Label The Components Of The Cardiac Conduction System
Holbox
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
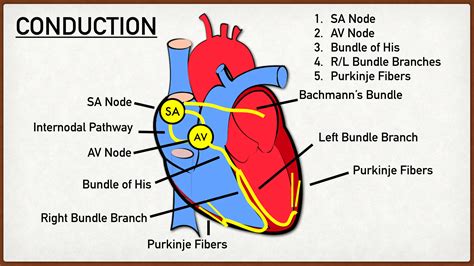
Table of Contents
- Label The Components Of The Cardiac Conduction System
- Table of Contents
- Label the Components of the Cardiac Conduction System: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Heart's Electrical Symphony: An Overview
- Key Components of the Cardiac Conduction System: A Detailed Exploration
- 1. Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The Heart's Natural Pacemaker
- 2. Atrial Myocardium: Spreading the Impulse
- 3. Atrioventricular (AV) Node: The Gatekeeper
- 4. Bundle of His: The Bridge
- 5. Bundle Branches: Dividing the Impulse
- 6. Purkinje Fibers: Rapid Conduction Network
- Clinical Significance and Diagnostic Tools
- Maintaining a Healthy Cardiac Conduction System
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Label the Components of the Cardiac Conduction System: A Comprehensive Guide
The human heart, a marvel of biological engineering, beats rhythmically and tirelessly throughout our lives. This rhythmic beating isn't a random event but a precisely orchestrated process controlled by a specialized network of tissues known as the cardiac conduction system. Understanding the components of this system is crucial for comprehending the mechanics of the heartbeat and diagnosing various cardiac conditions. This comprehensive guide will explore each component in detail, explaining its function and its role in the overall electrical activity of the heart.
The Heart's Electrical Symphony: An Overview
Before diving into the specifics of each component, let's establish a foundational understanding of the heart's electrical activity. The heart's ability to contract rhythmically is dependent on the generation and propagation of electrical impulses. These impulses initiate and coordinate the sequential contraction of the atria and ventricles, ensuring efficient blood flow throughout the body. The cardiac conduction system is responsible for generating and transmitting these electrical impulses in a highly organized manner. This coordinated process is often described as the heart's "electrical symphony," a precisely timed sequence of events that maintains the continuous rhythm of the heartbeat.
The failure of any part of this system can lead to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), which can have serious consequences. Understanding the components and their functions is therefore critical for diagnosing and managing these conditions.
Key Components of the Cardiac Conduction System: A Detailed Exploration
The cardiac conduction system comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in the generation and conduction of electrical impulses:
1. Sinoatrial (SA) Node: The Heart's Natural Pacemaker
The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium near the superior vena cava, is the primary pacemaker of the heart. It spontaneously generates electrical impulses at a rate of approximately 60-100 beats per minute in a healthy adult. These impulses initiate the heartbeat and determine the heart rate. The SA node's ability to spontaneously depolarize is due to the unique properties of its cells, which allow for the gradual influx of sodium ions, leading to the generation of an action potential. This inherent rhythmicity is crucial for maintaining a steady heart rate.
Key features of the SA node:
- Automaticity: The ability to generate its own electrical impulses without external stimulation.
- Rhythmicity: The ability to generate impulses at a regular and consistent rate.
- Conductivity: The ability to conduct impulses to other parts of the heart.
2. Atrial Myocardium: Spreading the Impulse
Once the SA node generates an impulse, it rapidly spreads throughout the atrial myocardium, the muscle tissue of the atria. This spread of electrical activity causes the atria to contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. The conduction pathway through the atrial myocardium is relatively fast, ensuring coordinated atrial contraction. This coordinated contraction is essential for efficient filling of the ventricles with blood. The atrial myocardium's role is often overlooked, but its efficient conduction is vital for effective heart function.
3. Atrioventricular (AV) Node: The Gatekeeper
The atrioventricular (AV) node, located in the right atrium near the tricuspid valve, plays a crucial role in regulating the transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node delays the impulse for about 0.1 seconds. This delay allows the atria to completely empty their blood into the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins. This delay is essential for optimal cardiac function. Without this delay, the atria and ventricles would contract simultaneously, greatly reducing the efficiency of blood pumping.
The AV node's key functions:
- Impulse Delay: Providing a brief delay to ensure efficient atrial emptying.
- Impulse Filtering: Preventing the transmission of abnormally rapid impulses from the atria, thus protecting the ventricles from rapid, disorganized contractions.
4. Bundle of His: The Bridge
The bundle of His, also known as the atrioventricular bundle, is a specialized collection of fibers that originates from the AV node and extends down into the interventricular septum, the wall separating the ventricles. This structure acts as a bridge, transmitting the electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The bundle of His is crucial for propagating the impulse to the ventricles, initiating their contraction. Its unique structure and specialized cells ensure efficient and rapid conduction of the electrical impulse.
5. Bundle Branches: Dividing the Impulse
The bundle of His quickly divides into two main branches, the right and left bundle branches. These branches travel down the interventricular septum, branching further into a network of Purkinje fibers. This branching pattern ensures that the impulse reaches all parts of the ventricles simultaneously, coordinating their contraction. This coordinated ventricular contraction is essential for generating strong and efficient heartbeats. Any blockage in these branches can disrupt the timing and coordination of ventricular contractions.
6. Purkinje Fibers: Rapid Conduction Network
The Purkinje fibers are a network of specialized conducting cells that spread throughout the ventricular walls. They are responsible for the rapid conduction of the electrical impulse to all parts of the ventricles, ensuring synchronized contraction. These fibers possess unique properties allowing for extremely rapid conduction, ensuring a near-simultaneous contraction of the ventricular muscle. This rapid and efficient spread of the impulse is vital for powerful and coordinated ventricular contraction. Disruptions to the Purkinje fibers can lead to inefficient or uncoordinated ventricular contractions.
Clinical Significance and Diagnostic Tools
Understanding the components of the cardiac conduction system is critical for diagnosing and managing a range of cardiac conditions, including:
- Heart Blocks: These occur when there is a disruption in the conduction pathway, resulting in a delay or complete blockage of the electrical impulse.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms caused by abnormal electrical activity in the heart.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): A common arrhythmia characterized by rapid and irregular atrial contractions.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): A serious arrhythmia characterized by rapid heartbeats originating in the ventricles.
Diagnostic tools such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) play a crucial role in identifying problems within the cardiac conduction system. An ECG provides a visual representation of the heart's electrical activity, allowing clinicians to identify abnormalities in the rhythm and conduction of impulses. The ECG can pinpoint areas of delay, blockage, or abnormal activity within the conduction system, guiding diagnosis and treatment.
Maintaining a Healthy Cardiac Conduction System
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preserving the integrity and function of the cardiac conduction system. Factors that contribute to a healthy heart include:
- Regular Exercise: Improves cardiovascular health and strengthens the heart muscle.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits increase the risk of heart disease.
Conclusion
The cardiac conduction system is a complex and intricately organized network of specialized tissues that orchestrates the rhythmic beating of the heart. Understanding the individual components – the SA node, atrial myocardium, AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers – and their roles in the generation and propagation of electrical impulses is vital for comprehending the mechanics of the heartbeat and diagnosing various cardiac conditions. Through proper lifestyle choices and regular medical checkups, we can work towards maintaining a healthy heart and ensuring the efficient function of this remarkable system. The coordinated electrical activity of this system is a testament to the sophisticated design of the human body and its continuous quest for maintaining homeostasis. Further research continues to unravel the intricate details of this system and its potential vulnerabilities, paving the way for improved diagnosis and treatment of cardiac conditions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Business Letters Are Important For Any Transaction That Requires
Apr 05, 2025
-
Rewards Included In Health Action Plans Should
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Inventory
Apr 05, 2025
-
Classify The Statements As True Or False
Apr 05, 2025
-
A Plastic Ocean Documentary Companion Questions
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Label The Components Of The Cardiac Conduction System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
