A Social Audit Is Used By Organizations To
Holbox
Mar 26, 2025 · 7 min read
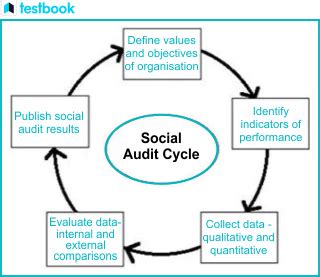
Table of Contents
- A Social Audit Is Used By Organizations To
- Table of Contents
- A Social Audit: How Organizations Use It to Measure and Improve Social Impact
- Why Conduct a Social Audit?
- Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image:
- Improved Stakeholder Relations:
- Risk Management and Mitigation:
- Improved Operational Efficiency:
- Increased Investor Confidence:
- Meeting Regulatory Requirements and Standards:
- Strategic Planning and Decision-Making:
- The Process of Conducting a Social Audit
- 1. Defining the Scope and Objectives:
- 2. Identifying Stakeholders:
- 3. Data Collection and Analysis:
- 4. Reporting and Communication:
- 5. Action Planning and Implementation:
- 6. Monitoring and Evaluation:
- Key Areas Covered in a Social Audit
- Environmental Performance:
- Labor Practices:
- Community Engagement:
- Supply Chain Management:
- Human Rights:
- Governance and Transparency:
- Choosing the Right Social Audit Methodology
- The Future of Social Audits
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Social Audit: How Organizations Use It to Measure and Improve Social Impact
A social audit is a systematic evaluation of an organization's social and environmental performance. It's a crucial tool for businesses striving to operate ethically and sustainably, going beyond simple profit maximization to encompass a broader commitment to societal well-being. Unlike a financial audit, which focuses solely on financial statements, a social audit examines a company's impact on various stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and the environment. This comprehensive assessment helps organizations identify areas for improvement, enhance their reputation, and contribute positively to the world.
Why Conduct a Social Audit?
In today's increasingly conscious world, consumers, investors, and employees are demanding more transparency and accountability from businesses. A social audit serves as a powerful instrument to meet these expectations. The benefits are multifaceted:
Enhanced Reputation and Brand Image:
By publicly showcasing their commitment to social responsibility through a transparent social audit, organizations can significantly improve their brand image and public perception. Consumers are more likely to support companies that demonstrate ethical and sustainable practices. This positive image translates into increased customer loyalty and brand preference.
Improved Stakeholder Relations:
A social audit fosters better relationships with stakeholders. By identifying and addressing concerns raised by employees, customers, and communities, organizations can build trust and strengthen collaborations. Open communication and demonstrable action based on the audit's findings enhance stakeholder confidence and engagement.
Risk Management and Mitigation:
Proactive identification of social and environmental risks is crucial for long-term sustainability. A social audit helps organizations assess potential risks related to labor practices, environmental impact, and community relations. Early detection of these issues allows for timely intervention and mitigation strategies, preventing significant reputational damage or legal issues.
Improved Operational Efficiency:
By pinpointing areas of inefficiency or unsustainable practices, a social audit can lead to operational improvements. This might involve streamlining processes, reducing waste, or adopting more efficient resource management strategies, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Increased Investor Confidence:
Socially responsible investing (SRI) is rapidly gaining traction. Investors are increasingly seeking out companies with strong ethical and sustainability records. A well-conducted social audit provides evidence of a company's commitment to these values, attracting socially conscious investors and potentially leading to improved access to capital.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements and Standards:
Many industries are subject to increasing regulatory pressure related to social and environmental performance. A social audit can help organizations demonstrate compliance with relevant laws and regulations, minimizing legal risks and penalties. Furthermore, it can aid in achieving certifications and industry standards related to sustainability and social responsibility.
Strategic Planning and Decision-Making:
The insights gleaned from a social audit provide valuable information for strategic planning and decision-making. Understanding the organization's social and environmental impact can guide the development of more sustainable business models, policies, and strategies.
The Process of Conducting a Social Audit
Conducting a thorough and effective social audit requires a systematic approach:
1. Defining the Scope and Objectives:
The first step involves clearly defining the scope of the audit, specifying the areas to be evaluated (e.g., environmental impact, labor practices, community engagement). Objectives should be clearly stated, outlining the specific goals of the audit, such as identifying areas for improvement or demonstrating compliance with specific standards.
2. Identifying Stakeholders:
Identifying key stakeholders is crucial. This involves determining the groups most significantly impacted by the organization's activities (employees, customers, suppliers, communities, government agencies, etc.). Their perspectives and concerns need to be considered throughout the audit process.
3. Data Collection and Analysis:
Various methods can be employed to gather data, including surveys, interviews, document reviews, site visits, and observation. The chosen methods should be appropriate to the specific objectives and scope of the audit. Data analysis involves organizing and interpreting the collected information, identifying trends and patterns.
4. Reporting and Communication:
The social audit report should clearly present the findings, including both positive and negative aspects of the organization's social and environmental performance. It should be transparent, objective, and easy to understand. Effective communication of the findings to stakeholders is essential, ensuring that the report's insights are used to drive positive change.
5. Action Planning and Implementation:
Based on the audit findings, the organization should develop an action plan outlining specific measures to address identified issues and opportunities for improvement. This plan should include timelines, responsibilities, and measurable targets. Implementation involves putting the action plan into effect and monitoring its progress.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation:
Regular monitoring and evaluation of the implemented action plan are essential to ensure that progress is being made and that the desired outcomes are achieved. This iterative process allows for adjustments and improvements to the action plan as needed.
Key Areas Covered in a Social Audit
A comprehensive social audit typically covers a wide range of areas, including:
Environmental Performance:
This involves assessing the organization's environmental footprint, including its energy consumption, waste generation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage. It also assesses compliance with environmental regulations and the adoption of sustainable practices. Keywords: environmental impact, sustainability, carbon footprint, waste management, resource efficiency.
Labor Practices:
This area focuses on evaluating the organization's treatment of its employees, including aspects like working conditions, wages, benefits, health and safety, and diversity and inclusion. Compliance with labor laws and industry best practices is a key consideration. Keywords: employee wellbeing, fair wages, workplace safety, diversity, inclusion, human rights.
Community Engagement:
This assesses the organization's relationship with the communities where it operates, including its contributions to local development, its support for community initiatives, and its efforts to address community concerns. Keywords: community relations, social responsibility, philanthropy, corporate citizenship.
Supply Chain Management:
This involves evaluating the social and environmental performance of the organization's suppliers. This includes assessing their labor practices, environmental impact, and ethical sourcing policies. Ensuring that the entire supply chain adheres to ethical and sustainable standards is crucial. Keywords: ethical sourcing, sustainable supply chain, supplier responsibility, traceability.
Human Rights:
This is increasingly important, focusing on the organization's commitment to upholding human rights throughout its operations and supply chain. This includes considerations such as forced labor, child labor, and discrimination. Keywords: human rights due diligence, ethical conduct, fair trade.
Governance and Transparency:
This element assesses the organization's governance structures, decision-making processes, and transparency in its operations. It also examines the organization's commitment to accountability and ethical conduct. Keywords: corporate governance, transparency, accountability, ethical leadership.
Choosing the Right Social Audit Methodology
Several methodologies can be used to conduct a social audit. The choice depends on the organization's specific needs and objectives. Some common approaches include:
-
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards: These widely recognized standards provide a framework for reporting on an organization's economic, environmental, and social performance.
-
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) Standards: These standards focus on the financially material ESG (environmental, social, and governance) issues for specific industries.
-
ISO 26000: This international standard provides guidance on social responsibility, offering a comprehensive framework for understanding and implementing responsible business practices.
-
Custom-Designed Audits: Organizations can also develop custom-designed audits tailored to their specific needs and context.
The Future of Social Audits
Social audits are evolving to keep pace with changing societal expectations and technological advancements. Several trends are shaping the future of this field:
-
Increased use of technology: Data analytics and AI are increasingly being used to gather, analyze, and report on social and environmental data, leading to more efficient and effective audits.
-
Focus on materiality: Social audits are increasingly focusing on the most material ESG issues for specific organizations and industries, ensuring that resources are directed towards the most impactful areas.
-
Integration with other reporting frameworks: Social audits are becoming more integrated with other reporting frameworks, such as financial reporting and sustainability reporting, providing a more holistic view of the organization's performance.
-
Greater stakeholder engagement: There's a growing emphasis on engaging stakeholders throughout the social audit process, ensuring that their perspectives and concerns are taken into account.
-
Emphasis on impact measurement: The focus is shifting from simply identifying issues to measuring the actual impact of the organization's actions on social and environmental outcomes.
In conclusion, a social audit is an indispensable tool for organizations committed to ethical and sustainable operations. By providing a comprehensive assessment of social and environmental performance, it enables organizations to identify areas for improvement, enhance their reputation, build stronger stakeholder relationships, and contribute positively to society. As societal expectations continue to evolve, the importance of social audits will only continue to grow. Embracing this practice is not just a matter of compliance, but a strategic imperative for long-term success and positive impact.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Consider The Partial Sequence Of A Peptide
Mar 29, 2025
-
Raises And Other Monetary Incentives Are Examples Of Rewards
Mar 29, 2025
-
Acme Drug Inc Is Developing A New Cancer Suppressant Drug
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Series Id For These Cpi Data Is
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Are The Group Numbers Of X And Y
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Social Audit Is Used By Organizations To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
