According To The Law Of Supply
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
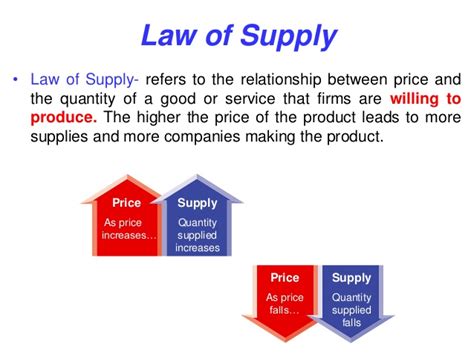
Table of Contents
According to the Law of Supply: A Comprehensive Guide
The law of supply is a fundamental principle in economics that describes the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied. Understanding this law is crucial for anyone involved in business, finance, or economics, as it influences pricing strategies, production decisions, and market equilibrium. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the law of supply, exploring its core concepts, influencing factors, exceptions, and real-world applications.
Understanding the Law of Supply: The Basics
The law of supply states that, all other factors being equal (ceteris paribus), as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied of that good or service will increase, and vice versa. In simpler terms, producers are willing to offer more of a product when they can sell it at a higher price and less when the price is low. This relationship is typically depicted graphically as an upward-sloping supply curve.
The Supply Curve: A Visual Representation
The supply curve visually represents the law of supply. The horizontal axis represents the quantity supplied, while the vertical axis represents the price. The upward slope signifies the positive relationship between price and quantity supplied. A movement along the supply curve indicates a change in quantity supplied due to a price change, while a shift of the entire curve indicates a change in supply caused by factors other than price.
Ceteris Paribus: The Importance of "All Other Factors Being Equal"
The phrase "ceteris paribus" is crucial to understanding the law of supply. It acknowledges that numerous factors can influence supply besides price. These factors, which we'll discuss in detail later, are held constant when analyzing the relationship between price and quantity supplied. If these other factors change, the entire supply curve will shift, rather than just a movement along the curve.
Factors Affecting the Supply Curve: Shifting the Curve
While the law of supply describes the relationship between price and quantity supplied, several factors can influence the overall supply of a good or service, causing the supply curve to shift to the left (decrease in supply) or to the right (increase in supply). These factors include:
1. Input Prices: The Cost of Production
Changes in the prices of inputs used in production significantly impact supply. Higher input prices (e.g., raw materials, labor, energy) increase the cost of production, leading to a decrease in supply (leftward shift). Conversely, lower input prices result in a increase in supply (rightward shift). For example, a rise in the price of wheat will reduce the supply of bread.
2. Technology: Improving Efficiency
Technological advancements can dramatically increase productivity and efficiency. Improved technology often leads to lower production costs and an increase in supply (rightward shift). For instance, the introduction of automated assembly lines can significantly boost the supply of manufactured goods.
3. Government Policies: Taxes, Subsidies, and Regulations
Government intervention through taxes, subsidies, and regulations can substantially affect supply. Taxes typically increase production costs, resulting in a decrease in supply (leftward shift). Subsidies, on the other hand, reduce production costs, leading to an increase in supply (rightward shift). Regulations, depending on their nature, can either increase or decrease supply. Stricter environmental regulations, for example, might decrease supply due to increased compliance costs.
4. Producer Expectations: Anticipating Future Prices
Producers' expectations about future prices play a significant role in their current supply decisions. If producers anticipate higher future prices, they may reduce current supply (holding back inventory) to capitalize on those higher prices later (leftward shift). Conversely, expectations of lower future prices might encourage producers to increase current supply to avoid losses (rightward shift).
5. Number of Sellers: Market Competition
The number of sellers in a market directly influences supply. An increase in the number of sellers leads to a greater quantity supplied at each price level, resulting in a rightward shift of the supply curve. Conversely, a decrease in the number of sellers leads to a leftward shift.
6. Natural Events and Disasters: Unforeseen Circumstances
Unforeseen events like natural disasters, pandemics, or extreme weather conditions can significantly impact supply. These events often disrupt production and distribution, leading to a decrease in supply (leftward shift). For example, a hurricane damaging a major agricultural region will reduce the supply of agricultural products.
Exceptions to the Law of Supply: When the Curve Doesn't Always Slope Upwards
While the law of supply generally holds true, there are some exceptions where the relationship between price and quantity supplied might not be strictly positive. These exceptions are often related to specific market conditions or time horizons.
1. Very Short Run: Fixed Supply
In the very short run, the supply of certain goods might be completely fixed. Producers might not be able to adjust their production levels immediately in response to price changes. For example, the supply of seats in a stadium for a specific event is fixed, regardless of ticket price fluctuations. In this case, the supply curve would be perfectly inelastic (vertical).
2. Very Long Run: Technological Advancements
In the very long run, technological advancements could fundamentally alter production processes, leading to unexpected supply responses. A breakthrough innovation might significantly reduce production costs, leading to a larger than expected increase in supply even at lower prices. This scenario can lead to a flatter or even backward-bending supply curve in the very long run.
The Interaction of Supply and Demand: Achieving Market Equilibrium
The law of supply interacts with the law of demand to determine market equilibrium – the point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The market equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. Any deviation from this equilibrium point leads to market forces pushing the price and quantity towards equilibrium.
Understanding Market Equilibrium: A Dynamic Process
Market equilibrium is not a static point but rather a dynamic process. Changes in supply or demand will shift the respective curves, leading to a new equilibrium price and quantity. For example, an increase in demand will increase both the equilibrium price and quantity, while an increase in supply will decrease the equilibrium price and increase the equilibrium quantity.
Illustrative Scenarios: Real-World Applications
Let’s consider some real-world examples to illustrate the interplay of supply and demand and how the law of supply shapes market outcomes:
-
The Oil Market: A disruption to oil production due to geopolitical instability can cause a significant decrease in oil supply. This leads to a sharp rise in oil prices, reflecting the law of supply.
-
The Housing Market: A surge in demand for housing in a growing city can drive up prices. Builders, responding to the law of supply, will increase the construction of new homes, but this increase in supply might not fully offset the increase in demand, leading to persistent price increases in the short term.
-
The Smartphone Market: Technological advancements in smartphone production have dramatically increased supply over the years, leading to lower prices and increased accessibility.
Conclusion: The enduring Relevance of the Law of Supply
The law of supply is a cornerstone of economic theory, providing a crucial framework for understanding how prices and quantities are determined in markets. While exceptions exist, the fundamental principle remains relevant across a wide range of goods and services. By understanding the law of supply and the various factors that can influence it, businesses can make informed decisions regarding pricing, production, and resource allocation. This knowledge is also essential for consumers to understand price fluctuations and market trends. Mastering the law of supply is therefore a valuable skill for navigating the complexities of the modern economy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Genes Is Not Correct
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Evidence Based Management Approach Is Based On
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Third Step Of Mbo Reminds Us That
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Resource Demand Curve Is Represented By The
Mar 16, 2025
-
Commercial Kitchen Walls And Floors Should Be Cleaned
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about According To The Law Of Supply . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
