How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
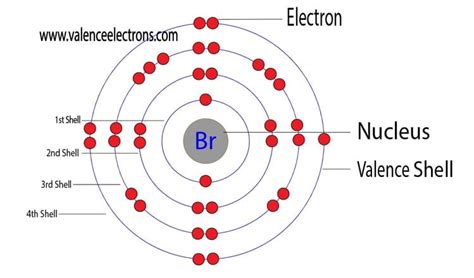
Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have
- Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have? A Deep Dive into Bromine's Electronic Structure
- Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Reactivity
- Bromine's Position in the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
- Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electronic Configuration
- Why Only 4s and 4p Electrons are Valence Electrons?
- Bromine's Chemical Behavior: A Consequence of Seven Valence Electrons
- Real-World Applications: From Photography to Flame Retardants
- Comparing Bromine to Other Halogens: The Role of Valence Electrons
- Conclusion: The Significance of Valence Electrons in Bromine's Chemistry
- Further Exploration:
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have? A Deep Dive into Bromine's Electronic Structure
Bromine, a fascinating element with a rich history and diverse applications, holds a key position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is crucial to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article delves into the specifics of bromine's valence electrons, exploring its position in the periodic table, electron configuration, and how its valence electrons dictate its chemical properties and bonding patterns. We'll also explore some real-world applications that highlight the importance of understanding bromine's valence electrons.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Reactivity
Before diving into bromine specifically, let's establish a fundamental understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (energy level) of an atom. These electrons are the most loosely held and, therefore, participate directly in chemical bonding with other atoms. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses significantly determines its reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. Atoms strive for a stable electron configuration, often achieving this by gaining, losing, or sharing valence electrons to attain a full outermost shell—a state often referred to as achieving a noble gas configuration.
Bromine's Position in the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
Bromine (Br) is a nonmetal located in Group 17 (also known as Group VIIA or the halogens) of the periodic table. The periodic table's organization provides crucial information about an element's electron configuration. Elements within the same group share similar valence electron configurations, leading to similar chemical properties. Halogens are known for their high reactivity, a direct consequence of their seven valence electrons.
Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electronic Configuration
To definitively determine the number of valence electrons in bromine, we must examine its electron configuration. Bromine has an atomic number of 35, meaning it has 35 protons and 35 electrons in a neutral atom. The electron configuration of bromine is:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵
Let's break this down:
- 1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These represent the filled inner electron shells. These electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and do not participate in chemical bonding.
- 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵: This represents the outermost electron shell, also known as the valence shell. This shell contains a total of seven electrons (2 + 10 + 5 = 17 - but only the 4s and 4p electrons are considered valence electrons).
Therefore, bromine has seven valence electrons.
Why Only 4s and 4p Electrons are Valence Electrons?
While the 3d electrons are in the third energy level, they are considered inner electrons in bromine. The energy levels are filled in order but the higher energy level (4s and 4p) contains the outermost electrons and dictates the atom's chemical reactivity and bonding capabilities.
Bromine's Chemical Behavior: A Consequence of Seven Valence Electrons
The seven valence electrons explain bromine's chemical behavior:
- High Reactivity: Bromine readily reacts with many elements because it needs only one more electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration (like krypton). This drive towards stability explains bromine's high reactivity.
- Formation of -1 Ions: Bromine readily accepts an electron to form the bromide ion (Br⁻), achieving a stable octet of electrons. This is a common feature of halogens.
- Covalent Bonding: Bromine can also share electrons with other atoms to form covalent bonds. This occurs when bromine shares electrons with other nonmetals such as hydrogen, oxygen, or carbon. Examples of compounds formed this way include hydrogen bromide (HBr) and bromine trifluoride (BrF₃).
- Oxidizing Agent: Bromine's tendency to gain an electron makes it a strong oxidizing agent. This means it can readily accept electrons from other substances, causing them to be oxidized (lose electrons).
Real-World Applications: From Photography to Flame Retardants
Understanding bromine's valence electrons is vital for understanding its numerous applications:
- Photography: Historically, silver bromide (AgBr) was crucial in photographic film. The silver bromide crystals are sensitive to light, and upon exposure, undergo a chemical change facilitating image formation. This reaction is directly linked to the reactivity of bromine and its ability to gain electrons.
- Flame Retardants: Organobromine compounds are widely used as flame retardants in various materials, including plastics, textiles, and electronic components. Their effectiveness in suppressing fires is related to the presence of bromine's reactive bonds that effectively interfere with combustion processes.
- Water Treatment: Bromine compounds are utilized in water purification as disinfectants. They effectively kill bacteria and other harmful microorganisms, owing to the reactivity of bromine and its ability to disrupt their cellular processes.
- Medical Applications: Certain bromine compounds find applications in medicine, although this area requires careful consideration of toxicity.
- Industrial Chemistry: Bromine is used in various industrial processes, including the production of other chemicals, dyes, and pesticides.
Comparing Bromine to Other Halogens: The Role of Valence Electrons
The halogens—fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine—all have seven valence electrons, which explains their many similarities in chemical behavior. However, there are also differences in reactivity. Fluorine is the most reactive halogen because its smaller size leads to stronger electron-nucleus attraction, making it easier to attract an electron. As you go down the group, the reactivity decreases. Bromine's reactivity is intermediate among the halogens, reflecting the balance between its electron affinity and the increased size of its atom.
Conclusion: The Significance of Valence Electrons in Bromine's Chemistry
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses is paramount in determining its chemical properties and reactivity. Bromine, with its seven valence electrons, showcases this principle perfectly. Its tendency to gain an electron to achieve a stable octet explains its high reactivity, its ability to form ionic and covalent bonds, and its role as an oxidizing agent. Understanding this fundamental aspect of bromine's electronic structure is crucial for comprehending its diverse applications in various fields, from photography and flame retardants to water treatment and medical applications. The consistent number of valence electrons across the halogen group also highlights the predictive power of the periodic table in understanding chemical behavior.
Further Exploration:
- Investigating the different types of organobromine compounds and their specific applications.
- Exploring the environmental impact of bromine-containing compounds and the search for more sustainable alternatives.
- Delving deeper into the photochemistry of silver bromide in photographic processes.
- Comparing and contrasting the various methods used for bromine extraction and purification.
- Researching the different compounds used as bromine disinfectants in water treatment and their relative effectiveness.
This deeper exploration can provide a more nuanced understanding of bromine's significance in our world and its role in chemistry and related fields. By understanding bromine's seven valence electrons and their implications, we can better appreciate the multifaceted nature of this important element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Adrenal Gland
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Activities Are Examples Of Data Gathering
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Term Flattened Management Hierarchies Refers To
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Are Correct
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Shown In The Image
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
