Cost Accounting Systems Are Used To
Holbox
Mar 31, 2025 · 7 min read
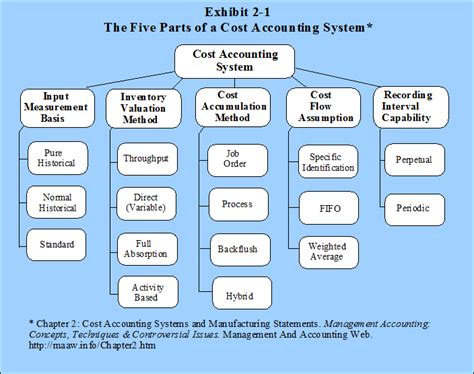
Table of Contents
- Cost Accounting Systems Are Used To
- Table of Contents
- Cost Accounting Systems: Their Uses and Importance in Modern Business
- Understanding the Core Functions of Cost Accounting Systems
- Key Uses of Cost Accounting Systems Across Diverse Industries
- 1. Product Costing and Pricing Strategies
- 2. Inventory Management and Control
- 3. Budgeting and Performance Evaluation
- 4. Decision-Making Support for Capital Investments
- 5. Process Improvement and Cost Reduction
- 6. Government Reporting and Compliance
- 7. Strategic Planning and Long-Term Growth
- Choosing the Right Cost Accounting System
- Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Cost Accounting Systems
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Cost Accounting Systems: Their Uses and Importance in Modern Business
Cost accounting, a specialized branch of accounting, goes beyond simply recording financial transactions. It delves deep into the identification, measurement, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of costs. This detailed examination provides crucial insights for businesses of all sizes, enabling informed decision-making and ultimately, improved profitability. But what exactly are cost accounting systems used for? The answer is multifaceted and crucial to business success. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse applications of cost accounting systems, showcasing their importance in today's dynamic business environment.
Understanding the Core Functions of Cost Accounting Systems
Before diving into specific uses, it's vital to understand the fundamental functions of cost accounting systems. These systems are designed to:
- Track and Classify Costs: This involves meticulous recording of all costs incurred, categorizing them according to various criteria (e.g., direct vs. indirect, fixed vs. variable, manufacturing vs. administrative). This foundational step is essential for accurate analysis.
- Allocate Costs: Cost accounting systems distribute costs to different products, services, departments, or projects. This allocation allows businesses to pinpoint cost drivers and areas for potential improvement.
- Analyze Costs: Analyzing cost data helps identify trends, inefficiencies, and areas of strength. This involves comparing actual costs to budgeted costs, identifying variances, and investigating the reasons behind those variances.
- Control Costs: By analyzing cost data and identifying cost drivers, businesses can develop and implement strategies to control costs, improving efficiency and profitability.
- Provide Decision-Making Information: Cost accounting provides crucial data for various managerial decisions, including pricing strategies, production planning, investment decisions, and performance evaluation.
Key Uses of Cost Accounting Systems Across Diverse Industries
The applications of cost accounting systems are vast, extending across various industries and business functions. Let's examine some key uses:
1. Product Costing and Pricing Strategies
One of the most critical uses of cost accounting is in determining the cost of producing goods or providing services. This involves calculating the direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead associated with each product. This information is crucial for:
- Setting Competitive Prices: Understanding the true cost of production allows businesses to set prices that are both profitable and competitive in the market. It prevents underpricing (resulting in lost profits) and overpricing (leading to lost sales).
- Identifying Profitable Products: By analyzing the cost and profitability of individual products, businesses can identify high-performing items and those that require attention or potential discontinuation.
- Optimizing Production Processes: Pinpointing cost-intensive aspects of production can reveal areas where improvements can be made, leading to cost reductions and enhanced profitability.
Example: A bakery uses cost accounting to determine the cost of producing a loaf of bread, factoring in flour, yeast, labor, oven usage, and packaging. This enables them to set a profitable selling price while remaining competitive with other bakeries.
2. Inventory Management and Control
Cost accounting systems play a vital role in inventory management, providing insights into:
- Inventory Valuation: Accurate cost accounting is essential for valuing inventory using methods like FIFO (First-In, First-Out), LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), or weighted average cost. This directly impacts financial reporting and tax calculations.
- Inventory Control: By tracking inventory levels and costs, businesses can avoid stockouts (loss of sales) and overstocking (increased storage costs and potential obsolescence). This leads to optimized inventory levels and reduced waste.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Cost accounting data helps support the implementation of JIT inventory systems, minimizing storage costs and reducing waste by ordering materials only as needed.
Example: A clothing retailer uses cost accounting to track the cost of each item in its inventory, allowing them to make informed decisions about markdowns, sales promotions, and replenishment orders.
3. Budgeting and Performance Evaluation
Cost accounting systems are indispensable tools for budgeting and performance evaluation:
- Budget Preparation: Historical cost data provides a strong foundation for developing realistic budgets. Analyzing past performance helps predict future costs and set achievable targets.
- Variance Analysis: Comparing actual costs to budgeted costs reveals variances that highlight areas of overspending or underspending. Investigating these variances helps identify the underlying causes and implement corrective actions.
- Performance Measurement: Cost accounting data provides key performance indicators (KPIs) for evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of various departments and processes. This helps identify areas of strength and weakness within the organization.
Example: A manufacturing company uses cost accounting to prepare its annual budget, comparing actual production costs against the budgeted figures to identify areas for cost reduction and process optimization.
4. Decision-Making Support for Capital Investments
Cost accounting information is critical for making informed decisions regarding capital investments:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Cost accounting provides data for evaluating the cost and benefits of potential investments, including new equipment, facilities, or technology. This helps determine the financial viability of such investments.
- Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation: Cost accounting data is used to calculate the ROI of capital investments, helping businesses prioritize projects that offer the highest returns.
- Break-Even Analysis: This technique, heavily reliant on cost accounting data, determines the sales volume needed to cover all costs and achieve profitability. It informs decisions about product pricing, production levels, and overall investment strategy.
Example: A company considering investing in new machinery uses cost accounting to estimate the costs of acquisition, installation, maintenance, and operation, comparing these with the projected increase in production efficiency and revenue.
5. Process Improvement and Cost Reduction
Cost accounting systems are vital for identifying and addressing areas of inefficiency:
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC): ABC is a cost accounting method that assigns costs based on activities rather than departments. This allows for a more accurate understanding of cost drivers and provides more focused areas for improvement.
- Value Engineering: By analyzing costs, businesses can identify areas where costs can be reduced without sacrificing quality or performance.
- Lean Manufacturing: Cost accounting data provides crucial information for implementing lean manufacturing principles, reducing waste and improving efficiency throughout the production process.
Example: A manufacturing plant uses ABC costing to identify specific activities that are driving high overhead costs, leading to process improvements and cost reductions.
6. Government Reporting and Compliance
Cost accounting data is often required for government reporting and compliance purposes:
- Tax Reporting: Accurate cost accounting is crucial for calculating cost of goods sold (COGS), which directly impacts taxable income.
- Regulatory Compliance: Certain industries are subject to specific regulations that require detailed cost accounting records.
- Auditing: Cost accounting information is subject to audits to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
Example: A construction company uses cost accounting to track labor costs, material costs, and overhead expenses to accurately report its financial performance to government agencies and meet regulatory requirements.
7. Strategic Planning and Long-Term Growth
Cost accounting isn't just about short-term efficiency; it's a crucial tool for strategic planning and long-term growth. It enables:
- Market Analysis: Understanding product costs allows businesses to analyze market trends, pricing strategies of competitors, and the potential profitability of entering new markets.
- Expansion Planning: Cost accounting data informs decisions about expansion, providing information about the costs associated with scaling operations, entering new markets, or launching new products.
- Long-Term Sustainability: By monitoring costs over time, businesses can identify trends and develop strategies to ensure long-term financial sustainability and competitiveness.
Choosing the Right Cost Accounting System
The specific cost accounting system chosen will depend on a company's size, industry, and specific needs. Factors to consider include:
- Complexity of Operations: Simple businesses may only need a basic system, while complex organizations might require a more sophisticated system.
- Type of Products/Services: The type of goods or services produced will influence the most appropriate costing method.
- Information Needs: The level of detail required in cost analysis will also affect system selection.
- Integration with other systems: The chosen system should integrate seamlessly with existing accounting and other business systems for efficient data flow.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Cost Accounting Systems
Cost accounting systems are far more than just tools for tracking expenses. They are powerful instruments that provide invaluable insights into a business's financial health, operational efficiency, and strategic positioning. From product pricing and inventory management to budgeting, decision-making, and long-term growth, cost accounting plays a crucial role in achieving success in today’s competitive business landscape. Understanding and effectively utilizing cost accounting systems is no longer a luxury; it's a necessity for any organization aiming for sustainable profitability and sustained growth. By embracing the power of cost accounting, businesses can gain a significant competitive edge and navigate the complexities of the modern marketplace with confidence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Hypocalcemia Could Be Caused By The
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Structure Indicated By Label E
Apr 03, 2025
-
Three Major Means Of Collusion By Oligopolists Are
Apr 03, 2025
-
I Am A Perfectionist But Only About Certain Things
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Do Recruiters Use Virtual Interviews
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cost Accounting Systems Are Used To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
