A Multiple Step Income Statement Reports Multiple Levels Of
Holbox
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
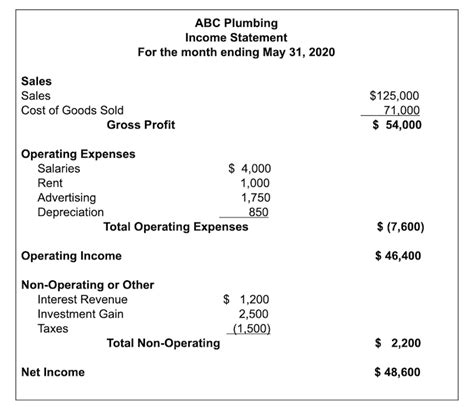
Table of Contents
A Multi-Step Income Statement: Reporting Multiple Levels of Profitability
The multi-step income statement provides a more detailed and nuanced view of a company's financial performance than its single-step counterpart. While a single-step statement simply subtracts total expenses from total revenues to arrive at net income, the multi-step statement breaks down this process into several crucial steps, revealing various levels of profitability along the way. This granular approach offers valuable insights for investors, creditors, and management alike, enabling a more thorough understanding of a company's operational efficiency and financial health.
Understanding the Structure of a Multi-Step Income Statement
A multi-step income statement is structured to showcase different profit margins, providing a layered perspective on a company's profitability. It typically presents the following key sections:
1. Revenue Section
This section begins with gross revenue, representing the total sales generated by the company during the reporting period. It might include sales returns and allowances, which are subsequently deducted to arrive at net sales. This represents the actual revenue earned after accounting for sales returns and allowances.
Key Considerations for the Revenue Section:
- Accuracy of revenue recognition: Ensure adherence to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to accurately reflect revenue earned.
- Segment reporting: For larger companies, breaking down revenue by product line, geographic region, or customer segment can provide valuable insights.
- Changes in revenue: Comparing revenue figures year-over-year reveals trends and growth patterns.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
This section shows the direct costs associated with producing the goods sold during the period. For a manufacturing company, this includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. For a retailer, it involves the cost of purchasing the goods sold. Subtracting COGS from net sales yields the gross profit.
Key Considerations for the COGS Section:
- Inventory valuation: The method used to value inventory (FIFO, LIFO, weighted-average cost) significantly impacts COGS and gross profit. Consistency is crucial for accurate comparisons over time.
- Inventory management: Efficient inventory management minimizes waste and ensures optimal stock levels, positively affecting COGS.
- Direct vs. indirect costs: Careful allocation of costs between direct (COGS) and indirect (operating expenses) is crucial for accurate reporting.
3. Operating Expenses
This section details the expenses incurred in running the business's day-to-day operations. It's typically broken down into several categories:
- Selling expenses: These include costs associated with marketing, advertising, sales commissions, and sales salaries.
- General and administrative expenses: These encompass costs like rent, utilities, salaries of administrative staff, insurance, and legal fees.
- Research and development expenses: For companies engaged in innovation, these expenses are crucial and represent investments in future growth.
- Depreciation and amortization: These are non-cash expenses reflecting the gradual reduction in the value of assets over time.
Subtracting operating expenses from gross profit yields the operating income (or earnings before interest and taxes, EBIT). This is a crucial measure of a company's profitability from its core operations.
Key Considerations for the Operating Expenses Section:
- Expense classification: Proper classification ensures accurate analysis and comparison with industry benchmarks.
- Expense control: Efficient cost management is crucial for maximizing profitability. Regular analysis of expenses can identify areas for potential savings.
- Fixed vs. variable costs: Understanding the nature of expenses (fixed or variable) is essential for forecasting and budgeting.
4. Non-Operating Items
This section includes income and expenses not directly related to the company's core operations. These items can significantly impact net income, but they provide insights into a company's financial strategies and risk profile. Examples include:
- Interest income or expense: Income from investments or expenses incurred on debt financing.
- Gain or loss on the sale of assets: Profits or losses from selling non-current assets.
- Other non-operating income or expense: This is a catch-all category for miscellaneous non-operating items.
After considering non-operating items, we arrive at income before taxes.
Key Considerations for the Non-Operating Items Section:
- Materiality: Only significant non-operating items should be separately reported.
- Transparency: Clear disclosure of the nature and significance of each non-operating item is crucial.
- Consistency: Maintain consistent reporting of non-operating items over time for accurate comparisons.
5. Income Taxes
The final step involves deducting income taxes from income before taxes to arrive at net income. This represents the company's bottom-line profit after all expenses and taxes.
Key Considerations for the Income Tax Section:
- Tax rate: The effective tax rate should reflect the company's actual tax liability.
- Tax planning: Effective tax planning can minimize tax burden while ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Interpreting Multiple Levels of Profitability
The multi-step income statement's layered structure reveals several key profitability metrics:
- Gross profit margin: (Gross Profit / Net Sales) * 100%. This indicates the profitability of the company's core operations, reflecting efficiency in managing the cost of goods sold.
- Operating profit margin: (Operating Income / Net Sales) * 100%. This shows the profitability of the company's core operations after deducting operating expenses, indicating operational efficiency.
- Net profit margin: (Net Income / Net Sales) * 100%. This is the overall profitability after all expenses, including taxes and non-operating items, reflecting the overall financial performance.
By analyzing these margins over time and comparing them to industry averages, investors and management can assess a company's performance and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of Using a Multi-Step Income Statement
The multi-step income statement offers several advantages:
- Detailed information: It provides a more detailed breakdown of revenues and expenses, offering a richer understanding of a company's financial performance than a single-step statement.
- Multiple profitability measures: It showcases various levels of profitability, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment of the company's financial health.
- Improved analysis: The detailed information allows for more in-depth analysis and comparisons over time and with competitors.
- Enhanced decision-making: The insights gained from the multi-step income statement help inform strategic business decisions regarding pricing, cost control, and investment strategies.
- Better understanding of operational efficiency: It highlights the relationship between gross profit, operating income, and net income, enabling a better understanding of the company's operational efficiency.
- Compliance with accounting standards: It aligns with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), ensuring transparency and consistency in financial reporting.
Limitations of a Multi-Step Income Statement
While the multi-step income statement provides a wealth of information, it does have some limitations:
- Complexity: Its detailed nature can make it more complex to understand than a single-step statement, particularly for users without a strong accounting background.
- Subjectivity: The classification of expenses can be subjective, leading to variations in reporting across different companies.
- Potential for manipulation: While less likely with proper accounting oversight, there's a potential for manipulation through aggressive accounting practices, especially regarding the classification of expenses.
Comparing Multi-Step and Single-Step Income Statements
The choice between a multi-step and single-step income statement depends on the specific needs of the user. While the single-step statement offers simplicity, the multi-step statement provides a significantly richer level of detail and analysis. For investors, creditors, and internal management teams requiring in-depth financial insights, the multi-step statement is generally preferred. However, for simpler businesses or users seeking a high-level overview, the single-step statement might suffice.
Conclusion
The multi-step income statement is a powerful financial reporting tool that provides a detailed and nuanced view of a company's financial performance. By presenting multiple levels of profitability, it allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the company's operational efficiency and financial health. While it's more complex than the single-step statement, the enhanced insights it provides are invaluable for informed decision-making by investors, creditors, and management. Understanding the intricacies of the multi-step income statement is essential for anyone involved in analyzing and interpreting financial statements. Through careful analysis of the various profit margins and expense categories, a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial performance can be achieved, leading to more informed and strategic decisions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Do Pumice And Scoria Have In Common
Mar 17, 2025
-
Classify Each Substance Based On The Intermolecular Forces
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Person In Charge Should Be Able To Identify Signs
Mar 17, 2025
-
Per Company Policy Tools With A Purchase Price
Mar 17, 2025
-
Things Of Value Owned By A Firm Are Called Its
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Multiple Step Income Statement Reports Multiple Levels Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
