How Many Dna Combinations Are There
Holbox
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
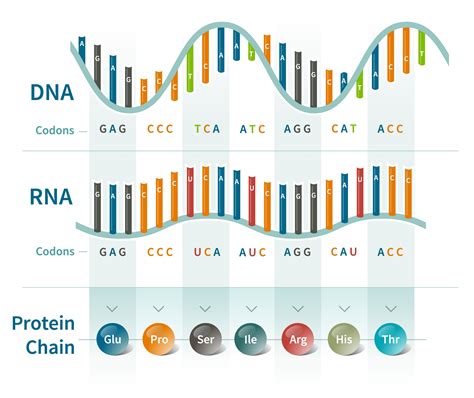
Table of Contents
How Many DNA Combinations Are There? Exploring the Vastness of Genetic Possibilities
The human genome, the complete set of instructions for building and maintaining a human being, is a remarkably complex structure. Encoded within its 3 billion base pairs lies the blueprint for our physical characteristics, predispositions to diseases, and even aspects of our personality. A fundamental question arises from this complexity: how many possible DNA combinations are there? The answer is staggering, defying easy comprehension, and highlighting the incredible diversity of life.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Nucleotides and Base Pairs
Before delving into the sheer number of combinations, let's review the basics. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-stranded helix composed of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases pair specifically: A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C. These base pairs are the fundamental units of genetic information.
The sequence of these base pairs along the DNA molecule determines the genetic code. The order of A, T, C, and G dictates the specific instructions for building proteins, which are the workhorses of our cells and bodies. Changes in this sequence, known as mutations, can lead to variations in traits, and in some cases, diseases.
Calculating the Number of Combinations: A Mathematical Approach
To determine the number of possible DNA combinations, we need to consider the length of the human genome and the number of possible bases at each position. The human genome is approximately 3 billion base pairs long. At each position in the sequence, there are four possibilities (A, T, C, or G).
To calculate the total number of possible combinations, we use the following formula:
4<sup>n</sup>
Where 'n' is the number of base pairs. In our case, n is approximately 3 billion.
This results in a number so astronomically large that it's difficult to comprehend or even express fully. It's far beyond the scale of numbers we encounter in everyday life, far exceeding the number of atoms in the observable universe. Scientists often use scientific notation to represent such vast numbers.
Using scientific notation, the number of possible human DNA combinations would be approximately 4<sup>3,000,000,000</sup>. This is a number with billions of digits. To put it in perspective, if you could write a digit every second, it would take far longer than the age of the universe to write out this number.
Beyond the Simple Calculation: Factors Influencing Genetic Diversity
The above calculation represents a simplified model. Several factors add layers of complexity and further increase the potential for genetic variation:
1. Mutations and Genetic Variations:
Mutations, changes in the DNA sequence, are a constant source of genetic variation. These mutations can be spontaneous or induced by environmental factors like radiation or certain chemicals. They can range from single base changes (point mutations) to larger-scale rearrangements of DNA segments. This constant flux of mutations contributes significantly to the vastness of possible DNA combinations.
2. Recombination during Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction shuffles the genetic deck in a powerful way. During meiosis, the process of forming gametes (sperm and egg cells), homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material through a process called recombination or crossing over. This recombination creates new combinations of alleles (different versions of a gene) that were not present in either parent. This process dramatically increases the genetic diversity within a population.
3. Gene Duplication and Rearrangements:
Entire genes or stretches of DNA can be duplicated or rearranged during evolution. These events create new genetic material that can be subject to further mutation and selection, leading to the evolution of new functions and traits. Gene duplication and rearrangement add yet another dimension to the potential for genetic variation.
4. Epigenetics: Beyond the DNA Sequence
Epigenetics refers to heritable changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. These changes can affect how genes are "read" and expressed, influencing traits without changing the actual DNA code. Factors such as DNA methylation and histone modification can affect gene expression, adding another layer of complexity to the total number of possible genetic outcomes. While not changing the base pair sequence, these epigenetic modifications drastically alter the phenotypic expression, significantly increasing the possible outcomes beyond the purely numerical calculation.
The Implications of Vast Genetic Diversity:
The sheer number of possible DNA combinations underscores several crucial points:
-
Uniqueness of Individuals: The probability of two individuals (excluding identical twins) having the exact same DNA sequence is infinitesimally small. This highlights the unique genetic makeup of every human being.
-
Evolutionary Potential: The vastness of possible genetic combinations provides the raw material for evolution. Natural selection acts upon this variation, favoring traits that enhance survival and reproduction. This process leads to the adaptation and diversification of species over time.
-
Challenges in Genetic Research: The immense complexity of the human genome poses significant challenges for genetic research. Analyzing and understanding the intricate interactions between genes and the environment requires sophisticated tools and analytical methods.
-
Personalized Medicine: The growing understanding of the human genome is driving the development of personalized medicine. This approach tailors medical treatments to an individual's unique genetic makeup, potentially leading to more effective and safer therapies.
Conclusion: A Universe Within Us
The question of how many DNA combinations are there leads us to a humbling realization: the human genome encompasses a vast, almost unimaginable, potential for genetic diversity. While a simple calculation provides a starting point, the reality is far more intricate, involving mutations, recombination, gene duplication, and epigenetic modifications. This complexity underlies the uniqueness of each individual, the remarkable diversity of the human population, and the ongoing evolution of our species. Understanding this vastness is crucial not only for furthering our knowledge of biology but also for advancing fields like personalized medicine and genetic engineering, promising revolutionary changes in healthcare and our understanding of ourselves. The universe within each of us is truly breathtaking in its complexity.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Documenting The Gba Plus Process Can Assist You With
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Is A Homonym For Soar
Mar 10, 2025
-
A Cashier Is Finishing A Transaction With A Customer
Mar 10, 2025
-
Hey Mom I Finished That Book About Jennifer
Mar 10, 2025
-
Documents Are Marked With A Number And Then A Name
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Dna Combinations Are There . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
