A _______ Is A Share Of Ownership In A Company.
Holbox
May 09, 2025 · 6 min read
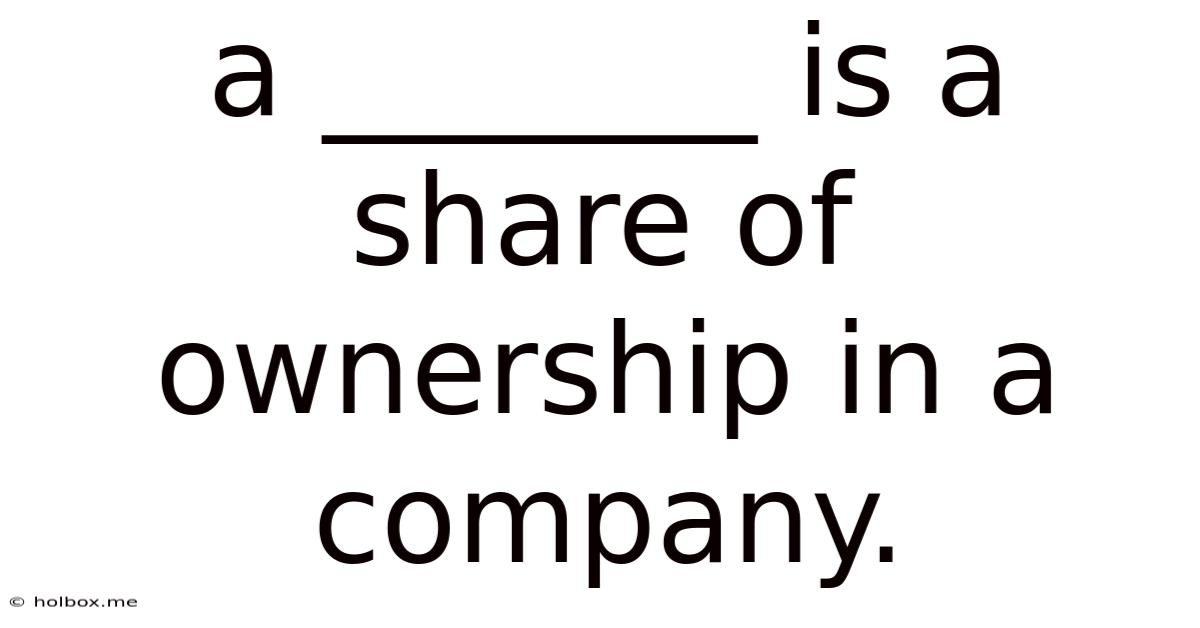
Table of Contents
- A _______ Is A Share Of Ownership In A Company.
- Table of Contents
- A Share is a Share of Ownership in a Company: Understanding Stocks and the Stock Market
- What Does Owning a Share Really Mean?
- 1. Ownership Proportionate to Shares Held:
- 2. Voting Rights:
- 3. Dividends (Potential):
- 4. Capital Appreciation (Potential):
- Different Types of Shares
- 1. Common Stock:
- 2. Preferred Stock:
- 3. Class A and Class B Shares:
- Understanding the Stock Market
- 1. Company Performance:
- 2. Economic Conditions:
- 3. Geopolitical Events:
- 4. Investor Sentiment:
- The Risks and Rewards of Investing in Shares
- 1. Potential for High Returns:
- 2. Volatility and Risk of Loss:
- How to Research Before Investing
- 1. Financial Statements:
- 2. Industry Analysis:
- 3. Management Team:
- 4. Competitive Advantage:
- 5. Valuation:
- Diversification: A Crucial Strategy
- Long-Term Investing vs. Short-Term Trading
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Share is a Share of Ownership in a Company: Understanding Stocks and the Stock Market
A share, also known as a stock, represents a fractional ownership in a company. When you buy a share, you become a shareholder, owning a tiny piece of that company's assets and profits. This seemingly simple concept underpins the vast and complex world of the stock market, a crucial engine of global economic growth. Understanding what a share is, how it works, and the risks and rewards involved is fundamental to navigating the world of investing.
What Does Owning a Share Really Mean?
Owning a share isn't just about owning a piece of paper; it's about participating in the company's success. As a shareholder, you're entitled to certain rights, including:
1. Ownership Proportionate to Shares Held:
The number of shares you own dictates your proportional ownership stake in the company. If a company has 1 million shares outstanding and you own 10,000, you own 1% of the company. This ownership is crucial for understanding your potential for profit or loss.
2. Voting Rights:
Many shares grant voting rights in company matters, such as electing the board of directors or approving major corporate decisions like mergers and acquisitions. These votes are usually proportional to your share ownership. The more shares you own, the greater your influence on company decisions.
3. Dividends (Potential):
Some companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders as dividends. These are typically paid quarterly or annually and represent a return on your investment. However, dividend payments aren't guaranteed; companies may choose not to pay dividends, especially if they're reinvesting profits for growth.
4. Capital Appreciation (Potential):
The primary way shareholders profit is through capital appreciation. This occurs when the share price increases. If you buy a share for $10 and it rises to $20, you've doubled your investment (excluding trading fees and commissions). This capital gain is realized only when you sell the share.
Different Types of Shares
Not all shares are created equal. Different classes of shares often exist, each with varying rights and privileges. Common share types include:
1. Common Stock:
This is the most common type of share, offering the rights outlined above: voting rights (usually), potential dividends, and the potential for capital appreciation. Common stockholders are last in line to receive assets in the event of company liquidation.
2. Preferred Stock:
Preferred stock offers shareholders preferential treatment over common stockholders in certain situations. They typically receive dividends before common stockholders and may have priority in asset distribution during liquidation. However, preferred stockholders often have limited or no voting rights.
3. Class A and Class B Shares:
Some companies issue different classes of common stock, often with differing voting rights. For example, Class A shares might carry one vote per share, while Class B shares might carry ten votes per share, giving the holders of Class B shares significantly more influence over company decisions. This structure is often used by founders to retain control even after a public offering.
Understanding the Stock Market
The stock market is a vast, interconnected network where shares of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. It's a dynamic environment influenced by countless factors, including:
1. Company Performance:
A company's financial health, growth prospects, and overall performance significantly impact its share price. Strong earnings, innovation, and market leadership generally lead to higher share prices, while poor performance often results in lower prices.
2. Economic Conditions:
Broad economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, influence investor sentiment and, consequently, share prices. Recessions tend to negatively impact stock markets, while periods of economic expansion often boost them.
3. Geopolitical Events:
Global events, like wars, political instability, and international trade disputes, can significantly impact investor confidence and market volatility. Unexpected geopolitical events can cause significant price swings.
4. Investor Sentiment:
Market psychology plays a significant role in share price movements. Optimism and confidence lead to buying pressure, pushing prices higher, while fear and uncertainty can trigger selling, driving prices down. This is often referred to as market sentiment.
The Risks and Rewards of Investing in Shares
Investing in shares offers the potential for significant returns but also carries substantial risk.
1. Potential for High Returns:
Historically, stocks have provided higher returns than other asset classes, such as bonds or savings accounts. The potential for capital appreciation and dividend income can lead to substantial wealth creation over the long term.
2. Volatility and Risk of Loss:
Share prices can fluctuate significantly in short periods, leading to potential losses. Market downturns, company-specific problems, or unexpected events can severely impact the value of your investments. You could lose some or all of your initial investment.
How to Research Before Investing
Before investing in any company's shares, thorough research is essential. Consider the following:
1. Financial Statements:
Analyze the company's financial reports (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement) to understand its profitability, debt levels, and financial health.
2. Industry Analysis:
Research the company's industry to assess its competitive landscape, growth potential, and future outlook.
3. Management Team:
Evaluate the company's management team, assessing their experience, competence, and track record.
4. Competitive Advantage:
Determine if the company possesses a sustainable competitive advantage, such as a strong brand, innovative technology, or cost leadership.
5. Valuation:
Use various valuation metrics (e.g., price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio) to determine if the company's shares are fairly valued.
Diversification: A Crucial Strategy
Diversification is a key principle in successful investing. Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across multiple companies and sectors to reduce your risk. A diversified portfolio can help cushion against losses in any single investment.
Long-Term Investing vs. Short-Term Trading
Many investors adopt a long-term approach, holding shares for years or even decades, benefiting from the power of compounding returns. Others engage in short-term trading, attempting to profit from short-term price fluctuations. The appropriate strategy depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Conclusion
Understanding that a share represents a piece of ownership in a company is the first step to navigating the world of stock market investing. While it offers significant potential for substantial returns, it’s crucial to remember the inherent risks involved. Thorough research, diversification, and a long-term perspective are essential for navigating the complexities of the stock market and achieving your investment goals. Remember to always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. They can help you develop a personalized investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. The stock market is a powerful tool, but understanding its intricacies is vital to using it effectively and responsibly. Don't be afraid to learn and adapt your approach over time as your knowledge and experience grow.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A _______ Is A Share Of Ownership In A Company. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.