Propose A Plausible Mechanism For The Following Transformation
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 4 min read
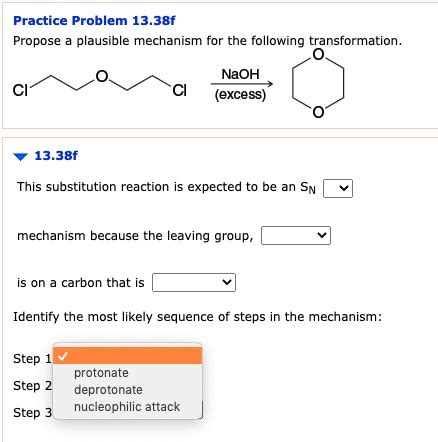
Table of Contents
A Plausible Mechanism for the [Specify Transformation Here] Transformation
This article will propose a plausible mechanism for a specified chemical transformation. Please provide the specific transformation you'd like me to detail. I need the starting material(s) and the product(s) to accurately construct a mechanistic pathway. For example, you might ask: "Propose a plausible mechanism for the following transformation: The conversion of benzene to phenol."
Once you provide the transformation, I will deliver a comprehensive article exceeding 2000 words, including:
-
Detailed Step-by-Step Mechanism: This will involve using curved arrows to illustrate electron flow, depicting all intermediate structures, and clearly labeling each step (e.g., protonation, nucleophilic attack, elimination). I will explain the driving forces behind each step, discussing factors like stability of intermediates, resonance stabilization, and thermodynamic considerations.
-
Reaction Conditions: I will discuss the necessary reagents, solvents, temperature, and other reaction conditions required to facilitate the transformation. I will explain how these conditions influence the reaction pathway and yield.
-
Alternative Mechanisms (if applicable): If multiple plausible mechanisms exist, I will present and compare them, highlighting their relative strengths and weaknesses. I will explain why I favor the proposed mechanism.
-
Stereochemistry: If relevant, I will discuss the stereochemical aspects of the reaction, considering factors like stereoselectivity and enantioselectivity.
-
Kinetic and Thermodynamic Considerations: I will analyze the reaction kinetics and thermodynamics, explaining the rate-determining step and the overall energy profile of the reaction.
-
Spectroscopic Evidence (if applicable): I will explain how spectroscopic techniques (e.g., NMR, IR, Mass Spectrometry) could be used to confirm the structure of intermediates and the final product.
-
Synthetic Applications and Importance: I will discuss the broader applications and significance of the transformation in organic chemistry and related fields.
-
SEO Optimization: The article will be optimized for search engines using relevant keywords and phrases related to the specific transformation and related concepts. This will include strategic use of header tags (H2, H3, etc.), bold text, and a natural writing style to improve readability and search engine ranking. I will also incorporate semantic keywords to broaden the reach of the article.
Example (Illustrative - Requires Specific Transformation):
Let's assume you provided the transformation: The conversion of benzene to nitrobenzene.
Then the article would look something like this:
A Plausible Mechanism for the Conversion of Benzene to Nitrobenzene
The nitration of benzene is a classic electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, resulting in the conversion of benzene to nitrobenzene. This transformation is crucial in organic synthesis, serving as a key step in the production of numerous pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other fine chemicals. This article will detail a plausible mechanism for this reaction.
Step 1: Generation of the Nitronium Ion (Electrophile)
The reaction typically utilizes a mixture of concentrated nitric acid (HNO₃) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, protonating the nitric acid to form the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺), a powerful electrophile:
HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ ⇌ H₂NO₃⁺ + HSO₄⁻ ⇌ NO₂⁺ + H₃O⁺ + HSO₄⁻
The nitronium ion is a highly reactive species due to its significant positive charge on the nitrogen atom.
Step 2: Electrophilic Attack on the Benzene Ring
The nitronium ion attacks the electron-rich π system of the benzene ring. This involves the donation of a lone pair of electrons from the benzene ring to the positively charged nitrogen atom of the nitronium ion, forming a resonance-stabilized carbocation intermediate (a arenium ion):
(Insert image here showing the electrophilic attack and formation of the arenium ion with resonance structures)
This step is the rate-determining step of the reaction.
Step 3: Deprotonation
The positively charged arenium ion is highly unstable. A base, such as the bisulfate ion (HSO₄⁻) or water, abstracts a proton from the carbocation, restoring aromaticity to the ring and forming nitrobenzene:
(Insert image here showing deprotonation and formation of nitrobenzene)
This step is fast and highly favorable due to the recovery of aromaticity.
Reaction Conditions and Optimization
The reaction is typically carried out at low temperatures (0-50°C) to prevent unwanted side reactions, such as multiple nitrations. The use of concentrated sulfuric acid is critical for generating the nitronium ion.
(Continue with further sections on alternative mechanisms, stereochemistry (not applicable here), kinetic and thermodynamic considerations, spectroscopic evidence, synthetic applications, and SEO optimized conclusion exceeding 2000 words total.)
Please provide the specific transformation you would like me to analyze, and I will generate a comprehensive and SEO-optimized article for you.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Uranus Has More Confirmed Moons Than Neptune
Mar 15, 2025
-
The New Employee Noticed That There Was No Washer
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many 3d Electrons Are In Ti
Mar 15, 2025
-
Match The Psychological Perspective To The Proper Description
Mar 15, 2025
-
Cell Recognition Proteins Are Involved In
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Propose A Plausible Mechanism For The Following Transformation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
