A Company's Environmental Sustainability Strategy Concerns
Holbox
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
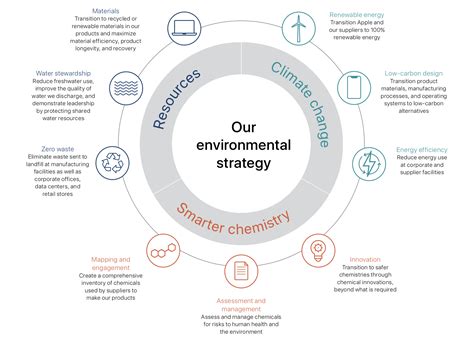
Table of Contents
- A Company's Environmental Sustainability Strategy Concerns
- Table of Contents
- A Company's Environmental Sustainability Strategy Concerns: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Corporate Responsibility
- Defining the Scope: Identifying Key Environmental Concerns
- 1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs):
- 2. Water Usage and Management:
- 3. Waste Generation and Management:
- 4. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection:
- 5. Air and Water Pollution:
- Challenges in Implementing an Effective Sustainability Strategy
- 1. Cost and Investment:
- 2. Measuring and Reporting Progress:
- 3. Supply Chain Complexity:
- 4. Lack of Data and Transparency:
- 5. Regulatory and Policy Landscape:
- 6. Stakeholder Engagement and Communication:
- 7. Balancing Sustainability with Business Objectives:
- Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Building a Robust Sustainability Strategy
- 1. Setting Ambitious but Achievable Goals:
- 2. Investing in Technology and Innovation:
- 3. Engaging with the Supply Chain:
- 4. Embracing Transparency and Disclosure:
- 5. Building a Culture of Sustainability:
- 6. Seeking External Expertise and Collaboration:
- 7. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
- Conclusion: The Long-Term Value of Environmental Sustainability
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Company's Environmental Sustainability Strategy Concerns: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Corporate Responsibility
The increasing global awareness of environmental issues has placed immense pressure on companies to adopt robust environmental sustainability strategies. No longer is "going green" a mere marketing tactic; it's a critical aspect of long-term business viability, impacting brand reputation, investor confidence, and regulatory compliance. However, developing and implementing a truly effective environmental sustainability strategy is far from simple. This article delves into the multifaceted concerns companies face in this arena.
Defining the Scope: Identifying Key Environmental Concerns
Before diving into specific challenges, it's crucial to clearly define the scope of a company's environmental impact. This involves conducting a thorough environmental audit, identifying key areas of concern, and prioritizing action based on materiality. Key areas often include:
1. Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHGs):
- Scope 1 Emissions: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, such as company vehicles and on-site energy generation. Reducing Scope 1 emissions is often a priority, involving transitions to renewable energy, energy efficiency improvements, and fleet electrification.
- Scope 2 Emissions: Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy, such as electricity consumed in offices and manufacturing facilities. Switching to renewable energy suppliers and improving energy efficiency are key strategies here.
- Scope 3 Emissions: Indirect emissions across the value chain, encompassing everything from raw material extraction to product transportation and end-of-life management. Addressing Scope 3 emissions is often the most challenging, requiring collaboration with suppliers and customers, and implementing circular economy principles.
2. Water Usage and Management:
Companies with high water consumption, particularly in water-stressed regions, face significant challenges. Strategies need to focus on water conservation techniques, efficient irrigation systems (if applicable), wastewater treatment, and responsible sourcing of water. Transparency in water usage and reporting is becoming increasingly important.
3. Waste Generation and Management:
Waste reduction, reuse, and recycling are crucial aspects of environmental sustainability. This involves implementing waste minimization strategies throughout the production process, investing in recycling infrastructure, and exploring opportunities for waste-to-energy conversion. The aim is to minimize landfill waste and promote a circular economy.
4. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Protection:
Companies operating in areas with high biodiversity face growing pressure to minimize their impact on ecosystems. This includes protecting habitats, avoiding deforestation, and minimizing pollution that affects local flora and fauna. Sustainable sourcing of raw materials is also crucial in this context.
5. Air and Water Pollution:
Emissions of pollutants into the air and water can have severe environmental and health consequences. Companies need to comply with environmental regulations and implement pollution control technologies to minimize their impact. Regular monitoring and reporting are vital to ensure compliance and continuous improvement.
Challenges in Implementing an Effective Sustainability Strategy
Even with a clear understanding of environmental concerns, implementing a successful strategy presents several significant hurdles:
1. Cost and Investment:
Transitioning to sustainable practices often requires substantial upfront investment. This can be a major barrier for companies, particularly SMEs, who may lack the financial resources to implement significant changes. Securing funding, exploring financing options, and demonstrating the long-term return on investment (ROI) of sustainability initiatives are crucial.
2. Measuring and Reporting Progress:
Accurately measuring and reporting on environmental performance is essential for tracking progress and demonstrating accountability. However, establishing robust metrics and reporting frameworks can be complex and time-consuming. Standardization and transparency in reporting are vital for building trust with stakeholders.
3. Supply Chain Complexity:
Managing environmental sustainability throughout the entire supply chain is a major challenge. Companies need to engage with their suppliers and ensure they adhere to responsible environmental practices. This often involves establishing robust supplier codes of conduct, conducting supplier audits, and fostering collaborative relationships.
4. Lack of Data and Transparency:
Accurate data is critical for informed decision-making and effective environmental management. However, access to reliable data can be limited, particularly for Scope 3 emissions. Improving data collection, analysis, and transparency is crucial for effective environmental management.
5. Regulatory and Policy Landscape:
The environmental regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with new regulations and standards being introduced regularly. Companies need to stay abreast of these changes, ensure compliance, and adapt their strategies accordingly. This requires ongoing monitoring and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies.
6. Stakeholder Engagement and Communication:
Effective communication with stakeholders, including employees, investors, customers, and local communities, is vital for building trust and support for sustainability initiatives. Transparency in reporting, engaging in dialogue, and responding to stakeholder concerns are crucial for successful implementation.
7. Balancing Sustainability with Business Objectives:
One of the greatest challenges is integrating sustainability into core business strategies without compromising profitability. Companies need to find innovative ways to reconcile environmental goals with economic objectives, demonstrating that sustainability is not a cost but a strategic advantage.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Building a Robust Sustainability Strategy
Addressing the challenges mentioned above requires a multi-pronged approach, encompassing:
1. Setting Ambitious but Achievable Goals:
Start by setting clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These goals should be aligned with international frameworks like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and incorporate targets for reducing emissions, conserving resources, and minimizing waste.
2. Investing in Technology and Innovation:
Investing in new technologies and innovations can significantly enhance environmental performance. This could include renewable energy technologies, energy-efficient equipment, water treatment systems, and waste management solutions. Exploring and adopting circular economy models is also crucial.
3. Engaging with the Supply Chain:
Collaborate with suppliers to improve their environmental performance. This could involve implementing supplier codes of conduct, providing training and support, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with sustainability standards.
4. Embracing Transparency and Disclosure:
Commit to transparent reporting of environmental performance using standardized frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). This demonstrates accountability and builds trust with stakeholders.
5. Building a Culture of Sustainability:
Foster a culture of sustainability within the organization by integrating environmental considerations into all aspects of the business. This involves training employees, engaging them in sustainability initiatives, and rewarding them for their contributions.
6. Seeking External Expertise and Collaboration:
Collaborate with external experts, such as environmental consultants and NGOs, to leverage their knowledge and experience in developing and implementing sustainability strategies. Participating in industry initiatives and sharing best practices can also facilitate progress.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
Regularly monitor environmental performance, identify areas for improvement, and adapt strategies as needed. This iterative process ensures continuous progress toward sustainability goals.
Conclusion: The Long-Term Value of Environmental Sustainability
In today's interconnected world, environmental sustainability is no longer a niche concern; it's a critical aspect of responsible business practice. While implementing a comprehensive environmental sustainability strategy presents numerous challenges, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. By proactively addressing environmental concerns, companies can enhance their brand reputation, attract investors, improve operational efficiency, and contribute to a more sustainable future. The journey towards sustainability is ongoing, requiring continuous adaptation and improvement. However, by embracing innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to transparency, companies can successfully navigate the complexities and unlock the significant value of environmental responsibility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match Each Term With Its Description
Mar 31, 2025
-
Income Smoothing Describes The Concept That
Mar 31, 2025
-
When Can A Notary Submit An Application For Reappointment
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Financial Advisor Schedules An Introductory Meeting
Mar 31, 2025
-
Match Each Principal Function Of Management With Its Definition
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Company's Environmental Sustainability Strategy Concerns . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
