Locate The Centroid Y Of The Area
Holbox
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
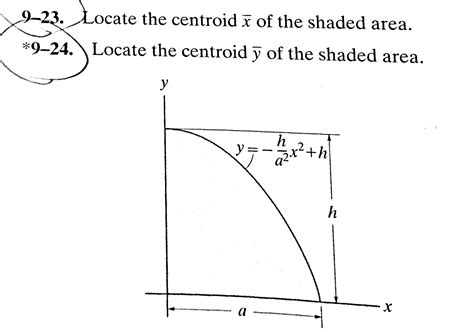
Table of Contents
Locating the Centroid y of an Area: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the centroid of an area is a fundamental concept in engineering, physics, and mathematics. Understanding its location, particularly the y-coordinate (centroid y), is crucial for various applications, from calculating moments of inertia to designing stable structures. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods and techniques used to locate the centroid y of an area, catering to both beginners and those seeking a deeper understanding.
Understanding Centroids and their Significance
The centroid of an area represents its geometric center. It's the point where the area would perfectly balance if it were a thin, flat lamina. For symmetrical shapes, the centroid is intuitively obvious; however, for irregular shapes, mathematical methods are necessary. The centroid's coordinates, (x̄, ȳ), define its position in a Cartesian coordinate system. This article focuses on finding ȳ, the y-coordinate of the centroid.
Knowing the centroid is vital for numerous applications:
- Structural Engineering: Determining the center of gravity for structural analysis and design, ensuring stability and load distribution.
- Mechanics: Calculating moments of inertia and centers of mass for various mechanical systems.
- Physics: Understanding the equilibrium and rotational dynamics of objects.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Used extensively in CAD software for analyzing and manipulating geometric shapes.
Methods for Locating the Centroid y
Several methods can be employed to locate the centroid y, each suitable for different scenarios. The choice of method depends on the complexity of the shape and the available information.
1. Using Integration: The Fundamental Method
For arbitrarily shaped areas, integration provides the most accurate method to determine the centroid y. This method involves defining the area as a function and applying the following formula:
ȳ = (∫[y*dA]) / (∫dA)
Where:
- ȳ is the y-coordinate of the centroid.
- y is the y-coordinate of an infinitesimal element of area dA.
- dA is an infinitesimal element of area.
- ∫dA represents the total area.
The integration limits depend on the specific shape's boundaries. This method requires proficiency in calculus and may involve complex integrations for intricate shapes. Let's illustrate with an example:
Example: Finding the centroid y of a parabolic segment
Consider a parabolic segment defined by the equation y = kx², where k is a constant, and bounded by the x-axis and x = a. To find ȳ:
-
Define dA: dA = y*dx = kx²dx
-
Integrate for the numerator: ∫[y*dA] = ∫[kx²(kx²)dx] = k²∫[x⁴dx] from 0 to a = (k²a⁵)/5
-
Integrate for the denominator (total area): ∫dA = ∫kx²dx from 0 to a = (ka³)/3
-
Calculate ȳ: ȳ = [(k²a⁵)/5] / [(ka³)/3] = (3ka²)/5
This example demonstrates the power of integration, but it also highlights the complexity that can arise with more intricate shapes.
2. Composite Areas Method: A Practical Approach
The composite areas method simplifies the centroid calculation for complex shapes by breaking them down into simpler, known shapes (rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.). This method leverages the centroid's properties of additivity. The centroid y of the composite area is calculated as the weighted average of the centroids of its individual components.
The formula is:
ȳ = Σ(Aᵢȳᵢ) / ΣAᵢ
Where:
- ȳ is the centroid y of the composite area.
- Aᵢ is the area of the i-th component.
- ȳᵢ is the y-coordinate of the centroid of the i-th component.
- Σ denotes summation over all components.
This method is highly practical and widely used in engineering applications. Its efficiency stems from readily available centroid coordinates for simple shapes, eliminating the need for complex integration.
Example: Finding the centroid y of an L-shaped area
An L-shaped area can be decomposed into two rectangles. By knowing the area and centroid y of each rectangle, we can easily calculate the overall centroid y using the composite areas method. This eliminates the complexities of direct integration for this irregular shape.
3. Using Numerical Methods: For Intricate Shapes
For extremely irregular shapes where analytical integration is impractical, numerical methods offer a viable solution. These methods approximate the area and centroid using numerical techniques such as:
- Simpson's rule: A numerical integration technique for approximating definite integrals.
- Trapezoidal rule: Another numerical integration technique, simpler than Simpson's rule but potentially less accurate.
- Finite element analysis (FEA): A powerful method for analyzing complex shapes by dividing them into smaller elements.
These numerical methods provide accurate approximations, especially when combined with powerful computational tools.
Practical Considerations and Applications
The accurate determination of the centroid y is essential in many real-world applications. Let's explore a few:
1. Structural Stability
In structural engineering, the centroid y (along with the centroid x) determines the center of gravity of a structure. This point is crucial for analyzing stability and ensuring that the structure doesn't topple over. For instance, designing a stable retaining wall requires careful consideration of the centroid's location to resist overturning moments.
2. Moment of Inertia Calculations
The moment of inertia is a crucial parameter in structural analysis, describing an object's resistance to bending or twisting. The centroid's location is vital in calculating the moment of inertia, as it serves as the reference point for the integration process. An accurate centroid calculation ensures accurate moment of inertia values, leading to safe and efficient structural designs.
3. Fluid Mechanics
In fluid mechanics, the centroid's location is essential for calculating hydrostatic forces on submerged objects. The pressure distribution on a submerged object depends on its depth, and the centroid acts as the point of application for the resultant hydrostatic force. Accurately locating the centroid is vital for designing structures that can withstand underwater pressure.
4. Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
CAD software extensively utilizes centroid calculations for various operations, including geometric modeling, mass property calculations, and finite element analysis. Accurate centroid calculations ensure the precision and reliability of the design process.
Advanced Topics and Further Exploration
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview of locating the centroid y, several advanced topics warrant further exploration:
- Centroids of three-dimensional objects: The principles extend to three dimensions, requiring triple integration or volume decomposition techniques.
- Theorems of Pappus-Guldinus: These theorems offer elegant ways to calculate surface areas and volumes of revolution using the centroid's location.
- Centroids of curved surfaces and lines: Special techniques are required to handle curved geometries.
Conclusion: Mastering Centroid Calculations
Locating the centroid y of an area is a fundamental concept with far-reaching applications across various disciplines. This guide provides a clear and comprehensive understanding of the various methods used, from basic integration techniques to more advanced numerical methods and composite area approaches. Mastering these methods is crucial for engineers, physicists, and anyone working with geometric shapes and their properties. By understanding the significance of the centroid and the different methods available, one can confidently tackle a wide range of problems and applications requiring the precise determination of the centroid y. Remember to choose the method best suited to the complexity of the shape and the desired level of accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Draw The Major Organic Product For The Reaction
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Solubility Product Constant Lab 17a Answers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Steven Roberts Oregon Mental Health Counselor Npi Number
Mar 14, 2025
-
In Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Rna Interference Occurs Through
Mar 14, 2025
-
Equilibrium Price Must Decrease When Demand
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Locate The Centroid Y Of The Area . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
