Firms Position Their Products Based On Methods Such As Blank______.
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
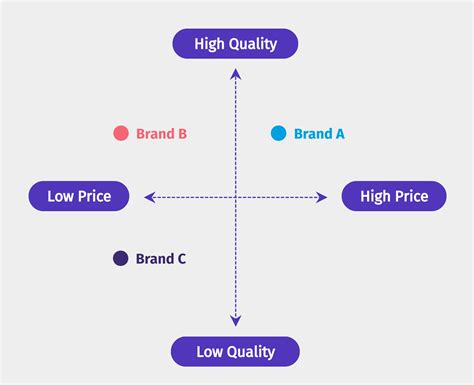
Table of Contents
How Firms Position Their Products: A Deep Dive into Strategic Positioning Methods
Positioning your product effectively is crucial for success in today's competitive marketplace. It's not just about what you sell, but how you convince consumers that your product is the best choice for their needs. This involves crafting a unique and compelling position in the minds of your target audience. This article explores various methods firms utilize for product positioning, delving into the strategies and considerations behind each approach.
Understanding Product Positioning: More Than Just Marketing
Product positioning isn't simply a marketing tactic; it's a strategic business decision that permeates all aspects of a company's operations. It dictates your product development, marketing communications, pricing strategies, and even distribution channels. A strong product position creates a clear, consistent message that resonates with your target market, differentiating you from competitors and building brand loyalty. The goal is to occupy a specific, valuable space in the consumer's mind, making your product the first choice when they consider their needs.
Key Methods Firms Use for Product Positioning
Firms employ a diverse range of methods to effectively position their products. These methods are often intertwined and used in combination to maximize impact. Let's examine some of the most common and effective approaches:
1. Positioning by Attributes: Highlighting Key Features and Benefits
This classic approach focuses on specific product attributes that are perceived as superior or unique compared to competitors. It involves identifying the key features that provide significant value to the target market and communicating these attributes effectively. This could involve emphasizing:
- Quality: Highlighting superior materials, craftsmanship, durability, or longevity. For example, a luxury car manufacturer may emphasize the quality of its leather interiors and advanced engineering.
- Performance: Focusing on speed, efficiency, power, or other performance-related aspects. A sports car manufacturer might highlight its engine's horsepower and acceleration.
- Innovation: Promoting groundbreaking technology, unique design, or cutting-edge features. A technology company might emphasize its innovative software or patented technology.
- Price: Positioning the product as a value leader, premium offering, or somewhere in between. This requires careful consideration of the target market's price sensitivity and the overall value proposition.
Example: A smartphone manufacturer might position its product based on its superior camera quality, longer battery life, or advanced processor speed.
2. Positioning by Price/Value: Appealing to Budget-Conscious or Luxury Consumers
Price plays a significant role in shaping consumer perception. Firms can position their products based on price points, targeting different market segments with varying levels of price sensitivity:
- Value for Money: This strategy emphasizes providing excellent features and quality at a competitive price, appealing to budget-conscious consumers. Discount retailers often employ this strategy.
- Premium Pricing: Charging a higher price to communicate superior quality, exclusivity, or prestige. Luxury brands often leverage this approach.
- Economy Pricing: Targeting price-sensitive consumers with a no-frills, basic product at the lowest possible price. Generic brands frequently utilize this strategy.
Example: A clothing retailer might offer a "value" line with affordable basics, a "premium" line with high-end materials and designs, and an "economy" line with extremely low-priced essentials.
3. Positioning by Use or Application: Focusing on Specific Needs and Situations
This method emphasizes the specific uses or applications of the product, highlighting how it solves a particular problem or fulfills a specific need for the target audience. This approach is effective when the product has multiple applications or caters to a niche market.
Example: A software company might position its project management software as ideal for teams of all sizes, highlighting different features and benefits relevant to small businesses versus large enterprises. Another example could be a multi-purpose cleaner positioned for various uses like kitchen cleaning, bathroom cleaning, and general household cleaning.
4. Positioning by Product User: Targeting Specific Demographics or Psychographics
This involves aligning the product with a specific target audience based on their demographics (age, gender, income, location) or psychographics (lifestyle, values, attitudes, interests). Understanding your target audience is essential for successful positioning.
Example: A cosmetics brand might position its products as ideal for young adults seeking trendy looks, while another brand might target mature women interested in anti-aging products.
5. Positioning by Competitor: Differentiating Based on Competitive Advantage
This strategy involves directly comparing your product to competitors, highlighting your unique advantages and superior attributes. It requires a strong understanding of the competitive landscape and the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors. This method must be used carefully and ethically, focusing on factual comparisons and avoiding disparaging remarks.
Example: A coffee company might position its product as having a richer, more flavorful taste compared to its competitors, or a more sustainable and ethically sourced supply chain.
6. Positioning by Product Category: Creating a Unique Niche or Sub-category
This method involves creating a distinct position within a larger product category, carving out a unique niche or sub-category for your product. This often involves introducing innovative features or targeting a specific segment within the broader market.
Example: A company might create a niche within the energy drink market by offering an organic, low-sugar option, differentiating itself from traditional high-sugar energy drinks.
Integrating Different Positioning Methods: A Holistic Approach
While the above methods are distinct, they are often integrated and used in combination to create a robust and comprehensive positioning strategy. For instance, a company might position its product based on its superior quality (attribute) while also highlighting its affordability (price/value) and appealing to a specific target demographic (product user). This holistic approach ensures a strong, consistent, and persuasive message that resonates with the target audience.
The Importance of Consistency and Long-Term Vision
Maintaining a consistent brand image and message across all marketing and communication channels is vital for effective product positioning. Inconsistent messaging can confuse consumers and dilute the brand’s unique selling proposition. Therefore, firms must develop a long-term vision for their product positioning strategy, ensuring that all marketing efforts align with the chosen position. A consistent approach builds brand recognition and trust, making your product a top-of-mind choice for consumers.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Product Positioning
The success of a product positioning strategy can be assessed through various metrics, including:
- Brand awareness: Measuring consumer awareness and recognition of your brand and its position in the market.
- Market share: Tracking the percentage of the market your product commands.
- Sales growth: Monitoring the increase in sales volume and revenue.
- Customer feedback: Gathering insights from customer surveys, reviews, and social media to gauge consumer perception and satisfaction.
- Competitor analysis: Continuously analyzing competitors' strategies to stay ahead of the curve and adapt your positioning as needed.
By actively monitoring these metrics and adapting your strategy as needed, businesses can ensure that their product positioning remains effective and continues to drive growth and success.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Brand Building and Market Success
Product positioning is the cornerstone of successful brand building and market dominance. By carefully selecting and integrating various positioning methods, companies can craft a powerful message that resonates with their target audience, distinguishes their product from competitors, and ultimately drives sales and revenue growth. Remember that effective product positioning is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring, adaptation, and a commitment to understanding the ever-evolving needs and preferences of your consumers. It's a journey of continuous refinement and improvement, ensuring your product stays relevant and desirable in a dynamic marketplace. By prioritizing a well-defined and strategically executed positioning plan, firms can solidify their market presence, achieve long-term success, and cultivate loyal customer relationships.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Conservation Of Momentum Is Most Closely Related To
Mar 19, 2025
-
Give The Correct Formula For Aluminum Sulfate
Mar 19, 2025
-
Flawed Ways To Pursue Competitive Efforts
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Does The Word Root In The Term Pyothorax Mean
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Is Brand Extension A Popular Marketing Strategy
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Firms Position Their Products Based On Methods Such As Blank______. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
