As Part Of An Operation's Food Defense Program
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
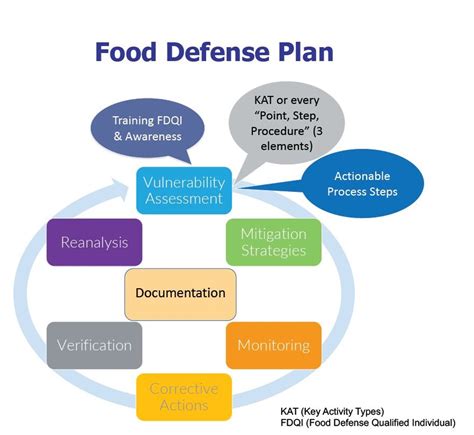
Table of Contents
- As Part Of An Operation's Food Defense Program
- Table of Contents
- A Comprehensive Guide to Food Defense as Part of Your Operations Program
- Understanding the Scope of Food Defense
- Key Differences Between Food Safety and Food Defense:
- Building a Robust Food Defense Plan: A Step-by-Step Approach
- 1. Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying Weak Points
- 2. Developing Mitigation Strategies: Strengthening Defenses
- 3. Emergency Response Plan: Preparedness is Key
- 4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: An Ongoing Process
- Best Practices for Implementing a Food Defense Program
- The Role of Personnel in Food Defense
- The Importance of Supply Chain Security
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations
- Conclusion: Proactive Protection for a Secure Future
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Comprehensive Guide to Food Defense as Part of Your Operations Program
Food defense is no longer a niche concern; it's a critical component of a robust food safety program. Protecting your food products from intentional adulteration is paramount, not just for maintaining consumer trust but also for ensuring the legal and financial viability of your operation. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential elements of a comprehensive food defense program, offering actionable strategies and best practices to safeguard your products and your business.
Understanding the Scope of Food Defense
Food defense focuses on proactively preventing intentional contamination of food products. This differs from food safety, which addresses unintentional contamination from biological, chemical, or physical hazards. While both are crucial, food defense requires a more proactive and security-minded approach, considering potential threats and vulnerabilities within your entire operation.
Key Differences Between Food Safety and Food Defense:
- Food Safety: Reactive; focuses on preventing unintentional contamination through practices like proper sanitation, temperature control, and employee hygiene.
- Food Defense: Proactive; focuses on preventing intentional contamination through security measures, vulnerability assessments, and response plans.
Building a Robust Food Defense Plan: A Step-by-Step Approach
Developing an effective food defense plan requires a systematic approach, incorporating multiple layers of protection. The following steps outline a robust framework:
1. Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying Weak Points
This crucial first step involves a thorough examination of your entire operation, from raw material sourcing to finished product distribution. Identify potential entry points for intentional contamination:
- Raw Material Sourcing: Are your suppliers reliable and vetted? Do you have procedures in place to verify the authenticity of incoming materials?
- Production Facilities: Are access points secured? Are there surveillance systems in place? What about potential weaknesses in equipment or processing areas?
- Transportation and Distribution: Are your transportation routes secure? Are your products adequately protected during shipment and storage?
- Personnel: Do you have thorough background checks for employees who have access to critical control points? Are employees trained on food defense procedures?
- Waste Management: How is waste disposed of? Could this present a risk of contamination or tampering?
Utilize tools like Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles, but adapt them to address intentional contamination scenarios. Consider using vulnerability checklists and risk assessment matrices to systematically evaluate potential threats.
2. Developing Mitigation Strategies: Strengthening Defenses
Once vulnerabilities are identified, develop targeted mitigation strategies to address each risk. Examples include:
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures, including key card systems, surveillance cameras, and limited access to sensitive areas.
- Employee Training: Conduct thorough training programs for all employees, emphasizing food defense procedures, suspicious activity reporting, and emergency response protocols. Regular refresher courses are crucial.
- Surveillance Systems: Install security cameras in strategic locations to monitor activity and deter potential threats.
- Physical Security: Enhance physical security measures, such as fencing, lighting, and alarm systems.
- Supply Chain Security: Establish strong relationships with suppliers, including verification of their own food defense programs and rigorous product testing upon arrival.
- Traceability: Implement robust traceability systems to quickly identify and isolate contaminated products should a threat materialize.
3. Emergency Response Plan: Preparedness is Key
An effective food defense plan must include a detailed emergency response plan outlining steps to take in the event of a suspected or confirmed intentional contamination incident. This plan should:
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities.
- Outline procedures for isolating affected products.
- Detail communication protocols with authorities, suppliers, and consumers.
- Include procedures for containment, investigation, and remediation.
- Specify the chain of custody for evidence collection.
- Address potential public relations and media management aspects.
Regular drills and simulations are essential to ensure that the plan is understood and that the team can respond effectively in a crisis.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: An Ongoing Process
Food defense is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process of monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. Regularly review your vulnerability assessment, update your mitigation strategies based on new threats or vulnerabilities, and conduct periodic audits to ensure the effectiveness of your food defense program.
Best Practices for Implementing a Food Defense Program
- Integrate Food Defense into HACCP: Align your food defense plan with your existing HACCP program, leveraging existing infrastructure and processes.
- Collaboration is Crucial: Work closely with your suppliers, distributors, and regulatory agencies to share information and coordinate efforts.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage technology such as RFID tracking, sensor networks, and advanced analytics to enhance your surveillance and monitoring capabilities.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on emerging threats and best practices by participating in industry conferences, attending training courses, and reviewing relevant publications.
- Document Everything: Maintain meticulous records of your vulnerability assessments, mitigation strategies, training programs, emergency response plans, and audits.
The Role of Personnel in Food Defense
Employees are often the first line of defense against intentional contamination. Comprehensive training is crucial to equip them to identify and report suspicious activity. Training should cover:
- Identifying suspicious activity: This includes unusual behavior, unauthorized access, or unusual packages.
- Reporting procedures: Employees should know exactly who to report suspicious activity to and how.
- Security awareness: Employees should be aware of their role in maintaining security and protecting the facility.
- Emergency response procedures: Employees should understand their roles and responsibilities in the event of a contamination incident.
The Importance of Supply Chain Security
Your supply chain is a critical point of vulnerability. To strengthen your food defense program, consider:
- Supplier vetting: Conduct thorough background checks on your suppliers, verifying their own food safety and defense measures.
- Product verification: Implement procedures to verify the authenticity of incoming materials and products.
- Transportation security: Ensure the secure transportation of your products from origin to destination.
- Documentation: Maintain complete documentation of your supply chain activities, including supplier information, transportation records, and product traceability data.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with relevant food safety and security regulations is paramount. Stay informed about current regulations and ensure your food defense program meets all legal requirements. Failure to maintain adequate food defense measures can result in significant legal repercussions, including fines, product recalls, and reputational damage.
Conclusion: Proactive Protection for a Secure Future
Implementing a comprehensive food defense program is not merely a compliance exercise; it’s a strategic investment in the long-term safety, security, and success of your food operation. By taking a proactive and systematic approach, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to intentional contamination, protect your brand reputation, and build greater trust with consumers. Remember, continuous improvement and adaptation are crucial in the ever-evolving landscape of food security. Regularly assess, update, and test your plan to ensure it remains effective against evolving threats. The proactive steps you take today will safeguard your business and the well-being of consumers for years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Based On The Above Income Statement Data And The Formula
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Largest Expense For Most Airlines Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
Formal Education As An Approach To Employee Development Includes
Mar 29, 2025
-
Vail Company Recorded The Following Transactions During November
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Coversheet Is Attached To Help Protect A Secret Document
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about As Part Of An Operation's Food Defense Program . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
