Histamine Serotonin And Bradykinin Are All
Holbox
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
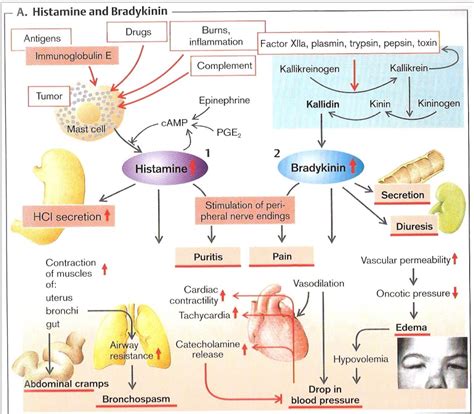
Table of Contents
- Histamine Serotonin And Bradykinin Are All
- Table of Contents
- Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin: All Key Players in Inflammation and Beyond
- What are Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin?
- Histamine: The Allergic Response Mediator
- Serotonin: The Mood Regulator and More
- Bradykinin: The Pain and Inflammation Signal
- The Interplay of Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin
- Clinical Significance and Therapeutic Implications
- Further Research and Future Directions
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin: All Key Players in Inflammation and Beyond
Histamine, serotonin, and bradykinin are all potent bioactive amines that play crucial roles in a wide array of physiological processes. While often associated with inflammation and allergic reactions, their functions extend far beyond these responses, influencing everything from mood regulation and sleep to blood pressure control and pain perception. Understanding their individual actions and intricate interactions is essential for comprehending a multitude of bodily functions and developing effective therapeutic strategies for various diseases.
What are Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin?
Before delving into their complex interplay, let's individually examine each of these crucial biomolecules:
Histamine: The Allergic Response Mediator
Histamine is a biogenic amine primarily synthesized from the amino acid histidine. It's stored in mast cells and basophils, immune cells that play a critical role in the body's inflammatory and allergic responses. The release of histamine is triggered by various stimuli, including:
- Allergens: Substances that provoke an allergic reaction, such as pollen, pet dander, or certain foods.
- Physical injury: Trauma or tissue damage can cause the release of histamine.
- Infections: The presence of pathogens can also trigger histamine release.
Once released, histamine acts on specific receptors (H1, H2, H3, and H4) located on various cell types, leading to a cascade of effects, including:
- Vasodilation: Widening of blood vessels, causing redness and warmth at the site of inflammation.
- Increased vascular permeability: Leaking of fluid from blood vessels into tissues, causing swelling.
- Bronchoconstriction: Narrowing of airways, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Itch and pain: Stimulation of nerve endings.
- Increased mucus secretion: Contributing to runny nose and congestion.
Serotonin: The Mood Regulator and More
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a neurotransmitter and hormone synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. Primarily located in the gastrointestinal tract (where it regulates gut motility), it's also found in the central nervous system (CNS) and platelets. Its diverse actions include:
- Mood regulation: Serotonin plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. Deficiencies are linked to depression and anxiety.
- Gastrointestinal function: It modulates gut motility and secretion.
- Hemostasis: It contributes to blood clotting by promoting platelet aggregation.
- Pain perception: It influences pain signaling pathways.
- Bone metabolism: It's involved in bone formation and resorption.
Bradykinin: The Pain and Inflammation Signal
Bradykinin is a peptide formed from the cleavage of kininogen, a large plasma protein, by the kallikrein enzyme system. It's a potent mediator of inflammation and pain, directly impacting:
- Vasodilation: Leading to increased blood flow and redness.
- Increased vascular permeability: Similar to histamine, resulting in swelling.
- Pain sensation: Directly stimulating pain receptors (nociceptors).
- Bronchoconstriction: Contributing to airway narrowing.
- Smooth muscle contraction: Affects various smooth muscles throughout the body.
The Interplay of Histamine, Serotonin, and Bradykinin
These three biomolecules don't operate in isolation; their effects often intertwine, creating complex interactions that shape inflammatory and other physiological responses. The interplay can be synergistic, with one amplifying the actions of another, or antagonistic, with one counteracting the effects of another. For instance:
-
Synergistic effects in inflammation: Histamine and bradykinin both cause vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, leading to a potentiated inflammatory response. Serotonin can also contribute to inflammation by influencing the release of other inflammatory mediators.
-
Antagonistic effects on blood pressure: Histamine, depending on receptor subtype activation, can either increase or decrease blood pressure. Bradykinin generally leads to vasodilation and hypotension (low blood pressure), while serotonin's effect on blood pressure is more complex and dependent on various factors.
-
Complex interactions in pain perception: Bradykinin is a direct pain mediator. Histamine can sensitize pain receptors, making them more responsive to other stimuli. Serotonin, on the other hand, can modulate pain signaling through different pathways, sometimes inhibiting and sometimes enhancing pain perception.
-
Interactions in allergic reactions: The release of histamine is central to the immediate allergic response. Bradykinin contributes to the subsequent inflammatory phase. Serotonin can influence both the immediate and later stages by modulating immune cell activity and vascular tone.
Clinical Significance and Therapeutic Implications
The diverse roles and interactions of histamine, serotonin, and bradykinin have significant clinical implications. Their dysregulation is implicated in a wide array of conditions, including:
-
Allergies: Antihistamines are commonly used to block histamine receptors and alleviate allergy symptoms.
-
Asthma: Bradykinin and histamine contribute to bronchoconstriction in asthma, and therapies often target these mediators.
-
Inflammation: Many inflammatory diseases involve the dysregulation of these biomolecules, requiring targeted therapies to modulate their activity.
-
Pain: Bradykinin and histamine are key players in pain signaling pathways, influencing the development of chronic pain conditions. Serotonin also influences pain perception, with some pain medications targeting the serotonin system.
-
Gastrointestinal disorders: Serotonin plays a critical role in gut motility and secretion, and its dysregulation is implicated in conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
-
Mental health disorders: Serotonin deficiency is linked to depression and anxiety, with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) being a cornerstone of their treatment.
Further Research and Future Directions
Our understanding of histamine, serotonin, and bradykinin is constantly evolving. Ongoing research focuses on:
-
Identifying novel therapeutic targets: Research continues to explore new ways to modulate the activity of these biomolecules for treating various diseases.
-
Understanding the complex interactions: Further studies are needed to unravel the intricate relationships between these mediators and their impact on various physiological processes.
-
Developing more effective therapies: The aim is to develop more specific and targeted therapies that minimize side effects while maximizing efficacy.
-
Personalized medicine approaches: Individual variations in the expression and function of these biomolecules may inform personalized medicine strategies.
Conclusion
Histamine, serotonin, and bradykinin are crucial biomolecules involved in a vast array of physiological processes, particularly those related to inflammation, pain, and mood regulation. Their intricate interactions shape the body's response to various stimuli and contribute to the pathogenesis of numerous diseases. A deeper understanding of their individual roles and synergistic/antagonistic effects is essential for developing effective therapeutic strategies and improving patient outcomes. Ongoing research continues to shed light on these fascinating biomolecules, opening new avenues for treating a wide range of human diseases. Their impact stretches far beyond the simple concept of inflammation, showcasing the intricate interconnectedness of bodily systems and the complexity of biological regulation. Further investigation is crucial to harness the full potential of this knowledge for therapeutic advancements and improved healthcare.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Social Media Advertising
Mar 29, 2025
-
A Car Travels Down A Straight Country Road
Mar 29, 2025
-
Because Advertising Is The Most Visible Form Of Marketing
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True Regarding The Heart
Mar 29, 2025
-
In Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trials Of A New Vaccine
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Histamine Serotonin And Bradykinin Are All . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
