Consider The Following Graph Of An Absolute Value Function
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
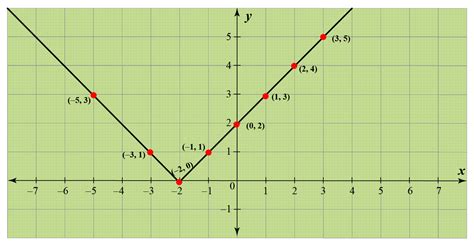
Table of Contents
Decoding the Absolute Value Function: A Comprehensive Guide
The absolute value function, denoted as |x|, is a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching applications. Understanding its graph and properties is crucial for success in algebra, calculus, and beyond. This article delves deep into the absolute value function, exploring its graph, key characteristics, transformations, and practical applications. We'll move beyond simple definitions and explore its nuances, providing a robust understanding you can utilize in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. This means that the absolute value of a number is always non-negative. Formally, the absolute value function is defined as:
|x| = x, if x ≥ 0 |x| = -x, if x < 0
This means that if x is positive or zero, the absolute value of x is simply x itself. If x is negative, the absolute value of x is the negative of x (making it positive).
Example:
- |5| = 5
- |-5| = 5
- |0| = 0
Graphing the Absolute Value Function: A Visual Representation
The graph of the absolute value function, y = |x|, is a V-shaped graph. The vertex of the V is located at the origin (0,0). The graph is symmetric about the y-axis because the absolute value of a number is the same regardless of its sign.
Key Features of the Graph:
- Vertex: (0, 0) - The sharp point of the "V".
- Symmetry: Symmetrical about the y-axis.
- Domain: (-∞, ∞) – All real numbers.
- Range: [0, ∞) – All non-negative real numbers.
- Slope: The slope is -1 for x < 0 and 1 for x > 0. At x = 0, the slope is undefined due to the sharp corner.
- x-intercept: (0, 0)
- y-intercept: (0, 0)
Transformations of the Absolute Value Function
The basic absolute value function, y = |x|, can be transformed in various ways by applying different transformations. These transformations affect the position, orientation, and shape of the graph. The general form of a transformed absolute value function is:
y = a|x - h| + k
Where:
- 'a' controls the vertical stretch or compression and reflection about the x-axis. If |a| > 1, the graph is stretched vertically. If 0 < |a| < 1, the graph is compressed vertically. If a is negative, the graph is reflected about the x-axis (flipped upside down).
- 'h' controls the horizontal shift. If h > 0, the graph shifts to the right. If h < 0, the graph shifts to the left.
- 'k' controls the vertical shift. If k > 0, the graph shifts upward. If k < 0, the graph shifts downward.
Examples of Transformations:
- y = 2|x|: Vertical stretch by a factor of 2. The graph becomes narrower.
- y = 0.5|x|: Vertical compression by a factor of 0.5. The graph becomes wider.
- y = -|x|: Reflection about the x-axis. The graph is inverted, forming an upside-down "V".
- y = |x - 3|: Horizontal shift 3 units to the right.
- y = |x| + 2: Vertical shift 2 units upward.
- y = 2|x - 1| + 3: Vertical stretch by a factor of 2, horizontal shift 1 unit to the right, and vertical shift 3 units upward.
Solving Equations and Inequalities Involving Absolute Value
Absolute value equations and inequalities require careful consideration of the definition of the absolute value function. Solving them often involves considering two cases: one where the expression inside the absolute value is positive or zero, and another where it is negative.
Example: Solving an Absolute Value Equation
|x - 2| = 5
Case 1: x - 2 = 5 => x = 7 Case 2: -(x - 2) = 5 => -x + 2 = 5 => x = -3
Therefore, the solutions are x = 7 and x = -3.
Example: Solving an Absolute Value Inequality
|x + 1| < 3
This inequality means that the distance between x + 1 and 0 is less than 3. This translates to:
-3 < x + 1 < 3
Subtracting 1 from all sides:
-4 < x < 2
Therefore, the solution is -4 < x < 2.
Applications of the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function has numerous applications across various fields:
- Physics: Calculating distances and displacements, where direction doesn't matter.
- Engineering: Error analysis and tolerance calculations.
- Computer Science: Determining distances in algorithms, like shortest path algorithms.
- Statistics: Calculating deviations from the mean (absolute deviation).
- Economics: Measuring deviations from equilibrium prices.
- Finance: Calculating percentage change regardless of whether it's an increase or decrease.
Advanced Topics: Piecewise Functions and Derivatives
The absolute value function can be expressed as a piecewise function:
f(x) = { x, if x ≥ 0; -x, if x < 0 }
This piecewise representation highlights the different functional definitions for positive and negative values of x.
The derivative of the absolute value function is not defined at x = 0 due to the sharp corner in the graph. For x ≠ 0, the derivative is:
f'(x) = 1, if x > 0 f'(x) = -1, if x < 0
Conclusion: Mastering the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, while seemingly simple, possesses a rich mathematical structure and broad applicability. By understanding its graph, transformations, and problem-solving techniques, you equip yourself with a powerful tool for tackling various mathematical challenges. From basic algebraic manipulations to advanced calculus concepts, a solid grasp of the absolute value function is essential for success in many mathematical and scientific endeavors. Remember to practice solving various equations and inequalities, and explore the different transformations to fully solidify your understanding. The more you work with this function, the more intuitive its behavior will become, making you a more confident and proficient problem solver.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Draw The Missing Organic Structures Do Not Draw Inorganic By Products
Mar 17, 2025
-
National Party Organizations Can Dictate The Day To Day Decisions Of
Mar 17, 2025
-
Dealing With Difficult Clients Negatively Impacts My Disposition
Mar 17, 2025
-
Your Company Offers A Single Premium Mobile Phone Handset
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True Select All That Apply
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Consider The Following Graph Of An Absolute Value Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
