Rna Plays A Role In Which Of The Following
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
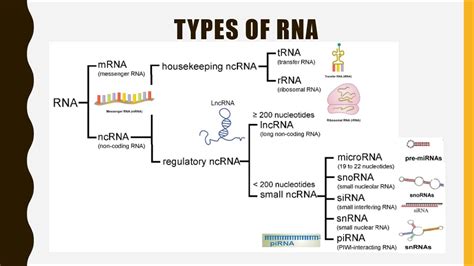
Table of Contents
RNA's Multifaceted Roles in Cellular Processes: Beyond Transcription
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a fundamental molecule in all known forms of life, playing a far more diverse and crucial role than simply serving as an intermediary between DNA and protein synthesis. While its role in protein synthesis (translation) is well-known, RNA's functions extend far beyond this, impacting virtually every aspect of cellular processes. This article delves deep into the multifaceted roles of RNA, exploring its involvement in gene regulation, catalysis, structural support, and even defense mechanisms within the cell.
RNA's Central Role in Protein Synthesis: The Well-Trodden Path
Before exploring RNA's less-known functions, it's crucial to briefly revisit its established role in protein synthesis. This process, central to life, involves two main types of RNA:
1. Messenger RNA (mRNA): The Blueprint
mRNA acts as the intermediary between DNA and ribosomes, carrying the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. The sequence of nucleotides in mRNA dictates the amino acid sequence of the protein being synthesized. Transcription, the process of creating mRNA from a DNA template, is the first crucial step in this pathway.
2. Transfer RNA (tRNA): The Amino Acid Shuttle
tRNA molecules are responsible for carrying specific amino acids to the ribosome based on the codons (three-nucleotide sequences) present in the mRNA. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that complements a specific codon, ensuring accurate amino acid placement during protein synthesis. This precise pairing is crucial for the synthesis of functional proteins.
3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): The Protein Synthesis Machinery
rRNA is a major structural component of ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for translating the mRNA sequence into a polypeptide chain. rRNA molecules not only provide structural support but also play a catalytic role in the process of peptide bond formation, linking amino acids together to build the protein.
Beyond Protein Synthesis: The Expanding World of RNA Functions
While the role of RNA in protein synthesis is fundamental, its impact extends far beyond this core function. Recent research has unveiled a remarkable diversity of RNA molecules and their roles in regulating gene expression, catalyzing reactions, and maintaining cellular structure.
Regulatory RNAs: The Orchestrators of Gene Expression
A significant portion of cellular RNA does not directly code for proteins but instead plays crucial roles in regulating gene expression. These regulatory RNAs encompass several types:
1. MicroRNAs (miRNAs): Tiny Regulators with Big Impact
miRNAs are small, non-coding RNA molecules (approximately 22 nucleotides long) that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally. They bind to complementary sequences in target mRNAs, leading to either mRNA degradation or translational repression. miRNAs play crucial roles in various cellular processes, including development, differentiation, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Dysregulation of miRNAs is linked to various diseases, including cancer.
2. Small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs): Targeted Gene Silencing
siRNAs are another class of small, non-coding RNAs involved in RNA interference (RNAi), a mechanism for gene silencing. They are typically generated from double-stranded RNA molecules and function similarly to miRNAs by binding to complementary sequences in target mRNAs, leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression. siRNAs are being explored as potential therapeutic agents for various diseases.
3. Long Non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs): The Versatile Regulators
lncRNAs are a diverse group of RNA molecules longer than 200 nucleotides that do not code for proteins. They are involved in various regulatory processes, including chromatin remodeling, transcription regulation, and mRNA splicing. Their functions are highly context-dependent and are still being actively investigated. The diverse roles of lncRNAs highlight the complexity of gene regulation.
4. Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs): Guardians of the Genome
piRNAs are a class of small non-coding RNAs primarily found in germline cells, playing a crucial role in silencing transposable elements (also known as "jumping genes"). These elements can disrupt genome stability, and piRNAs help prevent their uncontrolled proliferation, maintaining the integrity of the genome across generations.
Catalytic RNAs: Ribozymes - The RNA Enzymes
One of the most surprising discoveries in molecular biology was the realization that some RNA molecules possess catalytic activity, acting as enzymes. These catalytic RNAs are called ribozymes. This discovery challenged the dogma that only proteins could act as enzymes.
1. Ribozymes in RNA Processing
Several ribozymes are involved in RNA processing, including self-splicing introns (sequences within a gene that are removed during RNA processing) and RNase P, an enzyme involved in tRNA processing. These ribozymes demonstrate the versatility of RNA molecules.
2. The Ribosome: A Ribozyme at the Heart of Protein Synthesis
The ribosome, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis, is itself a ribonucleoprotein complex where the catalytic activity for peptide bond formation primarily resides within the rRNA component. This highlights the importance of RNA in this fundamental cellular process.
Structural RNAs: Maintaining Cellular Order
RNA also plays crucial structural roles within the cell. For instance, telomerase RNA provides a template for the synthesis of telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. This helps prevent chromosome degradation and maintain genome stability.
RNA in Defense Mechanisms: Viral Interference and Beyond
RNA molecules are also involved in the cell's defense mechanisms against viral infections. RNAi, mediated by siRNAs, plays a significant role in silencing viral genes, preventing viral replication.
RNA and Human Health: The Implications of RNA Dysfunction
Given the multifaceted roles of RNA, it's not surprising that RNA dysfunction is implicated in a wide range of human diseases. Mutations or dysregulation of RNA molecules can lead to various disorders, including:
- Cancer: Alterations in miRNA expression are frequently observed in cancerous cells, contributing to tumorigenesis and metastasis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Dysregulation of RNA processing and transport has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders.
- Infectious diseases: Viruses utilize RNA for their replication and pathogenesis, making RNA-targeted therapies a promising area of research.
- Genetic disorders: Mutations in genes encoding RNA-processing enzymes can lead to various genetic disorders.
RNA Therapeutics: Harnessing the Power of RNA
The growing understanding of RNA's diverse roles has led to the development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting RNA molecules. These include:
- RNA interference (RNAi) therapy: Using siRNAs or miRNAs to silence disease-causing genes.
- Antisense oligonucleotide therapy: Using short, synthetic DNA or RNA molecules to bind to and inhibit target RNA molecules.
- mRNA vaccines: Delivering mRNA encoding antigens to stimulate an immune response.
Conclusion: The Unfolding Story of RNA
The study of RNA is a rapidly evolving field, continuously unveiling new insights into its diverse roles and implications for human health. From its central role in protein synthesis to its involvement in gene regulation, catalysis, and defense mechanisms, RNA is a molecule of remarkable versatility and importance. Further research into RNA biology promises to revolutionize our understanding of cellular processes and lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for a wide range of diseases. The future of RNA research holds immense potential for advancing medicine and biotechnology. The continuous discovery of new RNA types and functions underscores the need for ongoing investigation, promising groundbreaking advancements in our comprehension of life itself. The intricate interplay between RNA molecules and other cellular components remains a fascinating area of study, promising further revelations about the complexities of cellular regulation and function. The exploration of RNA's therapeutic potential is particularly exciting, with RNA-based therapies offering innovative avenues for tackling previously intractable diseases. The ongoing unraveling of RNA's secrets promises to transform our approach to disease treatment and prevention.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Question Hamburger You Are Given Either An Aldehyde Or Ketone
Mar 15, 2025
-
Select The Statements That Best Explain Makalis Galt Activity Levels
Mar 15, 2025
-
You Optimize A Fitness Clubs Website To Include These Keywords
Mar 15, 2025
-
Aligining The Firm Philspy And Ethics
Mar 15, 2025
-
Order Qualifier Can Be Best Described As
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rna Plays A Role In Which Of The Following . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
