Choose All Characteristics Of Slow-twitch Fibers.
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
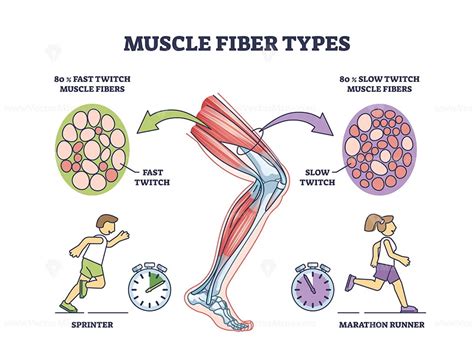
Table of Contents
- Choose All Characteristics Of Slow-twitch Fibers.
- Table of Contents
- Choose All Characteristics of Slow-Twitch Fibers: A Deep Dive into Type I Muscle Fibers
- Defining Slow-Twitch Muscle Fibers: The Endurance Champions
- Key Characteristics of Slow-Twitch Fibers: A Detailed Breakdown
- The Metabolic Machinery of Slow-Twitch Fibers: An Aerobic Powerhouse
- Slow-Twitch Fiber Recruitment: When Endurance is Key
- The Role of Slow-Twitch Fibers in Different Activities:
- Training Adaptations in Slow-Twitch Fibers: Enhancing Endurance
- Slow-Twitch Fibers vs. Fast-Twitch Fibers: A Comparison
- Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Slow-Twitch Fibers
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Choose All Characteristics of Slow-Twitch Fibers: A Deep Dive into Type I Muscle Fibers
Slow-twitch muscle fibers, also known as Type I fibers, are a fascinating subject in the field of exercise physiology. Understanding their characteristics is crucial for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in optimizing their physical performance and overall health. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the unique properties of slow-twitch fibers, exploring their structure, function, and implications for various activities. We'll cover everything you need to know to truly understand these essential components of human movement.
Defining Slow-Twitch Muscle Fibers: The Endurance Champions
Type I muscle fibers are characterized by their slow contraction speed and high resistance to fatigue. Unlike their fast-twitch counterparts (Type IIa and Type IIx), slow-twitch fibers are designed for endurance activities. They excel at sustained, low-intensity efforts, making them the workhorses of prolonged physical activity. Think marathon runners, cyclists, and long-distance swimmers – these athletes rely heavily on the power and resilience of their slow-twitch muscle fibers.
Key Characteristics of Slow-Twitch Fibers: A Detailed Breakdown
Let's explore the key features that define slow-twitch fibers:
-
Contraction Speed: As the name suggests, slow-twitch fibers contract slowly. This is due to their unique metabolic pathways and contractile protein isoforms. The slower contraction speed allows for sustained, efficient movement over extended periods.
-
Fatigue Resistance: The remarkable endurance of slow-twitch fibers stems from their efficient use of oxygen. They have a high capacity for aerobic metabolism, meaning they can produce energy (ATP) effectively using oxygen. This aerobic capacity allows them to sustain contractions for prolonged periods without significant fatigue.
-
Mitochondrial Density: Slow-twitch fibers are packed with mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell. These organelles are responsible for aerobic respiration, converting oxygen and nutrients into ATP. The high mitochondrial density contributes significantly to their impressive endurance capabilities.
-
Capillary Density: A dense network of capillaries surrounds slow-twitch fibers, delivering oxygen and nutrients directly to the muscle cells. This rich blood supply ensures a constant supply of oxygen, crucial for their aerobic metabolism and sustained function.
-
Myoglobin Content: Myoglobin is an oxygen-binding protein found within muscle cells. Slow-twitch fibers have a high myoglobin content, further enhancing their oxygen storage and utilization. This contributes to their ability to sustain prolonged activity.
-
Oxidative Enzymes: Slow-twitch fibers possess high levels of oxidative enzymes, which are critical for aerobic metabolism. These enzymes catalyze the reactions that convert oxygen and nutrients into ATP, fueling their sustained contractions.
The Metabolic Machinery of Slow-Twitch Fibers: An Aerobic Powerhouse
The metabolic pathways employed by slow-twitch fibers are primarily aerobic. This means they rely on oxygen to produce energy. Let's examine the specifics:
-
Oxidative Phosphorylation: This is the primary energy-producing pathway in slow-twitch fibers. It involves a series of chemical reactions within the mitochondria that convert oxygen and nutrients (primarily carbohydrates and fats) into ATP. This process is highly efficient, allowing for prolonged energy production.
-
Fat Oxidation: Slow-twitch fibers are particularly adept at utilizing fats as fuel. This is advantageous for endurance activities because fat stores are significantly larger than glycogen stores. The ability to efficiently utilize fats allows for prolonged activity without depleting energy reserves as quickly.
Slow-Twitch Fiber Recruitment: When Endurance is Key
The nervous system recruits muscle fibers based on the demands of the activity. For low-intensity, prolonged activities, the nervous system preferentially recruits slow-twitch fibers. This recruitment pattern maximizes energy efficiency and minimizes fatigue. As the intensity of activity increases, fast-twitch fibers are progressively recruited to supplement the efforts of the slow-twitch fibers.
The Role of Slow-Twitch Fibers in Different Activities:
-
Endurance Sports: Slow-twitch fibers are essential for endurance sports such as marathon running, cycling, swimming, and long-distance hiking. Their high fatigue resistance allows athletes to maintain performance for extended periods.
-
Postural Muscles: Slow-twitch fibers play a crucial role in maintaining posture. They are continuously active, providing the sustained contraction needed to hold the body upright against gravity.
-
Everyday Activities: Even everyday activities, such as walking, standing, and light housework, rely heavily on the function of slow-twitch fibers. Their ability to sustain contractions allows for these activities to be performed without significant fatigue.
Training Adaptations in Slow-Twitch Fibers: Enhancing Endurance
While the number of slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers is largely determined by genetics, training can significantly influence their characteristics and performance:
-
Endurance Training: Regular endurance training, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can lead to several positive adaptations in slow-twitch fibers. This includes increased mitochondrial density, capillary density, myoglobin content, and oxidative enzyme activity. These adaptations enhance the fibers' capacity for aerobic metabolism and fatigue resistance.
-
Mitochondrial Biogenesis: Endurance training stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, the process of producing new mitochondria. This increases the number of mitochondria within the slow-twitch fibers, further boosting their energy production capacity.
-
Capillary Angiogenesis: Endurance training also stimulates capillary angiogenesis, the formation of new capillaries. This improves blood flow to the muscles, ensuring a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to the slow-twitch fibers.
Slow-Twitch Fibers vs. Fast-Twitch Fibers: A Comparison
Understanding the differences between slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers is crucial for optimizing training programs. Here's a comparison:
| Feature | Slow-Twitch (Type I) | Fast-Twitch (Type IIa & IIx) |
|---|---|---|
| Contraction Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Fatigue Resistance | High | Low |
| Mitochondrial Density | High | Low |
| Capillary Density | High | Low |
| Myoglobin Content | High | Low |
| Metabolic Pathway | Primarily Aerobic | Primarily Anaerobic |
| Fiber Diameter | Smaller | Larger |
| Primary Fuel Source | Fats and Carbohydrates | Primarily Carbohydrates |
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Slow-Twitch Fibers
Slow-twitch fibers are essential for a wide range of activities, from everyday movements to elite athletic performances. Understanding their characteristics, metabolic pathways, and training adaptations is crucial for optimizing physical performance and overall health. Whether you're an athlete striving for peak performance or simply aiming to improve your fitness, appreciating the remarkable capabilities of these endurance champions is key to achieving your goals. By incorporating appropriate training strategies, you can leverage the power of your slow-twitch fibers and unlock your full athletic potential. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals or certified trainers to create a personalized training plan that aligns with your individual needs and goals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Most Processes For Managing Medical Errors Include
Mar 18, 2025
-
Locate The Centroid Of The Plane Area Shown
Mar 18, 2025
-
Hotspots And Plate Motions Activity 2 3
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Enzymes Is Responsible For Rna Synthesis
Mar 18, 2025
-
Weight Of Cubic Foot Of Gold
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Choose All Characteristics Of Slow-twitch Fibers. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
