A Purpose Of The Core Inflation Index Is _______________.
Holbox
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
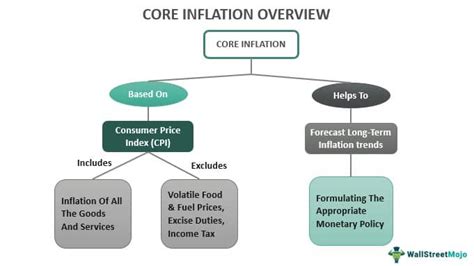
Table of Contents
A Purpose of the Core Inflation Index is to Measure Underlying Price Pressures
The core inflation index serves a vital purpose: to measure the underlying rate of inflation by excluding volatile components that can distort the overall picture. While headline inflation, which includes all items in a consumer price index (CPI) or producer price index (PPI), provides a snapshot of current price changes, it can be heavily influenced by temporary factors like energy price fluctuations or supply chain disruptions. These temporary shocks can obscure the true trend of underlying price pressures within an economy. The core inflation index, therefore, acts as a more stable and reliable indicator of persistent inflationary trends. Understanding its purpose and limitations is crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses alike.
Why Exclude Volatile Components?
The primary reason for excluding volatile components from the core inflation index is to gain a clearer understanding of persistent inflationary pressures. These volatile components, typically energy and food prices, are subject to significant short-term fluctuations due to various factors. For example:
- Energy prices: These are influenced by geopolitical events, weather patterns, OPEC decisions, and speculative trading. A sudden spike in oil prices, for instance, will immediately impact headline inflation but might not reflect a sustained increase in overall price levels.
- Food prices: These are susceptible to weather conditions (droughts, floods), agricultural production cycles, disease outbreaks, and global supply chain issues. A poor harvest season can cause temporary food price increases that don't reflect long-term inflation trends.
By excluding these volatile components, the core inflation index allows analysts to focus on the underlying trends in prices for goods and services that are less susceptible to short-term shocks. This provides a more accurate assessment of the persistent inflationary pressures affecting the economy and allows for more informed policy decisions.
Different Measures of Core Inflation: A Comparative Analysis
Several methods exist for calculating the core inflation index, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common approaches include:
-
Core CPI (excluding food and energy): This is the most widely used measure, simply removing food and energy prices from the overall CPI. It is straightforward to understand and calculate, making it readily accessible and easily comparable across different time periods and countries. However, its simplicity can also be a limitation, as it might still be affected by other volatile components not explicitly excluded.
-
Trimmed Mean CPI: This method calculates the core inflation rate by removing a specific percentage of the highest and lowest price changes from the overall CPI. This approach aims to reduce the influence of outliers and extreme price fluctuations while retaining more data points than simply excluding food and energy. The percentage removed is often set at around 16-20%, although this can vary depending on the specific methodology.
-
Median CPI: This focuses on the middle value of price changes. It identifies the inflation rate that represents the price change experienced by the 'typical' consumer, effectively mitigating the effect of both high and low price changes. The median is robust against outliers, making it less susceptible to extreme values.
-
Weighted Median CPI: Similar to the median CPI but incorporates weights reflecting the relative importance of various goods and services in the consumer basket. This enhances accuracy by considering the contribution of each item to overall inflation.
The choice of methodology can significantly influence the resulting core inflation rate. Therefore, it's crucial to understand the specific methodology used when comparing core inflation data from different sources or countries. Each method offers a slightly different perspective on underlying inflation, and comparing them can provide a more comprehensive understanding.
The Importance of Core Inflation for Policymakers
Core inflation is a crucial indicator for central banks and policymakers when making decisions about monetary policy. It provides a more reliable signal of underlying inflationary pressures than headline inflation, allowing for more informed judgments about the need for interest rate adjustments or other interventions.
-
Interest rate decisions: Central banks primarily use core inflation to assess whether inflationary pressures are building and whether monetary tightening (raising interest rates) or loosening (lowering interest rates) is warranted. If core inflation is persistently above the target rate, it signals a need for tightening to cool down the economy and prevent inflation from becoming entrenched. Conversely, if core inflation is below the target, it might suggest a need for easing to stimulate economic activity.
-
Fiscal policy adjustments: Governments also use core inflation data to inform fiscal policy decisions. Persistent high core inflation may indicate a need for fiscal restraint, such as reducing government spending or increasing taxes, to curb aggregate demand. Conversely, low core inflation might suggest a need for fiscal stimulus to boost economic growth.
-
Long-term economic planning: Core inflation provides a better basis for forecasting long-term economic trends than headline inflation. By removing temporary shocks, it allows for more accurate predictions of future price levels, enabling businesses and households to make better investment and spending decisions.
Core Inflation and Investment Strategies
For investors, understanding core inflation is vital for various reasons:
-
Asset allocation: Core inflation data can influence investment strategies by providing insights into the future trajectory of interest rates and asset prices. For instance, rising core inflation might prompt investors to shift towards assets that are expected to outperform during inflationary periods, such as inflation-protected securities (TIPS) or real estate.
-
Risk assessment: Persistent high core inflation can signal increased risk in the economy, potentially leading to reduced investment in riskier assets. Conversely, stable low core inflation might be viewed favorably, promoting investment in growth-oriented assets.
-
Valuation of assets: Core inflation is crucial for accurately valuing assets, especially those with long-term cash flows. High core inflation erodes the purchasing power of future cash flows, thereby reducing the present value of assets.
Limitations of Core Inflation Indices
Despite its usefulness, the core inflation index has limitations:
-
Subjectivity in choosing components: The selection of volatile components to exclude can be subjective. Different organizations may use different methods, leading to variations in the reported core inflation rate.
-
Delayed indicator: Core inflation data is typically released with a lag, often after headline inflation figures. This delay can limit its usefulness for immediate policy decisions.
-
Doesn't capture all aspects of inflation: The core inflation index only focuses on specific price changes and might miss broader aspects of inflation, such as changes in asset prices or the cost of healthcare.
-
Regional variations: Core inflation rates can vary significantly across different regions within a country, highlighting the need for regional-specific analyses.
Conclusion: Core Inflation as a Crucial Economic Indicator
In conclusion, a purpose of the core inflation index is to provide a more accurate and stable measure of underlying inflationary pressures by excluding volatile components like energy and food prices. This allows for a clearer understanding of persistent price trends, facilitating more informed policy decisions by central banks and governments, more effective investment strategies by businesses and individuals, and a more robust framework for long-term economic planning. While not without limitations, the core inflation index remains a crucial economic indicator used worldwide to monitor and manage inflationary pressures. Understanding its various measures, interpretations, and limitations is paramount for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the modern economy. By carefully considering the specific methodology employed and comparing it with other economic indicators, a more comprehensive picture of inflation and its potential impact can be formed.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Evaluate The Definite Integral D 0 Tan D 3 Dd
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Usual Starting Point For A Master Budget Is
Mar 15, 2025
-
A Constraint In A Decision Is Blank
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Goal Of Is To Share Resources Especilaly
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Are Diploid Cells Homologous Chromosomes And Alleles Related
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Purpose Of The Core Inflation Index Is _______________. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
