Place The Following Terms Or Examples With The Correct Category.
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
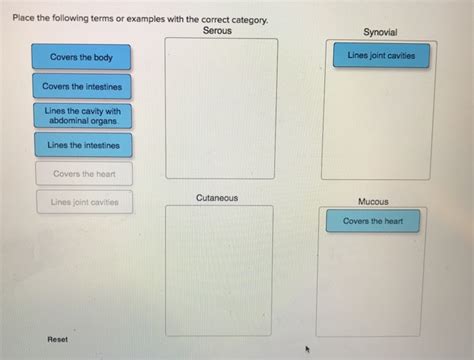
Table of Contents
Categorizing Concepts: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Organization
Organizing information effectively is crucial for clear communication and efficient knowledge management. Whether you're writing a research paper, building a database, or simply trying to make sense of a complex topic, understanding how to categorize information is key. This article explores different categorization methods and provides practical examples to help you master this essential skill. We'll cover several key categorization strategies, demonstrating how to correctly place various terms and examples into their respective categories.
Understanding Categorization Methods
Categorization, or classification, is the process of grouping similar items together based on shared characteristics. This process involves identifying relevant features and using them to create meaningful categories. Several methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
1. Taxonomic Categorization: Hierarchical Structure
Taxonomic categorization is a hierarchical system where broader categories are divided into increasingly specific subcategories. This approach is commonly used in biological classification (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species) and library organization (Dewey Decimal System, Library of Congress Classification).
Example:
Let's consider the category "Animals." This broad category can be broken down into:
- Mammals: (e.g., dogs, cats, elephants)
- Carnivores: (e.g., lions, tigers, wolves)
- Herbivores: (e.g., cows, horses, deer)
- Birds: (e.g., eagles, sparrows, penguins)
- Reptiles: (e.g., snakes, lizards, turtles)
- Amphibians: (e.g., frogs, toads, salamanders)
- Fish: (e.g., sharks, tuna, goldfish)
- Invertebrates: (e.g., insects, spiders, crustaceans)
This hierarchical structure allows for a systematic and organized approach to classifying a vast amount of information.
2. Thematic Categorization: Shared Themes or Concepts
Thematic categorization groups items based on shared themes, concepts, or ideas. This method is flexible and can be adapted to various contexts. Unlike taxonomic categorization, it doesn't necessarily follow a strict hierarchy.
Example:
Let's consider the theme "Environmental Concerns." Items could be categorized as follows:
- Pollution: Air pollution, water pollution, soil contamination, noise pollution, light pollution.
- Climate Change: Global warming, greenhouse gas emissions, sea-level rise, extreme weather events.
- Biodiversity Loss: Habitat destruction, deforestation, overfishing, poaching.
- Resource Depletion: Water scarcity, mineral depletion, fossil fuel depletion.
- Waste Management: Recycling, composting, landfill management.
This method allows for the grouping of diverse elements under a unifying theme, making it easier to understand complex relationships and patterns.
3. Functional Categorization: Based on Purpose or Use
Functional categorization groups items based on their purpose or function. This is particularly useful when dealing with tools, equipment, or software.
Example:
Consider the category "Kitchen Utensils." These could be categorized functionally as:
- Cooking Utensils: Pots, pans, spatulas, whisks, ladles.
- Serving Utensils: Plates, bowls, serving spoons, forks, knives.
- Baking Utensils: Baking sheets, muffin tins, mixing bowls, measuring cups, rolling pins.
- Cleaning Utensils: Sponges, dishcloths, brushes, scrubbers.
This categorization scheme allows users to quickly find the tools they need for a specific task.
4. Alphabetical Categorization: Simple and Straightforward
Alphabetical categorization is the simplest method, arranging items in alphabetical order based on their names or keywords. While simple, it can be less effective for complex datasets where relationships between items are important.
Example:
A list of countries can be easily categorized alphabetically:
- Afghanistan
- Albania
- Algeria
- ...and so on.
This method is useful for quick lookups but doesn't reveal any inherent relationships between the items.
5. Chronological Categorization: Ordered by Time
Chronological categorization arranges items based on their time of occurrence. This is commonly used for historical events, timelines, and project management.
Example:
A history lesson might organize events chronologically:
- 1775: The American Revolutionary War begins.
- 1776: The Declaration of Independence is signed.
- 1783: The Treaty of Paris is signed, ending the war.
This method clarifies the sequence of events and helps understand cause-and-effect relationships.
Practical Application: Categorizing Diverse Examples
Let's apply these methods to a diverse set of examples. Imagine you have the following list of items:
- Apple
- Banana
- Car
- Bicycle
- Orange
- Computer
- House
- Book
- Train
- Grapes
We can categorize these in several ways:
Categorization by Food Type:
- Fruits: Apple, Banana, Orange, Grapes
- Other (Non-Food): Car, Bicycle, Computer, House, Book, Train
Categorization by Mode of Transportation:
- Land Transportation: Car, Bicycle, Train
- Other (Non-Transportation): Apple, Banana, Orange, Computer, House, Book, Grapes
Categorization by Type of Asset:
- Real Estate: House
- Personal Property: Apple, Banana, Orange, Grapes, Car, Bicycle, Computer, Book, Train
Categorization by Use/Functionality:
- Food: Apple, Banana, Orange, Grapes
- Transportation: Car, Bicycle, Train
- Electronics: Computer
- Shelter: House
- Reading Material: Book
Each categorization method provides a different perspective on the same set of items. The best method to use depends on the specific goal and the relationships you want to highlight.
Advanced Categorization Techniques: Combining Methods
For complex datasets, combining categorization methods can be highly effective. For instance, you might use a hierarchical structure (taxonomic) for a primary categorization and then apply thematic or functional categorization within each subcategory.
Example: A library system might use a Dewey Decimal System (taxonomic) to categorize books by subject. Within each subject category, they might further categorize books by author (alphabetical) or publication date (chronological).
Choosing the Right Categorization Method
Selecting the appropriate categorization method is crucial for effective organization and retrieval of information. Consider the following factors:
- The nature of the data: What kind of items are you categorizing? Are they tangible objects, abstract concepts, or events?
- The purpose of categorization: What do you want to achieve by categorizing the data? Are you aiming for quick retrieval, detailed analysis, or knowledge discovery?
- The audience: Who will be using the categorized data? Tailor the method to their needs and understanding.
- Scalability: Will the categorization system need to accommodate new data in the future? Choose a method that can easily be expanded and updated.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate categorization method and create a clear, efficient, and meaningful organizational structure for your data. Mastering categorization is a key skill for anyone who works with information, enabling effective communication, knowledge management, and decision-making. Remember to always consider your specific needs and goals when deciding on the best way to organize your information. The examples provided here are just a starting point; experimentation and adaptation are key to finding the perfect categorization method for your unique context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit 8 Progress Check Mcq Answers
Mar 20, 2025
-
Folder Is To Document As Envelope Is To
Mar 20, 2025
-
Hospitality Sales And Marketing Amer Hotel
Mar 20, 2025
-
Simplify Your Answer As Much As Possible
Mar 20, 2025
-
In Airline Applications Failure Of A Component
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Place The Following Terms Or Examples With The Correct Category. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
