Is Nh4br Acidic Basic Or Neutral
Holbox
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
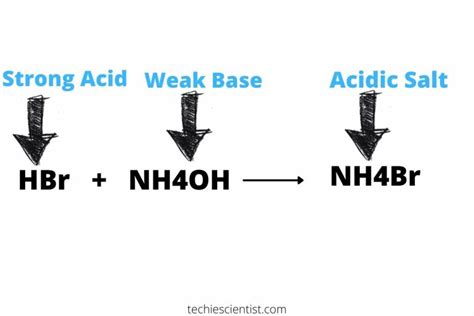
Table of Contents
- Is Nh4br Acidic Basic Or Neutral
- Table of Contents
- Is NH₄Br Acidic, Basic, or Neutral? A Deep Dive into Salt Hydrolysis
- Understanding Salts and Their Formation
- The Case of Ammonium Bromide (NH₄Br)
- Hydrolysis and its Effect on pH
- Determining the pH of an NH₄Br Solution
- Practical Applications and Implications
- 1. Buffer Solutions:
- 2. Photography:
- 3. Medicine:
- 4. Fire Retardants:
- Comparing NH₄Br to Other Salts
- Conclusion: NH₄Br is Acidic
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Is NH₄Br Acidic, Basic, or Neutral? A Deep Dive into Salt Hydrolysis
Understanding the acidity or basicity of a salt like ammonium bromide (NH₄Br) requires a solid grasp of acid-base chemistry, specifically the concept of salt hydrolysis. This article will explore the properties of NH₄Br, explain the process of hydrolysis, and definitively determine whether it forms an acidic, basic, or neutral solution in water. We'll also delve into the practical implications and applications of this knowledge.
Understanding Salts and Their Formation
Salts are ionic compounds formed from the reaction between an acid and a base. The reaction, known as a neutralization reaction, involves the combination of a cation (positive ion) from the base and an anion (negative ion) from the acid. The resulting salt can exhibit different properties depending on the strengths of the parent acid and base.
For example, the strong acid HCl reacting with the strong base NaOH produces the neutral salt NaCl (sodium chloride):
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
However, when one or both of the parent acids and bases are weak, the resulting salt can be acidic, basic, or neutral depending on the relative strengths of the conjugate acid and conjugate base formed.
The Case of Ammonium Bromide (NH₄Br)
Ammonium bromide (NH₄Br) is a salt formed from the reaction between a weak base, ammonia (NH₃), and a strong acid, hydrobromic acid (HBr):
NH₃(aq) + HBr(aq) → NH₄Br(aq)
To understand the acidity or basicity of NH₄Br, we need to examine the behavior of its ions in water:
- NH₄⁺ (Ammonium ion): This is the conjugate acid of the weak base ammonia (NH₃). It can donate a proton (H⁺) to water, forming hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) and ammonia. This process makes the solution acidic.
NH₄⁺(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ H₃O⁺(aq) + NH₃(aq)
- Br⁻ (Bromide ion): This is the conjugate base of the strong acid hydrobromic acid (HBr). Conjugate bases of strong acids are very weak and do not react significantly with water. Therefore, Br⁻ does not affect the pH of the solution.
Hydrolysis and its Effect on pH
Hydrolysis is the process where a salt reacts with water to produce an acidic or basic solution. In the case of NH₄Br, the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) undergoes hydrolysis, while the bromide ion (Br⁻) does not. The hydrolysis of NH₄⁺ produces H₃O⁺ ions, which increase the concentration of H⁺ in the solution, resulting in a lower pH.
Since the only ion affecting the pH is NH₄⁺ which acts as a weak acid, we conclude the solution will be acidic.
Determining the pH of an NH₄Br Solution
The exact pH of an NH₄Br solution depends on its concentration and the Ka (acid dissociation constant) of the ammonium ion. The Ka of NH₄⁺ is approximately 5.6 x 10⁻¹⁰. A higher concentration of NH₄Br will lead to a lower pH (more acidic).
Calculating the precise pH involves using the equilibrium expression for the hydrolysis of NH₄⁺ and solving for the concentration of H₃O⁺. This typically involves an ICE table (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) and the quadratic formula, or an approximation method if the Ka is small relative to the initial concentration. However, it's sufficient to know that the solution will be acidic due to the presence of the acidic ammonium ion.
Practical Applications and Implications
The acidic nature of NH₄Br solutions has various practical applications:
1. Buffer Solutions:
While NH₄Br alone doesn't form a buffer solution, it can be used in conjunction with ammonia (NH₃) to create a buffer solution. A buffer solution resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. This is crucial in many chemical and biological systems where maintaining a stable pH is essential.
2. Photography:
Ammonium bromide has been historically used in photographic processes, particularly in developing solutions. Its properties help in controlling the development process and image quality.
3. Medicine:
Ammonium bromide has had some applications in medicine, though its use is now largely restricted due to the availability of safer and more effective alternatives.
4. Fire Retardants:
Ammonium bromide has found use as a fire retardant in certain applications, though its use is being replaced by environmentally friendlier options.
Comparing NH₄Br to Other Salts
To solidify our understanding, let's compare NH₄Br to salts formed from different acid-base combinations:
-
NaCl (Sodium Chloride): Formed from a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH), NaCl is a neutral salt, producing a neutral solution in water.
-
NaCH₃COO (Sodium Acetate): Formed from a strong base (NaOH) and a weak acid (CH₃COOH), NaCH₃COO is a basic salt, producing a basic solution in water.
-
NH₄Cl (Ammonium Chloride): Similar to NH₄Br, NH₄Cl is formed from a weak base (NH₃) and a strong acid (HCl), resulting in an acidic solution.
The difference in the acidity or basicity of these salts stems from the relative strengths of the parent acid and base, and the subsequent behavior of the conjugate acid or base in water.
Conclusion: NH₄Br is Acidic
In summary, ammonium bromide (NH₄Br) is an acidic salt. This is because the ammonium ion (NH₄⁺), the conjugate acid of a weak base, undergoes hydrolysis in water, producing hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) and lowering the pH of the solution. The bromide ion (Br⁻), being the conjugate base of a strong acid, does not significantly affect the pH. Understanding the properties of NH₄Br and the process of salt hydrolysis is essential in various scientific and industrial applications. This knowledge allows for accurate prediction and control of pH in various chemical systems. Further exploration into the equilibrium calculations can provide a more precise understanding of the pH changes in various NH₄Br solutions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
New Cars Use Embedded Computers To Make Driving Safer
Apr 02, 2025
-
Traces Of Pesticide Are Found On Raw Poultry
Apr 02, 2025
-
The First Stage In The Rational Decision Making Process Involves
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Accounts Is An Asset
Apr 02, 2025
-
This Type Of Chemical Initiates Irreversible Alterations
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nh4br Acidic Basic Or Neutral . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
