How Many Valence Electrons Does Nitrogen Have
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
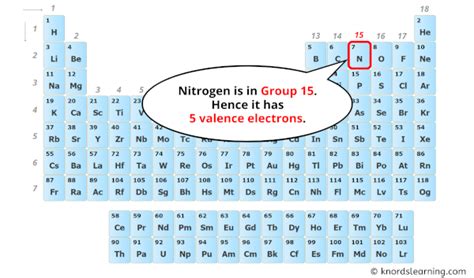
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Nitrogen Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Nitrogen, a ubiquitous element crucial for life as we know it, holds a fascinating position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is key to grasping its chemical behavior and the diverse roles it plays in various compounds and biological processes. This comprehensive guide will explore the question: How many valence electrons does nitrogen have? and delve into the underlying principles of atomic structure that dictate this number.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we pinpoint nitrogen's valence electrons, let's define the term. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell or energy level of an atom. These electrons are the most loosely bound to the nucleus and, therefore, are the ones involved in chemical bonding. They determine an element's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's chemical properties and its position within the periodic table.
Nitrogen's Atomic Structure: Unveiling the Mystery
Nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7, meaning it possesses 7 protons and 7 electrons in a neutral atom. To determine the number of valence electrons, we must understand how these electrons are arranged within the atom's electron shells. The distribution of electrons follows specific rules based on the principles of quantum mechanics.
Electron Shell Configuration
Electrons reside in distinct energy levels or shells, each capable of holding a specific number of electrons. The shells are labeled using integers, starting with n=1 (closest to the nucleus) and increasing outwards. The maximum number of electrons each shell can hold is given by the formula 2n², where 'n' is the shell number.
- Shell 1 (n=1): This shell can hold a maximum of 2 electrons (2(1)² = 2).
- Shell 2 (n=2): This shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons (2(2)² = 8).
Nitrogen's 7 electrons are distributed as follows:
- Shell 1: 2 electrons
- Shell 2: 5 electrons (7 total electrons - 2 in shell 1 = 5)
This electron configuration is often represented as 1s²2s²2p³. The '1s²' indicates two electrons in the 1s orbital, '2s²' indicates two electrons in the 2s orbital, and '2p³' indicates three electrons in the 2p orbitals.
Determining Nitrogen's Valence Electrons
Remember, valence electrons reside in the outermost shell. In nitrogen's case, the outermost shell is the second shell (n=2), which contains 5 electrons. Therefore, nitrogen has 5 valence electrons.
Nitrogen's Chemical Behavior: A Consequence of Valence Electrons
The presence of 5 valence electrons profoundly impacts nitrogen's chemical behavior. Atoms strive to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling the nearest noble gas. For nitrogen, this means aiming for a full outer shell of 8 electrons (octet rule). To achieve this stability, nitrogen readily forms covalent bonds by sharing its valence electrons with other atoms.
Covalent Bonding in Nitrogen
Nitrogen's 5 valence electrons allow it to form up to three covalent bonds. A classic example is ammonia (NH₃), where nitrogen shares three electrons with three hydrogen atoms, forming three single covalent bonds. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron to complete the nitrogen atom's octet. In some instances, nitrogen can form a triple bond, as seen in nitrogen gas (N₂), where two nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons, achieving a stable octet for each atom.
Other Chemical Properties Influenced by Valence Electrons
Nitrogen's 5 valence electrons also contribute to its other chemical characteristics, including:
- High electronegativity: Nitrogen strongly attracts electrons in a covalent bond, making it relatively electronegative.
- Formation of diverse compounds: Nitrogen's ability to form various bonds with different atoms leads to the formation of a wide array of compounds with diverse properties. Examples include nitrates, nitrites, amino acids, and nucleic acids – all crucial for biological processes.
- Relatively low reactivity under standard conditions: While nitrogen can form strong bonds, the triple bond in N₂ requires significant energy to break, resulting in its relative inertness under standard conditions. This is why nitrogen gas makes up a large portion of the Earth's atmosphere.
Nitrogen's Role in Biological Systems: A Valence Electron Perspective
Nitrogen's 5 valence electrons make it a vital component of life. Its ability to form stable covalent bonds is essential for the formation of:
- Amino acids: The building blocks of proteins, amino acids contain nitrogen atoms in their amine groups.
- Nucleic acids: DNA and RNA, the carriers of genetic information, incorporate nitrogen in their nucleotide bases.
- Chlorophyll: The molecule responsible for photosynthesis in plants contains nitrogen.
- Other biomolecules: Numerous other vital biomolecules rely on nitrogen's bonding capabilities.
Beyond the Basics: Orbital Hybridization and Molecular Geometry
The simplistic picture of electron shells and valence electrons provides a foundational understanding, but a deeper exploration involves orbital hybridization and molecular geometry. While nitrogen's 5 valence electrons dictate its bonding capacity, the specific arrangement of those electrons in hybridized orbitals determines the shape of the molecules it forms.
Orbital Hybridization in Nitrogen
In reality, nitrogen's valence electrons occupy not just s and p orbitals but also hybridized orbitals, which are combinations of atomic orbitals that have different energies and shapes. This hybridization further fine-tunes the bonding capabilities and influences the resulting molecular geometry. For example, in ammonia (NH₃), nitrogen's orbitals undergo sp³ hybridization, resulting in a tetrahedral molecular geometry (though with a lone pair on the nitrogen, making it pyramidal).
Applications of Nitrogen and its Compounds: Leveraging Valence Electrons
The properties dictated by nitrogen's valence electrons translate into a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen-containing compounds are essential components of fertilizers, crucial for agriculture and food production. The ease with which nitrogen bonds with other elements allows for the creation of compounds readily absorbed by plants.
- Explosives: Certain nitrogen compounds, such as nitroglycerin, are powerful explosives due to the strong bonds formed, which release a substantial amount of energy upon decomposition.
- Pharmaceuticals: Nitrogen is a vital component of numerous pharmaceutical drugs, contributing to their biological activity and effectiveness. Nitrogen's ability to form a variety of bonds makes it a versatile tool in drug design.
- Materials Science: Nitrogen is used in the synthesis of advanced materials with specific properties, enhancing their durability, reactivity, or other desirable characteristics.
Conclusion: The Significance of Nitrogen's Valence Electrons
The seemingly simple question, "How many valence electrons does nitrogen have?" opens a door to a fascinating world of atomic structure, chemical bonding, and the element's profound impact on the natural world and human society. Nitrogen's 5 valence electrons are not merely a number; they are the key to understanding its reactivity, the bonds it forms, and the vital roles it plays in biological systems and industrial applications. Understanding these fundamental principles is crucial for advancements in various fields, from agriculture and medicine to materials science and technology. Therefore, comprehending the significance of nitrogen's valence electrons is far more than an academic exercise; it’s essential for addressing many of humanity's greatest challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cyclic Amp Phosphodiesterase Is An Enzyme That Catalyzes The Conversion
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Usual Starting Point For A Master Budget Is
Mar 17, 2025
-
When Preparing To Begin A Speech Positive Nervousness Refers To
Mar 17, 2025
-
An Increase In Income Will Blank
Mar 17, 2025
-
Management Is Defined As The Pursuit Of Organizational Goals
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Nitrogen Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
