate chromosome segregation during anaphase A. It contains several proteins, including Aurora B kinase, which is crucial for proper kinetochore-microtubule attachment. Aurora B ensures that chromosomes attach correctly to the spindle before anaphase onset. Improper attachment can lead to errors in chromosome segregation and aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number).
Anaphase B: Spindle Pole Separation
While anaphase A focuses on chromosome movement, anaphase B involves the separation of the spindle poles themselves. This process contributes to the overall elongation of the cell and ensures sufficient distance between the separating chromosomes. Several factors contribute to anaphase B:
1. Kinesin-5: Sliding Microtubules:
Kinesin-5, a plus-end-directed motor protein, is located on the overlapping microtubules in the spindle midzone. It moves along these microtubules, causing them to slide past each other. This sliding force pushes the spindle poles apart, contributing significantly to spindle elongation.
2. Kinesin-4 and Kinesin-10: Microtubule Depolymerization at the Plus-ends:
These plus-end-directed motor proteins work in conjunction with other factors to influence microtubule dynamics at the spindle poles. They contribute to the overall separation of the poles by interacting with and modulating the stability of microtubules.
3. Dynein at the Cortex:
Dynein, in addition to its role in anaphase A, also anchors the spindle poles to the cell cortex. By pulling on the astral microtubules (microtubules that radiate outward from the spindle poles), it helps to move the poles further apart. This contributes to cell elongation and the overall separation of the chromosomes.
4. The Role of the Cell Cortex:
The cell cortex, the cell's outer layer, plays a passive but essential role in anaphase B. It acts as an anchor point for the astral microtubules, providing a resistance point against which the dynein-mediated pulling force can act. This anchoring is crucial for effective pole separation.
The Checkpoint Mechanisms: Ensuring Accuracy
Throughout anaphase, numerous checkpoints ensure the fidelity of chromosome segregation. The most crucial checkpoint is the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). The SAC monitors the attachment of chromosomes to the spindle microtubules. If any errors in attachment are detected, the cell cycle is arrested at the metaphase-anaphase transition, preventing premature separation of chromosomes. This is vital to prevent aneuploidy and maintain genomic stability. If the SAC is overcome, the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is activated, triggering the events of anaphase.
Consequences of Anaphase Errors:
Errors during anaphase can have significant consequences, often leading to aneuploidy, a condition characterized by an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell. Aneuploidy can cause developmental defects, developmental disorders, and increased susceptibility to cancer. Errors in chromosome segregation can result from various factors, including:
- Improper kinetochore-microtubule attachments: If chromosomes are not properly attached to the spindle microtubules, they may not segregate correctly during anaphase.
- Defects in motor proteins: Mutations or dysregulation of motor proteins like kinesin and dynein can compromise chromosome movement and lead to aneuploidy.
- Errors in spindle assembly: Defects in spindle formation can lead to unequal chromosome distribution during anaphase.
- Failures in the SAC: If the SAC fails to detect or respond to errors in chromosome attachment, premature anaphase onset can occur, resulting in aneuploidy.
Anaphase in Meiosis: Key Differences
While the principles of chromosome segregation during anaphase are similar in both mitosis and meiosis, there are crucial differences. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, while in meiosis II, sister chromatids separate, as in mitosis. Meiosis I involves unique mechanisms to ensure proper segregation of homologous chromosomes, including the formation of chiasmata (crossovers) during prophase I and the precise coordination of microtubule attachments to kinetochores.
Concluding Remarks: The Intricate Dance of Chromosomes
Anaphase, with its two distinct phases – anaphase A and anaphase B – represents a meticulously choreographed event in cell division. The precise coordination of microtubule dynamics, motor protein activity, and checkpoint mechanisms ensures accurate chromosome segregation. Understanding the intricacies of anaphase is crucial for gaining insights into fundamental cellular processes, comprehending the consequences of errors, and developing strategies to address the challenges posed by chromosome instability in various human diseases, including cancer. Future research will likely focus on further elucidating the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying anaphase and their regulation, potentially revealing new therapeutic targets for combating diseases stemming from chromosome segregation errors.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Select All Of The Events That Happen In Anaphase. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.