Blood Clotting Is An Example Of How Multiple Choice Question.
Holbox
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
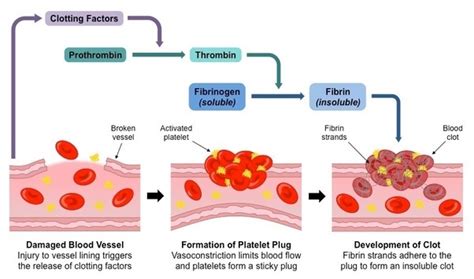
Table of Contents
Blood Clotting: A Multifaceted Example of Homeostasis
Blood clotting, also known as haemostasis, is a complex process crucial for maintaining the body's integrity. It's a prime example of how multiple physiological systems work in concert, responding to injury and preventing excessive blood loss. Understanding this process requires considering multiple factors, making it a perfect subject for multiple-choice questions (MCQs) testing various aspects of biology and physiology. This article will delve into the intricacies of blood clotting, highlighting key concepts relevant to MCQs and offering examples to illustrate their application.
The Stages of Blood Clotting: A Cascade of Events
The process of blood clotting isn't a single event but a carefully orchestrated cascade of events, broadly divided into three phases:
1. Vascular Spasm: The Initial Constriction
Upon injury to a blood vessel, the immediate response is vasoconstriction, a narrowing of the blood vessel. This reduces blood flow to the injured area, minimizing blood loss. This initial phase is a crucial part of haemostasis and often overlooked in favor of the more complex enzymatic cascades. MCQs could test your understanding of the mechanisms behind vasoconstriction, including the role of:
- Endothelin: A potent vasoconstrictor released by the damaged endothelium.
- Serotonin: Released from platelets, further contributing to vasoconstriction.
- Nervous System Reflexes: Local reflexes can trigger further constriction, reducing blood flow.
Example MCQ: Which of the following is NOT a primary contributor to vascular spasm during haemostasis? (a) Endothelin (b) Serotonin (c) Fibrinolysis (d) Nervous System Reflexes
Answer: (c) Fibrinolysis (Fibrinolysis is the breakdown of blood clots, occurring after the initial vasoconstriction).
2. Platelet Plug Formation: Temporary Patch
Following vasoconstriction, platelets—small, anucleated cells—play a crucial role. They adhere to the exposed collagen fibers in the damaged vessel wall, a process called platelet adhesion. This adhesion is mediated by von Willebrand factor (vWF), a glycoprotein produced by endothelial cells. Activated platelets then change shape, becoming spiky and releasing various factors including:
- ADP (adenosine diphosphate): Recruits more platelets to the site of injury.
- Thromboxane A2: A potent vasoconstrictor and platelet activator.
- Serotonin: Further enhances vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation.
The aggregation of platelets forms a platelet plug, a temporary seal to prevent further blood loss. This phase is crucial and can be the subject of several MCQs.
Example MCQ: Which of the following molecules is NOT directly involved in platelet aggregation? (a) ADP (b) Thromboxane A2 (c) Fibrinogen (d) Heparin
Answer: (d) Heparin (Heparin is an anticoagulant that inhibits clotting).
3. Coagulation Cascade: Formation of a Stable Clot
The coagulation cascade is the most complex phase, involving a series of enzymatic reactions that ultimately lead to the formation of fibrin, an insoluble protein forming the meshwork of a stable blood clot. This cascade involves two pathways:
- Intrinsic Pathway: Activated by factors within the blood itself (e.g., contact with negatively charged surfaces).
- Extrinsic Pathway: Activated by tissue factor (TF), a protein released by damaged cells outside the blood vessel.
Both pathways converge at the activation of factor X, leading to the formation of thrombin. Thrombin then converts fibrinogen (a soluble plasma protein) into fibrin (an insoluble protein), creating a stable clot that effectively seals the injury.
Several clotting factors (I-XIII) participate, each acting as an enzyme activating the next in the chain. This intricacy provides ample opportunities for MCQs focusing on specific factors, their roles, and the consequences of their deficiencies.
Example MCQ: Which clotting factor is the key enzyme responsible for converting fibrinogen to fibrin? (a) Factor V (b) Factor VII (c) Factor X (d) Thrombin (Factor IIa)
Answer: (d) Thrombin (Factor IIa)
Regulation of Blood Clotting: A Delicate Balance
The coagulation cascade is tightly regulated to prevent uncontrolled clotting. Several mechanisms ensure that clotting is localized and does not spread throughout the circulatory system, a condition known as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). These regulatory mechanisms include:
- Anticoagulants: Substances that inhibit clotting, such as antithrombin, protein C, and protein S.
- Fibrinolysis: The breakdown of fibrin clots by plasmin, an enzyme activated by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
- Natural Inhibitors: The body produces several inhibitors that regulate the activity of specific clotting factors.
Example MCQ: Which of the following is a key anticoagulant protein? (a) Thrombin (b) Fibrinogen (c) Antithrombin (d) Factor VIII
Answer: (c) Antithrombin
Blood Clotting Disorders: Consequences of Imbalance
Dysfunction in any stage of the clotting process can lead to serious bleeding disorders or thrombotic conditions (excessive clotting). These disorders highlight the importance of a tightly regulated haemostatic system. Some common examples include:
- Hemophilia: A hereditary bleeding disorder due to deficiencies in specific clotting factors (e.g., Factor VIII in Hemophilia A).
- Von Willebrand Disease: A common bleeding disorder due to a deficiency or dysfunction of von Willebrand factor (vWF).
- Thrombophilia: An increased tendency to form blood clots, often due to inherited or acquired factors.
Example MCQ: Hemophilia A is characterized by a deficiency in which clotting factor? (a) Factor V (b) Factor VII (c) Factor VIII (d) Factor IX
Answer: (c) Factor VIII
Clinical Relevance and Diagnostic Approaches
Understanding blood clotting is crucial for medical professionals in diagnosing and treating various conditions. Diagnostic tests, such as:
- Prothrombin Time (PT): Assesses the extrinsic and common pathways of coagulation.
- Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT): Assesses the intrinsic and common pathways.
- Platelet count: Measures the number of platelets in the blood.
These tests are instrumental in identifying clotting disorders and guiding treatment strategies.
Example MCQ: Which coagulation test primarily assesses the extrinsic pathway? (a) aPTT (b) PT (c) Platelet count (d) Bleeding time
Answer: (b) PT
Blood Clotting and Multiple Choice Questions: A Broader Perspective
The complexity of blood clotting makes it an ideal subject for MCQs testing a wide range of biological and medical concepts, from basic biochemistry to clinical diagnostics. Crafting effective MCQs requires a thorough understanding of the process and the ability to formulate questions that assess different levels of comprehension, including knowledge recall, application, and analysis.
Advanced Example MCQ: A patient presents with prolonged bleeding after minor trauma, a normal platelet count, and a prolonged PT but a normal aPTT. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? (a) Hemophilia A (b) Hemophilia B (c) Factor V Leiden (d) Vitamin K deficiency
Answer: (d) Vitamin K deficiency (Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of several clotting factors involved in the extrinsic pathway, explaining the prolonged PT).
This article has only scratched the surface of the multifaceted nature of blood clotting. However, by understanding the key stages, regulatory mechanisms, and associated disorders, one can develop a strong foundation for answering MCQs and appreciating the vital role of this process in maintaining human health. The intricate details, coupled with the clinical implications, make blood clotting a compelling and consistently relevant topic for assessment in various biomedical fields. Further study and exploration will enhance understanding and allow for more nuanced analysis of this remarkable physiological process.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Monopolistically Competitive Industry Is Characterized By
Mar 21, 2025
-
A Six Sigma Program Has How Many Defects Per Million
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True Of A Corporation
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Social Death And Psychological Death
Mar 21, 2025
-
When Economists Describe A Market They Mean
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Blood Clotting Is An Example Of How Multiple Choice Question. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
