Match The Hormone Abbreviations With Their Function
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
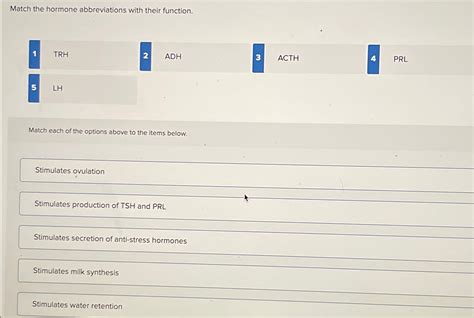
Table of Contents
- Match The Hormone Abbreviations With Their Function
- Table of Contents
- Matching Hormone Abbreviations with Their Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
- Key Hormones and Their Functions: A Detailed Breakdown
- 1. Hormones Involved in Growth and Development:
- 2. Hormones Regulating Metabolism and Energy Balance:
- 3. Hormones Involved in Reproduction and Sexual Development:
- 4. Hormones Regulating Calcium Metabolism:
- 5. Hormones Involved in Water Balance and Blood Pressure:
- Understanding Hormonal Imbalances and Their Consequences
- The Importance of Maintaining Hormonal Balance
- Conclusion: A Holistic View of Hormonal Regulation
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Matching Hormone Abbreviations with Their Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a vast array of bodily functions, from growth and development to metabolism and reproduction. Understanding the roles of different hormones is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into various hormone abbreviations and their corresponding functions, providing a detailed overview of the endocrine system's intricate workings. We'll explore the roles of these hormones in maintaining homeostasis, and highlight potential consequences of hormonal imbalances.
Key Hormones and Their Functions: A Detailed Breakdown
The human body produces a wide array of hormones, each with specific functions and targets. This section will examine some of the most important ones, categorized for easier understanding.
1. Hormones Involved in Growth and Development:
-
GH (Growth Hormone): GH, secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, plays a pivotal role in stimulating growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration. It's particularly crucial during childhood and adolescence, influencing linear bone growth and muscle mass development. Insufficient GH can lead to dwarfism, while excess can cause gigantism or acromegaly.
-
IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1): Often referred to as somatomedin C, IGF-1 is produced primarily in the liver in response to GH stimulation. It mediates many of GH's effects on growth and development, promoting protein synthesis and cell proliferation. IGF-1 levels are also linked to aging and overall health.
-
TH (Thyroid Hormones): These include thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), produced by the thyroid gland. THs are essential for regulating metabolism, influencing heart rate, body temperature, and growth. Hypothyroidism (low TH levels) leads to fatigue, weight gain, and slowed metabolism, while hyperthyroidism (high TH levels) can cause anxiety, weight loss, and rapid heart rate.
2. Hormones Regulating Metabolism and Energy Balance:
-
Insulin (INS): Produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, insulin is crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. It promotes glucose uptake by cells, converting it into energy or storing it as glycogen. Insulin deficiency leads to diabetes mellitus, characterized by high blood sugar levels.
-
Glucagon (GLU): Also secreted by the pancreas (alpha cells), glucagon has the opposite effect of insulin. It raises blood glucose levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in the liver. This is crucial during periods of fasting or low blood sugar.
-
Cortisol (COR): A steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, cortisol is a key player in the body's stress response. It regulates metabolism, blood pressure, and immune function. Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, causing various health issues.
-
Leptin (LEP): Produced by adipose tissue (fat cells), leptin signals to the brain about the body's energy stores. It suppresses appetite and increases energy expenditure. Leptin resistance, a condition where the brain doesn't respond properly to leptin, is associated with obesity.
-
Ghrelin (GHR): This hormone, also produced in the stomach, stimulates appetite. It acts as a counter-regulatory hormone to leptin, promoting food intake. Imbalances in ghrelin can contribute to eating disorders.
3. Hormones Involved in Reproduction and Sexual Development:
-
FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone): Secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries (females) and sperm production in the testes (males).
-
LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Also from the anterior pituitary, LH triggers ovulation in females and testosterone production in males.
-
Estrogen (EST): The primary female sex hormone, estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. It influences menstruation, pregnancy, and secondary sexual characteristics.
-
Progesterone (PROG): Another crucial female sex hormone, progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy and supports its maintenance during pregnancy.
-
Testosterone (TEST): The primary male sex hormone, testosterone is essential for the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, and muscle mass.
4. Hormones Regulating Calcium Metabolism:
-
PTH (Parathyroid Hormone): Produced by the parathyroid glands, PTH regulates calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood. It increases calcium absorption from the intestines and releases calcium from bones.
-
Calcitonin (CAL): Secreted by the thyroid gland, calcitonin has the opposite effect of PTH. It lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption.
5. Hormones Involved in Water Balance and Blood Pressure:
-
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone) or Vasopressin: Released by the posterior pituitary gland, ADH regulates water reabsorption in the kidneys, influencing blood volume and concentration. Insufficient ADH leads to diabetes insipidus, characterized by excessive urination.
-
Aldosterone (ALD): A mineralocorticoid hormone produced by the adrenal glands, aldosterone regulates sodium and potassium levels in the body, affecting blood volume and blood pressure.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalances and Their Consequences
Disruptions in hormone production or action can lead to various health problems. These imbalances can stem from genetic factors, lifestyle choices, or underlying medical conditions. Some examples include:
-
Diabetes Mellitus: Characterized by insufficient insulin production or resistance to insulin's effects, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
-
Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid gland, leading to low levels of thyroid hormones and slowed metabolism.
-
Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid gland, leading to elevated thyroid hormone levels and a sped-up metabolism.
-
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): A hormonal disorder in women characterized by irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and high levels of androgens.
-
Growth Hormone Deficiency: Insufficient GH production, resulting in stunted growth.
-
Cushing's Syndrome: Excess cortisol production, leading to weight gain, high blood pressure, and other metabolic disturbances.
The Importance of Maintaining Hormonal Balance
Maintaining hormonal balance is crucial for overall health and well-being. Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep quality significantly impact hormone levels. A healthy lifestyle can help regulate hormone production and minimize the risk of hormonal imbalances. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are also important for detecting and managing any hormonal irregularities.
Conclusion: A Holistic View of Hormonal Regulation
This comprehensive guide has explored a range of crucial hormones and their functions, highlighting the complex interplay within the endocrine system. Understanding the roles of these hormones is essential for maintaining health and well-being. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical attention when necessary, individuals can strive to maintain hormonal balance and prevent associated health complications. Remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns about your health or hormonal imbalances. Further research into specific hormones and their interactions can provide a deeper understanding of this fascinating and vital aspect of human biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Table Contains Information On The Price Per Month
Mar 30, 2025
-
Use A Row Level Button To Collapse Worksheet Rows
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Hormone Abbreviations With Their Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
