Match Each Supreme Court Document To Its Definition.
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 8 min read
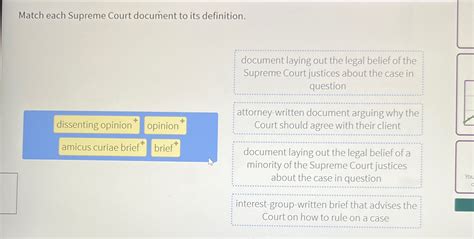
Table of Contents
Matching Supreme Court Documents to Their Definitions: A Comprehensive Guide
The Supreme Court of the United States, the highest court in the land, generates a vast amount of documentation throughout the year. Understanding the different types of documents and their significance is crucial for anyone interested in following legal proceedings, understanding constitutional law, or researching specific cases. This comprehensive guide will delve into various Supreme Court documents, providing clear definitions and explaining their importance within the judicial system. We'll explore key documents, focusing on their structure, content, and the role they play in the overall legal process. This will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of Supreme Court documentation and effectively utilize these resources for research and understanding.
Key Supreme Court Documents and Their Definitions:
This section provides detailed explanations of common Supreme Court documents, crucial for comprehending the Court's workings.
1. Writs of Certiorari (Certs):
-
Definition: A writ of certiorari is a request to the Supreme Court to review a lower court's decision. It's essentially a petition asking the Court to grant "cert," meaning they agree to hear the case. The Supreme Court receives thousands of certiorari petitions annually but only grants a small percentage, typically cases involving significant constitutional questions or conflicts among lower courts’ decisions.
-
Significance: The issuance of a writ of certiorari signals the Supreme Court's willingness to hear a case, indicating the legal importance and potential impact of the issues involved. The denial of certiorari does not indicate agreement with the lower court's ruling; it simply means the Court chooses not to review the case at that time.
-
Structure: A certiorari petition includes a detailed summary of the case, the legal questions at issue, and arguments demonstrating why the Supreme Court should review the case. It meticulously lays out the petitioner's legal standing and the significance of the case’s outcome.
2. Opinions of the Court (Majority Opinions):
-
Definition: The opinion of the Court, also known as the majority opinion, is the Court's official decision in a case. It outlines the majority's reasoning and legal justification for their ruling, setting a precedent that lower courts must follow. This document is the bedrock of legal understanding resulting from a Supreme Court case.
-
Significance: This opinion carries the force of law and significantly influences future legal interpretations and judgments in similar cases. It establishes legal precedents that guide the application of law throughout the nation.
-
Structure: A majority opinion typically begins with a summary of the facts and the procedural history of the case. It then analyzes the relevant legal arguments, cites relevant precedents, and articulates the Court's reasoning and conclusion. The majority opinion often includes a detailed explanation of the legal principles involved and their application to the specific facts of the case.
3. Dissenting Opinions:
-
Definition: A dissenting opinion is written by one or more justices who disagree with the majority's decision. It presents an alternative legal perspective and reasoning, outlining why the dissenting justices believe the majority's decision is incorrect.
-
Significance: While not legally binding, dissenting opinions are incredibly important. They can offer valuable insights into the legal issues involved and sometimes become influential in future cases, eventually shaping the legal landscape. They represent a powerful check on the majority's reasoning.
-
Structure: Similar in structure to the majority opinion, dissenting opinions outline the dissenting justice’s reasoning, cite relevant case law, and explain why they disagree with the majority. They often serve as a forceful critique of the majority’s interpretation of the law.
4. Concurring Opinions:
-
Definition: A concurring opinion is written by a justice who agrees with the majority's decision but for different reasons. They agree with the outcome but may offer different legal reasoning or emphasize different aspects of the case.
-
Significance: Concurring opinions can clarify or add nuance to the majority opinion. They may highlight specific legal points and offer alternative interpretations, enriching the overall understanding of the case's implications. They can influence the future development of legal principles, offering a perspective that's distinct from the majority.
-
Structure: Concurring opinions lay out the justice’s reasoning for agreeing with the majority's decision but from a distinct legal perspective. They might focus on particular aspects of the law or facts not fully addressed in the majority opinion.
5. Per Curiam Opinions:
-
Definition: A per curiam opinion is an unsigned opinion of the Court. It's typically brief and lacks the individual attribution of a justice's authorship. Often used for less significant cases or to address procedural matters.
-
Significance: Per curiam opinions are issued when the Court wants to make a ruling quickly or where the issue doesn't require extensive legal reasoning or detailed analysis. While less detailed, they still carry the weight of a Supreme Court decision.
-
Structure: Per curiam opinions are typically concise and address the key legal issue directly, lacking the detailed rationale often found in signed opinions.
6. Briefs (Amicus Curiae Briefs):
-
Definition: Briefs are formal legal documents submitted by parties to a case outlining their arguments. Amicus curiae briefs ("friend of the court" briefs) are submitted by individuals or groups not directly involved in the case but who have a strong interest in the outcome. They provide additional perspectives and information to the Court.
-
Significance: Amicus briefs play a vital role in shaping the Court's understanding of the issues presented. They offer expert opinions, statistical data, and other relevant information that can influence the Court's decision.
-
Structure: Amicus briefs typically include a summary of the case, a statement of interest, relevant legal arguments, and a conclusion suggesting how the Court should rule. They are structured to persuasively present additional perspectives to the Court.
7. Orders:
-
Definition: Orders are brief announcements from the Court regarding procedural matters or dispositions of cases, such as granting or denying certiorari petitions. They typically lack detailed legal reasoning.
-
Significance: Orders provide essential updates on the Court's actions, indicating which cases are accepted for review, decisions on motions, and other administrative matters. They are crucial for those tracking specific cases or Supreme Court activities.
-
Structure: Orders are typically short and concise, clearly stating the Court's ruling or procedural action without extensive explanations.
8. Oral Argument Transcripts:
-
Definition: These are verbatim records of the oral arguments presented by lawyers representing each party involved in a case. They capture the exchange between the justices and attorneys, providing insights into the Court's thinking and the arguments made.
-
Significance: Oral argument transcripts are valuable resources for understanding the legal and factual nuances presented before the Court. They reveal the dynamics of the questioning and provide context for the eventual opinions.
-
Structure: Transcripts present a sequential account of the arguments, questions, and responses between justices and lawyers in a formal question-and-answer format.
9. Docket Sheets:
-
Definition: Docket sheets are official records detailing the procedural history of a case, including filings, scheduling information, and other relevant actions.
-
Significance: They provide a chronological summary of the entire case, from its initial filing to the final decision. They are vital tools for tracking the progress of a case and understanding the procedural steps involved.
-
Structure: Docket sheets present a summary of events in a case's life cycle, listed chronologically with specific dates and descriptions of the actions taken.
Understanding the Context: The Supreme Court's Role
The Supreme Court's primary function is judicial review – the power to interpret laws and determine their constitutionality. The documents discussed above are integral to this process. They allow the Court to systematically consider legal issues, establish precedents, and shape the legal landscape of the nation. Understanding each document type is key to grasping the complexity and significance of the Supreme Court's role in the American legal system.
Utilizing Supreme Court Documents for Research and Analysis:
These documents are invaluable resources for legal scholars, researchers, students, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of American jurisprudence. They provide a wealth of information on various legal issues, the interpretation of laws, and the evolution of constitutional principles.
Effective use of these resources requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of their respective roles within the judicial process. By systematically comparing and contrasting different opinions—majority, dissenting, and concurring—researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities of a Supreme Court case. Careful analysis of the oral argument transcripts can reveal subtle nuances and hidden dimensions that might not be fully captured in the written opinions.
Further, the utilization of amicus briefs can enrich research by providing diverse perspectives and supplemental information that may not be present in the main arguments of the parties involved.
Conclusion:
The Supreme Court generates a diverse array of documents, each playing a crucial role in the nation's legal system. From the initial writ of certiorari to the final opinions, every document contributes to the Court's decision-making process and the development of legal precedents. By understanding the definitions and significance of each document type, individuals can effectively navigate the complexities of Supreme Court proceedings, enriching their understanding of the law and the Court's profound influence on American society. Proficient use of these resources is invaluable for legal professionals, scholars, and citizens alike, fostering a deeper appreciation for the workings of the highest court in the land. The thorough analysis of these documents empowers individuals to understand the nuanced complexities of legal interpretation and the enduring legacy of Supreme Court decisions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
In C3 Plants The Conservation Of Water Promotes
Mar 16, 2025
-
Food Preservation Does All Of The Following Except
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats 2 1 8 25 3 0
Mar 16, 2025
-
Alternate Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Statements Are True Check All That Apply
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match Each Supreme Court Document To Its Definition. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
