Consumption Investment Government Spending Exports And Imports Are
Holbox
Mar 12, 2025 · 5 min read
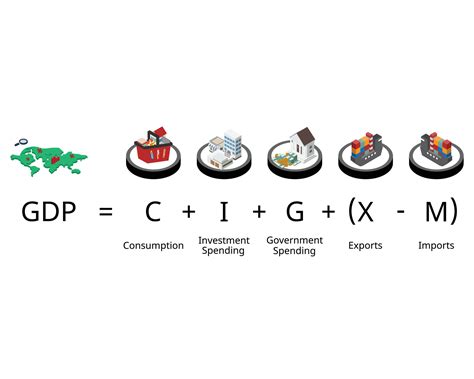
Table of Contents
- Consumption Investment Government Spending Exports And Imports Are
- Table of Contents
- Consumption, Investment, Government Spending, Exports, and Imports: The Pillars of Macroeconomic Activity
- Consumption: The Engine of Economic Growth
- Factors Affecting Consumption
- Investment: Fueling Future Growth
- Factors Affecting Investment
- Government Spending: A Powerful Tool for Economic Management
- Government Spending and its Impact
- Net Exports: The International Dimension
- Factors Affecting Net Exports
- The Interconnectedness of the Components
- Conclusion: A Dynamic Equilibrium
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Consumption, Investment, Government Spending, Exports, and Imports: The Pillars of Macroeconomic Activity
Understanding the dynamics of an economy requires a grasp of its fundamental components. Macroeconomics, the study of the economy as a whole, relies heavily on analyzing aggregate demand and supply. Four key components drive aggregate demand: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). This article will delve deep into each of these components, examining their individual roles and their interconnectedness in shaping economic growth, stability, and fluctuations.
Consumption: The Engine of Economic Growth
Consumption represents the largest component of aggregate demand in most economies. It encompasses all spending by households on goods and services, ranging from everyday necessities like food and clothing to durable goods such as cars and appliances, and services such as healthcare and entertainment. Consumer spending is influenced by a multitude of factors:
Factors Affecting Consumption
-
Disposable Income: This is the most significant factor. Higher disposable income (income after taxes) generally leads to higher consumption, while lower disposable income leads to lower consumption. Changes in income levels, employment rates, and tax policies all directly impact disposable income.
-
Consumer Confidence: Optimistic consumers are more likely to spend, anticipating future prosperity. Conversely, pessimistic consumers tend to save more and spend less, fearing economic uncertainty. Consumer confidence surveys are closely monitored by economists and policymakers.
-
Interest Rates: Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, discouraging purchases of durable goods and large-ticket items financed through loans. Lower interest rates have the opposite effect, stimulating consumption.
-
Wealth Effect: Increases in household wealth, such as rising house prices or stock market gains, can lead to increased consumption as individuals feel wealthier and more secure. The reverse is true when wealth declines.
-
Consumer Debt: High levels of consumer debt can constrain future consumption as individuals dedicate a larger portion of their income to debt repayment.
-
Inflation: Unexpectedly high inflation erodes purchasing power, leading to reduced consumption unless wages rise proportionally.
The Multiplier Effect: A crucial concept related to consumption is the multiplier effect. An initial increase in spending (e.g., government stimulus) can lead to a larger overall increase in economic output. This happens because the increased spending generates income for others, who in turn spend a portion of that income, creating further income and spending. The size of the multiplier effect depends on the marginal propensity to consume (MPC), which is the fraction of additional income that households spend on consumption.
Investment: Fueling Future Growth
Investment represents spending by firms on capital goods – equipment, machinery, buildings, and inventories. Investment is crucial for long-term economic growth as it enhances productivity and expands the economy's capacity to produce goods and services.
Factors Affecting Investment
-
Interest Rates: Like consumption, investment is highly sensitive to interest rates. Higher rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing investment. Lower rates stimulate investment.
-
Business Confidence: Optimistic firms are more likely to invest in expansion and modernization. Conversely, pessimistic firms may postpone investment or even reduce existing capacity. Economic forecasts and industry-specific factors significantly influence business confidence.
-
Technological Change: Technological advancements can create opportunities for investment as firms seek to adopt new technologies to improve efficiency and productivity.
-
Government Policies: Tax incentives for investment, deregulation, and government infrastructure projects can stimulate investment.
-
Expected Profitability: Firms invest when they expect future profits to be high enough to justify the investment costs. Uncertainty about future demand can discourage investment.
Government Spending: A Powerful Tool for Economic Management
Government spending represents purchases of goods and services by all levels of government (federal, state, and local). This includes infrastructure projects (roads, bridges, schools), national defense, social welfare programs, and salaries for government employees.
Government Spending and its Impact
-
Stabilization Policy: Government spending can be used as a tool to stabilize the economy during recessions. Increased government spending can stimulate demand and help pull the economy out of a downturn (fiscal stimulus).
-
Public Goods: Government spending provides essential public goods that the private sector might under-provide, such as national defense, public education, and environmental protection.
-
Income Redistribution: Government spending through social welfare programs can redistribute income from higher-income earners to lower-income earners, reducing income inequality.
-
Crowding Out Effect: Large increases in government spending can potentially lead to the crowding-out effect. This happens when government borrowing to finance spending increases interest rates, which reduces private investment.
Net Exports: The International Dimension
Net exports represent the difference between a country's exports (goods and services sold to other countries) and its imports (goods and services purchased from other countries). A positive net export figure indicates a trade surplus, while a negative figure indicates a trade deficit.
Factors Affecting Net Exports
-
Exchange Rates: A stronger domestic currency makes exports more expensive and imports cheaper, reducing net exports. A weaker currency has the opposite effect, boosting net exports.
-
Global Economic Conditions: Strong global economic growth increases demand for exports, while weak global growth reduces demand.
-
Domestic Demand: High domestic demand can reduce the availability of goods for export, while low domestic demand can free up goods for export.
-
Trade Policies: Tariffs, quotas, and other trade restrictions can impact both exports and imports.
The Interconnectedness of the Components
It's crucial to understand that these four components are interconnected and influence each other. For example, increased consumer confidence can lead to higher consumption, which in turn stimulates investment and potentially increases imports. Similarly, government spending can influence consumption through income redistribution or affect net exports through changes in exchange rates. These interactions create complex feedback loops that shape the overall economic performance.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Equilibrium
Consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports are the fundamental building blocks of aggregate demand. Understanding their individual roles, the factors that influence them, and their interrelationships is essential for analyzing economic performance and forecasting future trends. The interplay of these forces creates a constantly shifting equilibrium, making macroeconomic analysis a dynamic and fascinating field of study. Policymakers continually grapple with managing these elements to achieve sustainable economic growth, price stability, and full employment. Further research into each component, as well as the various macroeconomic models used to analyze their interactions, offers a richer understanding of the complexities of the global and national economies. The study of these components helps predict economic booms and busts and allows for better financial planning at both the individual and national levels.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Consumption Investment Government Spending Exports And Imports Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.