If Forces Pull On The Horizontal Ring In Direction
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
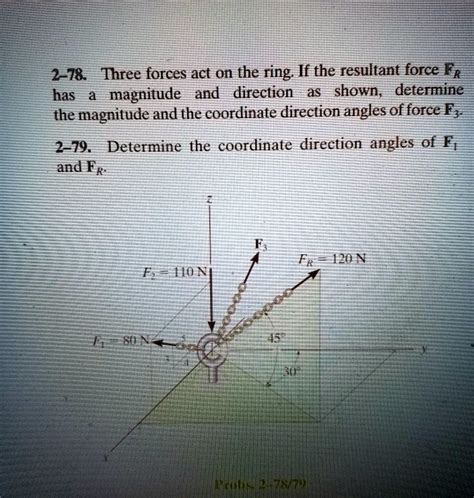
Table of Contents
If Forces Pull on a Horizontal Ring in Different Directions: A Comprehensive Analysis
Understanding how forces interact on a horizontal ring, especially when those forces pull in different directions, is crucial in various fields like engineering, physics, and even everyday scenarios. This comprehensive analysis will delve into the principles governing these interactions, exploring different scenarios and calculating resultant forces. We'll cover equilibrium, tension, and the importance of considering the vector nature of forces. Understanding these concepts is fundamental to predicting the behavior of systems under stress.
Understanding Forces and Vectors
Before we dive into the specific case of forces on a horizontal ring, let's establish a firm understanding of forces and their vector nature. A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to accelerate, change direction, or deform. Crucially, a force is a vector quantity, meaning it possesses both magnitude (strength) and direction. We represent forces graphically as arrows, where the arrow's length corresponds to the force's magnitude and the arrow's direction indicates the force's direction.
Vector Addition and Resolution
When multiple forces act on an object, their combined effect is determined by vector addition. We cannot simply add their magnitudes; instead, we must consider their directions. There are several methods for vector addition:
- Graphical Method: This involves drawing the force vectors to scale, head-to-tail. The resultant force is the vector drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
- Trigonometric Method: Using trigonometry (sine, cosine, and tangent rules), we can calculate the magnitude and direction of the resultant force based on the individual force magnitudes and angles.
- Component Method: This involves resolving each force vector into its horizontal and vertical components. The resultant force's horizontal component is the sum of the individual horizontal components, and similarly for the vertical component. The magnitude and direction of the resultant force can then be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometry.
Forces on a Horizontal Ring: Equilibrium and Tension
Imagine a horizontal ring, perhaps a circular metal ring or a similar structure. Forces are pulling on this ring from various directions. The ring's behavior depends heavily on the magnitudes and directions of these forces. A key concept here is equilibrium.
A system is in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero. In simpler terms, all the forces balance each other out. For our horizontal ring, this means the vector sum of all the forces acting on it must equal zero. If the ring is in equilibrium, it will remain stationary or move with a constant velocity (according to Newton's First Law).
Tension plays a vital role in the forces acting on a ring. Tension is the force transmitted through a rope, cable, wire, or similar one-dimensional continuous object, when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. In our horizontal ring scenario, if the ring is flexible, the tension will distribute itself along the ring's circumference. The tension at any point will be affected by the forces applied to the ring.
Analyzing Different Scenarios
Let's analyze some specific scenarios involving forces pulling on a horizontal ring.
Scenario 1: Two Equal and Opposite Forces
If two forces of equal magnitude pull on the ring in exactly opposite directions, the ring will be in equilibrium. The forces cancel each other out, resulting in a net force of zero. The tension in the ring will be equal to the magnitude of each of the individual forces.
Scenario 2: Two Unequal Forces in Opposite Directions
If two forces of unequal magnitude pull on the ring in opposite directions, the ring will not be in equilibrium. The net force will be equal to the difference between the two forces, and it will act in the direction of the larger force. The ring will likely accelerate in that direction. The tension in the ring will vary depending on the location around the ring's circumference, being greater on the side subjected to the greater force.
Scenario 3: Multiple Forces at Different Angles
This is the most complex scenario. Imagine three or more forces pulling on the ring at various angles. To determine whether the ring is in equilibrium, we must use vector addition techniques.
- Graphical Method: Draw the force vectors head-to-tail. If the last vector's head meets the tail of the first vector, the ring is in equilibrium.
- Component Method: Resolve each force into its horizontal and vertical components. Sum the horizontal and vertical components separately. If both sums are zero, the ring is in equilibrium. If not, the resultant force can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, and its direction determined using trigonometry.
Scenario 4: Forces and Friction
If we introduce friction into the scenario (for example, the ring resting on a rough surface), this adds another force to consider. Friction opposes motion and acts in the direction opposite to the net force trying to move the ring. The presence of friction will affect the equilibrium conditions and can significantly alter the ring's behaviour under the influence of applied forces.
Practical Applications and Examples
Understanding forces on a horizontal ring has significant practical applications in various engineering and physics contexts.
- Load-bearing structures: Bridges, buildings, and other structures often have circular or ring-like components that must withstand significant forces from different directions. Accurate force analysis is critical to ensure structural integrity.
- Mechanical systems: Many mechanical systems, such as gears and pulleys, involve rotating components that experience forces in various directions. Analyzing these forces helps engineers design efficient and reliable systems.
- Satellite orbits: The forces acting on a satellite orbiting the Earth can be modeled as forces acting on a ring, although the ring's geometry would be more complex. Understanding these forces is essential for maintaining stable orbits and controlling satellite trajectories.
Advanced Concepts and Further Considerations
This analysis has focused on relatively simple scenarios. However, more complex scenarios may require advanced techniques.
- Dynamic Equilibrium: This refers to a situation where the ring is moving with a constant velocity while the forces are balanced. This is distinct from static equilibrium, where the ring is stationary.
- Stress and Strain: For a more realistic analysis, we must consider how the forces cause stress and strain within the material of the ring. This requires an understanding of material properties and elasticity.
- Three-Dimensional Forces: Our analysis has focused on forces acting within a single plane. In a more general scenario, forces might act in three dimensions, requiring the use of three-dimensional vector analysis.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay of forces on a horizontal ring is fundamental to various fields. Whether you're dealing with simple scenarios involving two forces or complex systems with multiple forces and friction, applying the principles of vector addition and equilibrium analysis provides a rigorous framework for predicting the ring's behavior. From understanding static equilibrium to appreciating the impact of dynamic forces and considering material properties, this in-depth analysis helps us to not just solve problems but design safer, more efficient, and more reliable systems. Remember to always consider the vector nature of forces and use appropriate methods (graphical, trigonometric, or component) to determine the resultant forces and understand the state of equilibrium within the system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Statement About Groupthink Is Correct
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids Are
Mar 20, 2025
-
To Avoid Fatigue When Should Team Roles
Mar 20, 2025
-
Which Sentence Uses The Underlined Word Correctly
Mar 20, 2025
-
The Great Compromise Did All Of The Following Except
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about If Forces Pull On The Horizontal Ring In Direction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
