Label The Appropriate Images In The Atp Cycle
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
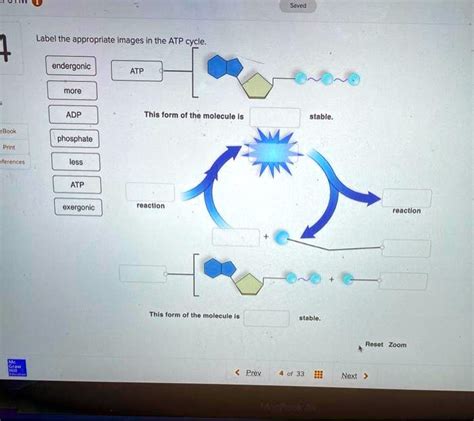
Table of Contents
- Label The Appropriate Images In The Atp Cycle
- Table of Contents
- Labeling the Appropriate Images in the ATP Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Stages of the Citric Acid Cycle and Their Corresponding Enzymes
- 1. Citrate Synthase: Condensation of Acetyl-CoA and Oxaloacetate
- 2. Aconitase: Isomerization of Citrate to Isocitrate
- 3. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: Oxidative Decarboxylation of Isocitrate
- 4. α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase: Oxidative Decarboxylation of α-Ketoglutarate
- 5. Succinyl-CoA Synthetase: Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
- 6. Succinate Dehydrogenase: Oxidation of Succinate
- 7. Fumarase: Hydration of Fumarate
- 8. Malate Dehydrogenase: Oxidation of Malate
- Visualizing the Cycle: Tips for Effective Diagram Labeling
- The Importance of Accurate Labeling and Understanding the ATP Cycle
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Labeling the Appropriate Images in the ATP Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway in aerobic organisms. It's a central component of cellular respiration, responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP, the cell's primary energy currency. Understanding this cycle requires visualizing its intricate steps, and accurately labeling diagrams is key to mastering this complex process. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the ATP cycle, explaining each step and providing detailed instructions on how to correctly label accompanying images.
The Stages of the Citric Acid Cycle and Their Corresponding Enzymes
The citric acid cycle is a cyclical series of eight enzymatic reactions that occur in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. Each step involves specific enzymes, substrates, and products. Let's break down each stage, providing crucial labeling information for accompanying diagrams:
1. Citrate Synthase: Condensation of Acetyl-CoA and Oxaloacetate
- Image Labeling: The image should clearly show the condensation reaction between acetyl-CoA (a two-carbon molecule derived from pyruvate oxidation) and oxaloacetate (a four-carbon molecule). Label the following:
- Acetyl-CoA: Indicate the two-carbon acetyl group attached to Coenzyme A.
- Oxaloacetate: Identify the four-carbon molecule.
- Citrate Synthase: Clearly mark the enzyme responsible for catalyzing this condensation reaction.
- Citrate: Label the six-carbon molecule formed, citric acid.
- CoA-SH: Indicate the release of Coenzyme A.
2. Aconitase: Isomerization of Citrate to Isocitrate
- Image Labeling: This step involves the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate, a structural isomer. The enzyme aconitase facilitates this process. Label the following:
- Citrate: The initial six-carbon molecule.
- Aconitase: The enzyme performing the isomerization.
- Isocitrate: The resulting six-carbon isomer.
- Water: Show the involvement of water molecules in this dehydration/hydration reaction.
3. Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: Oxidative Decarboxylation of Isocitrate
- Image Labeling: This is the first of two oxidative decarboxylation steps. Isocitrate is oxidized, releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide (CO2). Label the following:
- Isocitrate: The starting six-carbon molecule.
- Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme catalyzing the reaction.
- NAD+: Label the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form) acting as an electron acceptor.
- NADH + H+: Label the reduced form of NAD+ resulting from electron transfer.
- α-Ketoglutarate: Label the resulting five-carbon molecule.
- CO2: Indicate the release of carbon dioxide.
4. α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase: Oxidative Decarboxylation of α-Ketoglutarate
- Image Labeling: Similar to step 3, this is another oxidative decarboxylation reaction. α-Ketoglutarate is oxidized, releasing another molecule of CO2. Label the following:
- α-Ketoglutarate: The five-carbon molecule entering the reaction.
- α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme complex involved. This is a large complex similar to pyruvate dehydrogenase.
- NAD+: Label the NAD+ acting as an electron acceptor.
- NADH + H+: Label the reduced form of NAD+.
- Succinyl-CoA: Label the four-carbon molecule produced.
- CoASH: Show the participation of Coenzyme A.
- CO2: Indicate the release of carbon dioxide.
5. Succinyl-CoA Synthetase: Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
- Image Labeling: This step involves substrate-level phosphorylation, directly producing GTP (guanosine triphosphate), which is readily converted to ATP. Label the following:
- Succinyl-CoA: The four-carbon molecule entering the reaction.
- Succinyl-CoA Synthetase: The enzyme catalyzing the reaction.
- GDP: Label guanosine diphosphate.
- GTP: Label guanosine triphosphate, the direct product.
- Succinate: Label the resulting four-carbon molecule.
- CoA-SH: Indicate the release of Coenzyme A.
- Pi: Indicate the inorganic phosphate.
6. Succinate Dehydrogenase: Oxidation of Succinate
- Image Labeling: Succinate is oxidized, and the electrons are transferred to FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide), producing FADH2. Label the following:
- Succinate: The four-carbon molecule.
- Succinate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme catalyzing the oxidation.
- FAD: Label the oxidized form of flavin adenine dinucleotide.
- FADH2: Label the reduced form of FAD.
- Fumarate: Label the four-carbon molecule resulting from the oxidation.
7. Fumarase: Hydration of Fumarate
- Image Labeling: Fumarate is hydrated, adding a molecule of water to form malate. Label the following:
- Fumarate: The four-carbon molecule.
- Fumarase: The enzyme catalyzing the hydration reaction.
- Malate: Label the four-carbon molecule formed.
- H2O: Indicate the addition of water.
8. Malate Dehydrogenase: Oxidation of Malate
- Image Labeling: Malate is oxidized, and the electrons are transferred to NAD+, producing NADH. Label the following:
- Malate: The four-carbon molecule.
- Malate Dehydrogenase: The enzyme catalyzing this final step.
- NAD+: Label the NAD+ acting as an electron acceptor.
- NADH + H+: Label the reduced form of NAD+.
- Oxaloacetate: Label the four-carbon molecule that regenerates, completing the cycle.
Visualizing the Cycle: Tips for Effective Diagram Labeling
When labeling images of the citric acid cycle, consider these tips for clarity and accuracy:
- Use clear and concise labels: Avoid jargon and overly technical terms unless necessary.
- Use arrows to indicate the flow of the cycle: Show the direction of the reactions.
- Use different colors for different molecules: This enhances visual appeal and understanding.
- Maintain consistent labeling style: Use the same font, size, and style throughout the diagram.
- Include a legend if necessary: If using abbreviations or complex labels, provide a key to clarify their meaning.
- Ensure accuracy: Double-check all labels for accuracy in terms of chemical formulas, names, and reaction steps.
The Importance of Accurate Labeling and Understanding the ATP Cycle
Accurate labeling of diagrams associated with the ATP cycle is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved comprehension: Visual aids significantly enhance understanding of complex biological processes. Correct labeling clarifies each step.
- Effective learning: By actively engaging with diagrams and labeling them, students can reinforce their knowledge of the cycle.
- Enhanced problem-solving: A solid understanding of the cycle, reinforced by accurate labeling, improves the ability to solve related biological problems.
- Scientific communication: Accurate and detailed labeling is essential for effectively communicating scientific findings to others.
The ATP cycle is a fundamental process in biology. By diligently studying its stages, understanding the roles of enzymes, and meticulously labeling corresponding diagrams, you will build a solid foundation for deeper exploration of cellular respiration and metabolism. Remember, accurate labeling is not just about memorization; it's about building a comprehensive understanding of this vital biochemical pathway. Practice labeling different diagrams of the cycle, using varying styles and levels of detail, to solidify your grasp of this critical metabolic process. The more you practice, the more confident you'll become in your ability to understand and explain the intricacies of the ATP cycle.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Formal Education As An Approach To Employee Development Includes
Mar 29, 2025
-
Vail Company Recorded The Following Transactions During November
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Coversheet Is Attached To Help Protect A Secret Document
Mar 29, 2025
-
Elimination Reactions Are Favored Over Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Mar 29, 2025
-
One Important Role Of Purchasing Is To
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Label The Appropriate Images In The Atp Cycle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
