A Competitive Market Is A Market In Which
Holbox
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
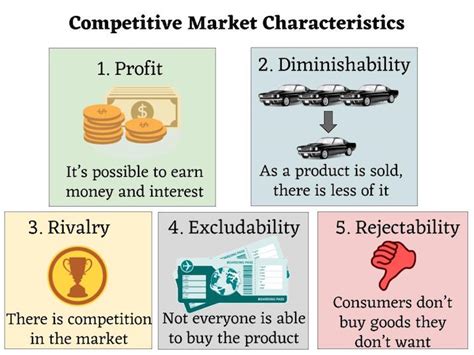
Table of Contents
A Competitive Market Is a Market in Which… Opportunities Abound
A competitive market is a market in which numerous firms offer similar products or services. This seemingly simple definition belies a complex reality brimming with opportunities and challenges for businesses of all sizes. Understanding the dynamics of a competitive market is crucial for success, requiring a deep dive into its characteristics, strategies for thriving within it, and the potential pitfalls to avoid.
Defining the Competitive Landscape: More Than Just "Many Players"
While the presence of many players is a key indicator, a truly competitive market goes beyond sheer numbers. Several factors contribute to its definition:
1. Numerous Sellers and Buyers: The Foundation of Competition
The most basic characteristic is the existence of many sellers offering similar products or services and a significant number of buyers with choices. This abundance of options fosters rivalry and keeps businesses on their toes. The sheer number of participants prevents any single entity from dominating the market and dictating prices.
2. Product Differentiation: Finding Your Niche
In a truly competitive market, products aren't always identical. While the core offering might be similar (e.g., coffee, smartphones), businesses differentiate themselves through branding, features, quality, customer service, and pricing. This differentiation allows businesses to carve out a niche and appeal to specific customer segments. Understanding your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is paramount.
3. Easy Entry and Exit: Dynamic Market Fluctuations
The ease with which new businesses can enter the market and existing ones can exit is another defining factor. Low barriers to entry—minimal capital requirements, readily available resources—encourage competition. Conversely, high barriers to entry (e.g., substantial capital investment, stringent regulations) limit the number of competitors, potentially leading to less competition. Similarly, the ability to easily exit the market prevents businesses from being trapped in unprofitable ventures, fostering market efficiency.
4. Perfect Information (Theoretically): The Ideal State
In an idealized competitive market (often referred to as "perfect competition"), buyers and sellers possess perfect information about prices, products, and market conditions. This transparency prevents price gouging or exploitation. While perfect information is a theoretical ideal rarely achieved in reality, the closer a market gets to it, the more competitive it tends to be.
5. Price as the Primary Competitive Weapon: The Battle for Value
In intensely competitive markets, price often becomes a key battleground. Businesses must carefully balance pricing strategies with profitability, considering factors like production costs, customer perceptions of value, and competitor pricing. Price wars, while potentially damaging, are a common occurrence in highly competitive environments.
Navigating the Competitive Market: Strategies for Success
Successfully competing in a crowded marketplace requires a well-defined strategy encompassing several key areas:
1. Differentiation: Standing Out From the Crowd
Product differentiation is essential. This goes beyond simply offering a slightly different version of an existing product. It requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences and the ability to deliver a product or service that meets those needs better than the competition. This can be achieved through:
- Innovation: Introducing new features, technologies, or functionalities.
- Branding: Creating a strong brand identity that resonates with your target audience.
- Customer Service: Providing exceptional customer support and building strong relationships.
- Quality: Ensuring superior quality in materials, manufacturing, and overall product performance.
- Niche Marketing: Focusing on a specific segment of the market with unique needs.
2. Cost Leadership: The Efficiency Advantage
Achieving cost leadership involves becoming the most efficient producer in the market. This allows you to offer lower prices than your competitors while maintaining profitability. Strategies include:
- Streamlining Operations: Optimizing production processes and reducing waste.
- Economies of Scale: Increasing production volume to reduce per-unit costs.
- Supply Chain Management: Establishing efficient and reliable supply chains.
- Technological Advancements: Leveraging technology to automate processes and improve efficiency.
3. Marketing and Branding: Building Awareness and Loyalty
Effective marketing and branding are critical for attracting and retaining customers. This involves:
- Market Research: Understanding your target audience, their needs, and their preferences.
- Targeted Advertising: Reaching your ideal customers through the most effective channels.
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable and engaging content that attracts and educates your audience.
- Building Brand Awareness: Establishing a strong and recognizable brand identity.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Building and maintaining relationships with customers.
4. Innovation: The Engine of Growth
Continuous innovation is vital for maintaining a competitive edge. This involves:
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development to develop new products and services.
- Adaptability: Being able to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- Experimentation: Trying new things and learning from successes and failures.
- Embracing Technology: Utilizing new technologies to improve products, services, and processes.
5. Strategic Alliances and Partnerships: Expanding Reach and Resources
Collaborating with other businesses through strategic alliances and partnerships can provide access to new markets, technologies, and resources. This can be achieved through:
- Joint Ventures: Creating new businesses in collaboration with other companies.
- Licensing Agreements: Granting other businesses the right to use your intellectual property.
- Distribution Partnerships: Partnering with distributors to expand your reach.
The Challenges of a Competitive Market: Avoiding the Pitfalls
While competitive markets offer opportunities, they also present significant challenges:
1. Price Wars: The Race to the Bottom
Intense competition can lead to price wars, where businesses constantly lower prices to attract customers, often at the expense of profitability. This can be a destructive cycle that harms all participants.
2. High Marketing Costs: The Battle for Attention
Attracting customers in a crowded marketplace requires significant marketing investments. This can be a substantial drain on resources, especially for smaller businesses.
3. Increased Risk of Failure: The High-Stakes Game
The competitive nature of the market means a higher risk of failure. Businesses that fail to adapt, innovate, or differentiate themselves are likely to be outcompeted.
4. Difficulty in Building Brand Loyalty: Constant Competition for Customer Attention
Building strong brand loyalty can be challenging when customers are constantly bombarded with choices. Businesses must work hard to establish themselves as the preferred option.
Examples of Competitive Markets: Across Industries
Numerous industries demonstrate the characteristics of competitive markets:
- Fast Food: Numerous chains and independent restaurants compete for customers based on price, convenience, and menu offerings.
- Smartphones: Major players like Apple and Samsung compete fiercely through innovation, features, and branding.
- Online Retail: Websites like Amazon, eBay, and countless smaller retailers compete on price, selection, and convenience.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Many businesses offer similar software solutions, competing on features, pricing, and customer support.
- Grocery Retail: Supermarkets and hypermarkets compete fiercely on price, selection, and convenience, often leading to localized competition based on geographical location.
Conclusion: Embracing the Challenge, Seizing the Opportunity
A competitive market, while demanding, is a dynamic environment rife with opportunities for businesses that adapt, innovate, and differentiate themselves. Understanding the nuances of competition—from product differentiation and cost leadership to effective marketing and strategic alliances—is crucial for success. By embracing the challenges and strategically navigating the complexities, businesses can not only survive but thrive in even the most saturated markets. The key is to identify your unique strengths, understand your target market deeply, and consistently deliver value. This approach, coupled with adaptability and a commitment to continuous improvement, will empower businesses to not just compete, but to win in the competitive marketplace.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Not A N Expense Account
Mar 16, 2025
-
In C3 Plants The Conservation Of Water Promotes
Mar 16, 2025
-
Food Preservation Does All Of The Following Except
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats 2 1 8 25 3 0
Mar 16, 2025
-
Alternate Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Competitive Market Is A Market In Which . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
