Give The Name For This Molecule
Holbox
Apr 04, 2025 · 6 min read
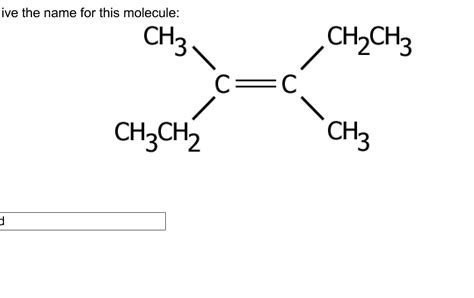
Table of Contents
- Give The Name For This Molecule
- Table of Contents
- Give the Name for This Molecule: A Deep Dive into IUPAC Nomenclature
- Understanding the Fundamentals of IUPAC Nomenclature
- Identifying the Parent Chain
- Functional Groups: The Heart of the Molecule
- Substituents: Adding Complexity
- Step-by-Step Guide to Naming Molecules
- Handling Multiple Functional Groups and Complex Structures
- Advanced Nomenclature Techniques
- The Importance of IUPAC Nomenclature in Chemistry
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Give the Name for This Molecule: A Deep Dive into IUPAC Nomenclature
Naming molecules, particularly organic molecules, can seem like a daunting task. The seemingly endless combinations of atoms and bonds can lead to incredibly complex structures. However, a systematic approach, guided by the principles of IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature, provides a clear and unambiguous method for naming even the most intricate molecules. This article will delve into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, providing a comprehensive guide to naming molecules with various functional groups and complexities. We'll explore the fundamental rules, prioritize functional groups, handle substituents, and unravel the logic behind the seemingly complex naming conventions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of IUPAC Nomenclature
Before embarking on naming specific molecules, it's crucial to grasp the underlying principles of IUPAC nomenclature. This system, globally accepted by chemists, ensures that every molecule has a unique and unambiguous name, irrespective of its complexity or the language used. The core principles revolve around identifying the parent chain, functional groups, and substituents.
Identifying the Parent Chain
The parent chain forms the foundation of the molecule's name. It's typically the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. However, certain functional groups, like ketones and carboxylic acids, dictate the parent chain even if a longer chain exists elsewhere in the molecule. Consider the following:
-
Alkanes: The simplest hydrocarbons, alkanes, form the base for many other organic molecules. Their names (methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc.) dictate the base name of more complex molecules. The number of carbons in the parent alkane chain directly influences the prefix of the molecule's name.
-
Branching Chains: If the parent chain contains branches, those branches are treated as substituents. The parent chain remains the longest continuous chain, even if it's not the chain with the most carbons.
Functional Groups: The Heart of the Molecule
Functional groups are specific atoms or groups of atoms within a molecule that are responsible for its characteristic chemical reactions. These groups have specific names and influence the molecule's overall name and properties. They are prioritized in the naming process, often dictating the suffix of the molecule's name. Examples include:
- Hydroxyl (-OH): Alcohols
- Carbonyl (C=O): Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides
- Carboxyl (-COOH): Carboxylic acids
- Amino (-NH2): Amines
- Ether (-O-): Ethers
Substituents: Adding Complexity
Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms attached to the parent chain. They are named using prefixes, and their positions on the parent chain are indicated using numbers. The numbering of the parent chain starts from the end closest to the highest priority functional group.
- Alkyl Substituents: These are derived from alkanes by removing a hydrogen atom (e.g., methyl, ethyl, propyl).
- Halo Substituents: Halogens (F, Cl, Br, I) are also common substituents.
Step-by-Step Guide to Naming Molecules
Let's apply the principles discussed above to name a few sample molecules. This step-by-step guide will illustrate the process:
Example 1: CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
- Identify the parent chain: This is a straight chain of four carbon atoms.
- Determine the base name: Four carbons correspond to butane.
- Name the molecule: Butane
Example 2: CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)CH₃
- Identify the parent chain: The longest continuous chain contains four carbons.
- Number the carbons: Start numbering from the end closest to the methyl group, resulting in a methyl group at position 2.
- Name the substituent: The substituent is a methyl group.
- Name the molecule: 2-Methylbutane
Example 3: CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
- Identify the parent chain: A three-carbon chain.
- Identify the functional group: A hydroxyl group (-OH) indicating an alcohol.
- Determine the base name: Three carbons suggest propane. The alcohol suffix is "-ol".
- Name the molecule: Propan-1-ol (the "1" indicates the hydroxyl group is on the first carbon).
Example 4: CH₃CH₂COOH
- Identify the parent chain: A two-carbon chain, dictated by the carboxylic acid functional group.
- Identify the functional group: A carboxyl group (-COOH), indicating a carboxylic acid.
- Determine the base name: Two carbons suggest ethane. The carboxylic acid suffix is "-oic acid".
- Name the molecule: Ethanoic acid (also known as acetic acid).
Example 5: A more complex molecule: Consider a molecule with multiple substituents and a functional group. For example, a molecule with a chain of 6 carbons, a hydroxyl group on carbon 3, a methyl group on carbon 2, and a chlorine atom on carbon 5.
- Identify the parent chain: Six carbons indicate hexane.
- Identify the functional groups and substituents: Hydroxyl (-OH), methyl (CH3), and chloro (Cl). Hydroxyl (alcohol) has higher priority than the other substituents.
- Number the chain: Start numbering from the end closest to the hydroxyl group.
- Arrange substituents alphabetically: Chloro, methyl.
- Name the molecule: 5-Chloro-2-methylhexan-3-ol
Handling Multiple Functional Groups and Complex Structures
When molecules contain multiple functional groups, determining the priority order is crucial. IUPAC prioritizes functional groups based on a hierarchical system. The highest priority functional group dictates the base name's suffix, while the remaining groups are treated as substituents (using prefixes). This priority order ensures a consistent and unambiguous naming system.
Advanced Nomenclature Techniques
For exceptionally complex molecules with numerous substituents, rings, or multiple functional groups, the naming process can become significantly more intricate. These situations often require the use of more advanced techniques, such as:
- Locants: Numbers used to indicate the position of substituents or functional groups on the parent chain.
- Parentheses and Brackets: Used to group substituents or complex branches.
- Greek Letters: Used to designate positions on side chains.
- Systematic numbering: Ensuring the lowest set of locants.
The Importance of IUPAC Nomenclature in Chemistry
The rigorous system of IUPAC nomenclature is not merely a matter of convention; it is essential for effective communication within the scientific community. The unambiguous naming of molecules facilitates:
- Clear communication: Chemists worldwide can understand and synthesize the same molecule using its IUPAC name.
- Precise identification: Eliminates ambiguity and confusion, ensuring accurate scientific record-keeping.
- Database organization: Essential for organizing and searching vast chemical databases.
- Patent protection: Accurate and unambiguous naming is crucial for intellectual property rights.
Conclusion
Mastering IUPAC nomenclature is a cornerstone of chemical literacy. While the rules might seem complex initially, a systematic approach and a firm understanding of functional group priorities will enable you to name even the most intricate molecules effectively. This comprehensive guide serves as a foundation for navigating the world of organic chemistry nomenclature. Further exploration of specific functional groups and more complex examples will enhance your understanding and skills in naming molecules accurately and consistently. This ability is critical for success in chemistry, ensuring clear communication and accurate scientific documentation. Remember to practice regularly, and soon you will find that naming molecules becomes an easier and more intuitive process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Recent Post Being Shared On Facebook
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Theory Of Corporate Social Responsibility Concerns
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Set Of Business Processes Culture And Behavior
Apr 06, 2025
-
Match The Description Of Each Wbc
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Does Research Show About Men And Women In Conflict
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Give The Name For This Molecule . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
