Evaluate The Definite Integral. 2 E 1/x4 X5 Dx 1
Holbox
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
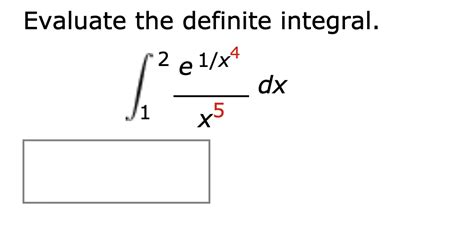
Table of Contents
Evaluating the Definite Integral: ∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to evaluate the definite integral ∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx. We'll explore various methods, focusing on substitution techniques, and meticulously detail each step to ensure clarity and understanding. We will also discuss the importance of understanding the underlying concepts of integration and how to apply them effectively to solve similar problems.
Understanding the Problem
The integral we are tasked with solving is:
∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx
This integral presents a challenge because of the complex composition of the integrand. The presence of the exponential function coupled with a power of x in the denominator requires a strategic approach to simplification. A direct approach won't be effective; instead, we will utilize a substitution method to transform the integral into a more manageable form.
Employing the Substitution Method
The key to solving this integral lies in identifying a suitable substitution. Observing the integrand, we notice that the derivative of 1/x⁴ is closely related to the x⁵ in the denominator. This suggests that a substitution involving 1/x⁴ might be beneficial.
Let's define our substitution:
Let u = 1/x⁴ = x⁻⁴
Now, we need to find the differential of u with respect to x:
du/dx = -4x⁻⁵ = -4/x⁵
Solving for dx, we get:
dx = -x⁵/4 du
Now, we can substitute u and dx into our original integral:
∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx = ∫₂¹ (2eᵘ/x⁵) (-x⁵/4 du)
Notice that x⁵ cancels out, simplifying the expression:
= ∫₂¹ (-1/2)eᵘ du
Simplifying and Solving the Integral
The integral has now been significantly simplified. We can pull the constant -1/2 out of the integral:
= (-1/2) ∫₂¹ eᵘ du
The integral of eᵘ with respect to u is simply eᵘ:
= (-1/2) [eᵘ]₂¹
Now, we substitute back the original variable x:
= (-1/2) [e^(1/x⁴)]₂¹
Evaluating the Definite Integral
Finally, we evaluate the expression at the limits of integration (1 and 2):
= (-1/2) * [e^(1/1⁴) - e^(1/2⁴)]
= (-1/2) * [e¹ - e^(1/16)]
= (-1/2) * [e - e^(1/16)]
This result can be further approximated using a calculator:
e ≈ 2.71828 e^(1/16) ≈ 1.0645
Therefore:
≈ (-1/2) * [2.71828 - 1.0645]
≈ (-1/2) * [1.65378]
≈ -0.82689
Therefore, the approximate value of the definite integral ∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx is -0.82689.
Understanding the Significance of the Result
The negative value of the integral signifies that the area under the curve of the function 2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵ between the limits 1 and 2 is below the x-axis. This is a crucial interpretation, emphasizing the importance of understanding not just the numerical result, but also its graphical representation and contextual meaning.
Further Exploration: Alternative Methods and Considerations
While the substitution method proved highly effective in this case, other approaches could potentially be employed, although they may not be as straightforward. Numerical integration techniques, such as the trapezoidal rule or Simpson's rule, could provide an approximate solution. However, these methods generally require more computational effort and might not yield the exact analytical solution achieved through substitution.
Practical Applications and Extensions
Definite integrals find extensive applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and finance. For instance, they are crucial in calculating areas, volumes, work done by a force, and probabilities. The principles discussed here can be extended to evaluate more complex integrals involving exponential functions and rational expressions. Mastering substitution techniques is a vital skill for tackling such challenges.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When evaluating definite integrals, several common pitfalls should be avoided:
- Incorrect Substitution: Carefully choose the substitution variable and ensure the differential is calculated accurately. A small error in this step can significantly impact the final result.
- Forgetting the Limits of Integration: Always remember to substitute the original limits of integration after the integration step, before evaluating the final expression.
- Algebraic Errors: Pay close attention to algebraic manipulations, especially when dealing with fractions and exponents. A single mistake can lead to an incorrect answer.
- Improper Use of Properties of Integrals: Familiarize yourself with the properties of definite integrals, such as linearity and the interval additivity property. Misapplying these properties can lead to inaccurate solutions.
Conclusion
Evaluating definite integrals like ∫₂¹ (2e^(1/x⁴)/x⁵) dx requires a strategic approach, often involving substitution methods. By carefully selecting a substitution variable and meticulously executing the steps, we can transform a seemingly complex integral into a much simpler one. Understanding the underlying concepts, avoiding common pitfalls, and interpreting the result are vital for accurate and meaningful solutions. This process strengthens one's analytical skills and provides the foundation for tackling increasingly complex integration problems in various scientific and engineering applications. The result, approximately -0.82689, highlights the importance of not just calculating the numerical value but also understanding its significance within the context of the problem. This holistic approach ensures a more complete and comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Business Plan Is A Document That Outlines
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Tough And Tuff
Mar 19, 2025
-
Locking Out Tagging Out Refers To The Practice Of
Mar 19, 2025
-
John Is Rollerblading Down A Long
Mar 19, 2025
-
Hydrolysis Of Sucrose A Disaccharide Results In
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Evaluate The Definite Integral. 2 E 1/x4 X5 Dx 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
