Identify The Structure Indicated By The Lines.
Holbox
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
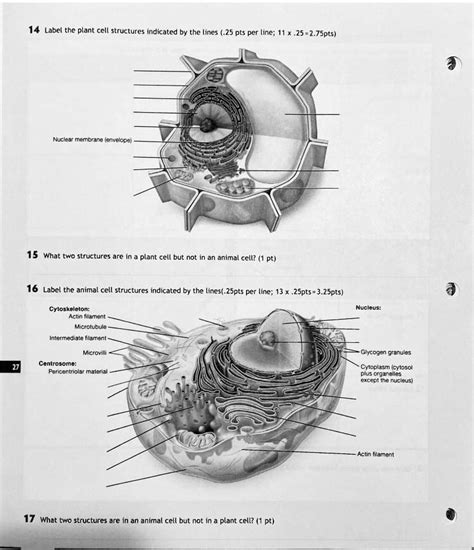
Table of Contents
- Identify The Structure Indicated By The Lines.
- Table of Contents
- Identify the Structure Indicated by the Lines: A Comprehensive Guide to Line Analysis
- Understanding the Language of Lines
- Analyzing Lines in Different Contexts
- 1. Geometric Structures
- 2. Architectural Drawings and Designs
- 3. Engineering Diagrams and Schematics
- 4. Artistic Representations
- 5. Cartography and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Advanced Techniques for Line Analysis
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Identify the Structure Indicated by the Lines: A Comprehensive Guide to Line Analysis
Identifying the structure indicated by lines is a fundamental skill across various disciplines, from art and architecture to engineering and computer science. Lines, seemingly simple elements, possess immense power in conveying information, creating form, and establishing relationships within a given context. This comprehensive guide will explore different approaches to interpreting lines and their structural implications, focusing on how to analyze them effectively to understand the underlying structure they represent.
Understanding the Language of Lines
Before delving into specific examples, let's establish a foundational understanding of how lines communicate. Lines are not merely visual elements; they are carriers of meaning, capable of expressing:
-
Direction and Movement: Horizontal lines often suggest stability and calmness, while vertical lines communicate strength and authority. Diagonal lines convey dynamism, action, and instability. Curved lines suggest fluidity, grace, and sometimes deception.
-
Relationships and Connections: Lines can connect points, define boundaries, and illustrate relationships between different elements. Parallel lines suggest harmony and order, while converging lines might indicate perspective or a focal point. Intersecting lines create tension and complexity.
-
Form and Shape: Lines define the edges and contours of shapes, creating the illusion of three-dimensionality. The arrangement and type of lines used determine the overall form and its perceived characteristics.
-
Emphasis and Hierarchy: The thickness, color, and style of lines can be used to create visual hierarchy and emphasize specific elements within a structure. Thicker lines often draw more attention than thinner ones.
Analyzing Lines in Different Contexts
The interpretation of lines heavily depends on the context in which they are presented. Let's explore several key areas:
1. Geometric Structures
In geometry, lines form the basis of various shapes and figures. Analyzing the lines in a geometric structure involves identifying:
-
Types of Lines: Are the lines straight, curved, parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting? Understanding these classifications is crucial for describing the structure.
-
Angles and Relationships: Measuring the angles formed by intersecting lines helps define the shapes and understand their properties (e.g., right angles, acute angles, obtuse angles).
-
Symmetry and Patterns: Look for symmetry and repeating patterns formed by the lines. This reveals underlying geometric principles and organization.
Example: A square is defined by four straight lines of equal length, forming four right angles. This simple example illustrates how lines define a shape's fundamental properties.
2. Architectural Drawings and Designs
Architectural drawings rely heavily on lines to represent structural elements, spatial relationships, and design details. Analyzing the lines in architectural drawings involves:
-
Identifying Structural Components: Lines represent walls, beams, columns, and other structural members. The arrangement of these lines reveals the building's overall skeletal framework.
-
Understanding Spatial Relationships: Lines define rooms, corridors, and open spaces. The spatial relationships illustrated by lines help visualize the building's layout and functionality.
-
Interpreting Perspective and Dimension: Lines are used to create perspective drawings, showing how the structure appears from a specific viewpoint. The convergence of lines helps define depth and distance.
Example: A floor plan uses lines to delineate walls, doors, and windows, clearly illustrating the spatial organization of a building's interior.
3. Engineering Diagrams and Schematics
Engineering diagrams often employ lines to represent connections, flows, and processes. Analyzing these lines requires:
-
Understanding Line Symbols: Specific lines might represent different components, signals, or data flows (e.g., solid lines for physical connections, dashed lines for logical connections).
-
Tracing Pathways and Relationships: Following the lines allows you to understand the flow of information or materials within a system.
-
Identifying Components and Interactions: Lines connect various components, illustrating their interactions and dependencies.
Example: A circuit diagram uses lines to represent wires and connections between different electronic components, revealing the circuit's overall functionality.
4. Artistic Representations
In art, lines are powerful expressive tools used to create mood, form, and movement. Analyzing lines in artwork requires sensitivity to:
-
Line Quality and Style: The weight, texture, and character of lines (e.g., thick, thin, jagged, smooth) contribute to the artwork's overall effect.
-
Implied Lines and Movement: Lines can imply movement and direction even if not physically drawn. The viewer's eye follows the path suggested by the lines.
-
Emotional Impact: The type and arrangement of lines contribute to the artwork's emotional impact. Harsh lines might convey tension, while soft lines might suggest tranquility.
Example: In a painting, the use of thick, bold lines might convey a sense of power and strength, while delicate, thin lines might suggest fragility and grace.
5. Cartography and Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Maps and GIS data rely heavily on lines to represent features, boundaries, and networks. Analysis involves:
-
Identifying Geographic Features: Lines represent roads, rivers, coastlines, and political boundaries. Their arrangement reveals the geographical context.
-
Understanding Spatial Relationships: Lines illustrate the relationships between different geographical features, such as the proximity of cities or the course of a river.
-
Interpreting Data and Patterns: Lines can represent data like elevation contours or population density, showing spatial patterns and variations.
Example: A road map uses lines to represent roads and highways, showcasing their network and connectivity.
Advanced Techniques for Line Analysis
Beyond basic identification, more advanced techniques can provide deeper insights:
-
Vector Analysis: In computer graphics and engineering, vector analysis provides a mathematical framework for describing and manipulating lines and shapes.
-
Image Processing and Computer Vision: Algorithms can automatically identify and analyze lines within images, enabling automated analysis of complex structures.
-
Fractal Geometry: Fractal geometry examines lines with self-similar patterns, revealing intricate structures found in nature.
Conclusion
Identifying the structure indicated by lines is a multifaceted skill requiring careful observation, contextual awareness, and a solid understanding of the underlying principles. By mastering the techniques outlined in this guide, you will be equipped to analyze lines effectively across a variety of contexts, gaining valuable insights into the structures they represent and the information they convey. Whether analyzing geometric figures, architectural drawings, or artistic representations, the ability to decipher the language of lines empowers you to unlock deeper meaning and understanding. Remember that the interpretation of lines is often subjective, influenced by personal experience and cultural background. However, a systematic approach to analysis allows for a more objective and accurate understanding of the underlying structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
75 00 An Hour Is How Much A Year
May 19, 2025
-
16 55 An Hour Is How Much A Year
May 19, 2025
-
What Is 61 Kg In Lbs
May 19, 2025
-
122 Cm Is How Many Inches
May 19, 2025
-
What Is 63 Inches In Centimeters
May 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Identify The Structure Indicated By The Lines. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.