A Calendar Year-end Reporting Period Is Defined As A
Holbox
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
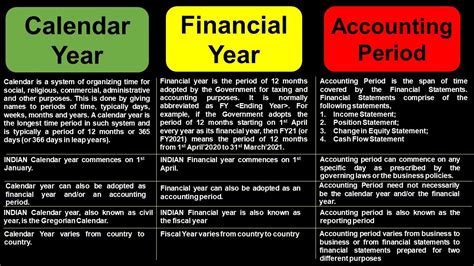
Table of Contents
- A Calendar Year-end Reporting Period Is Defined As A
- Table of Contents
- A Calendar Year-End Reporting Period is Defined As: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Definition: More Than Just Dates
- Key Aspects of the Definition:
- The Significance of Year-End Reporting
- 1. Financial Performance Evaluation:
- 2. Operational Efficiency Assessment:
- 3. Strategic Planning and Forecasting:
- 4. Compliance and Regulatory Reporting:
- The Year-End Reporting Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 1. Data Collection and Verification:
- 2. Financial Statement Preparation:
- 3. Performance Analysis and KPI Review:
- 4. Internal Review and Audit:
- 5. External Audit (If Required):
- 6. Report Compilation and Distribution:
- Best Practices for Effective Year-End Reporting
- Conclusion: A Foundation for Future Success
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
A Calendar Year-End Reporting Period is Defined As: A Comprehensive Guide
The calendar year-end reporting period, a crucial aspect of financial accounting and business operations, signifies the concluding twelve months of a calendar year, typically spanning from January 1st to December 31st. This period isn't just about summarizing the past; it's a critical juncture for analysis, planning, and strategic decision-making for the upcoming year. Understanding its definition, implications, and best practices is essential for businesses of all sizes.
Understanding the Definition: More Than Just Dates
While the simple definition—January 1st to December 31st—is accurate, a deeper understanding requires acknowledging the broader context. The calendar year-end reporting period is defined by its purpose: to provide a comprehensive, standardized overview of a company's financial performance, operational efficiency, and overall health over a specific, consistent timeframe. This standardized period facilitates comparison across years, allowing for trend analysis and informed strategic planning.
Key Aspects of the Definition:
- Standardization: The use of a calendar year ensures consistency across industries and companies, enabling easier comparison and benchmarking.
- Comprehensive Reporting: The period necessitates a complete review of all financial transactions, operational activities, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Many legal and regulatory requirements mandate year-end reporting for tax purposes, audits, and investor relations.
- Strategic Planning: The year-end report serves as a crucial foundation for developing future strategies, setting realistic goals, and allocating resources effectively.
- Internal and External Communication: The report is used for internal communication amongst management and employees, as well as for external communication with stakeholders like investors, lenders, and government agencies.
The Significance of Year-End Reporting
The significance of the calendar year-end reporting period extends far beyond simply fulfilling legal obligations. It’s a vital process that drives informed decision-making and overall business success. Let's delve into some key aspects:
1. Financial Performance Evaluation:
The year-end report provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial health. This includes:
- Revenue and Expenses: Detailed analysis of revenue streams, operating expenses, and the overall profit or loss for the year.
- Profitability Ratios: Key metrics like gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on investment (ROI) are calculated to assess profitability.
- Liquidity and Solvency: Evaluation of the company’s ability to meet its short-term and long-term obligations through liquidity ratios and solvency ratios.
- Cash Flow Analysis: Assessment of the movement of cash within the business, including cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities.
2. Operational Efficiency Assessment:
Beyond financial performance, the reporting period assesses operational efficiency:
- Productivity Metrics: Analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to production, sales, and marketing efficiency.
- Process Optimization: Identification of areas where processes can be streamlined and improved to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Inventory Management: Review of inventory levels, turnover rates, and potential waste or obsolescence.
- Supply Chain Management: Assessment of the effectiveness of the supply chain in delivering goods and services.
3. Strategic Planning and Forecasting:
The comprehensive data gathered during the year-end reporting period is crucial for:
- Budgeting: Development of accurate budgets for the upcoming year based on past performance and anticipated trends.
- Investment Decisions: Informed decisions regarding capital investments and resource allocation based on financial projections.
- Market Analysis: Review of market trends, competitive landscape, and potential opportunities and threats.
- Risk Management: Identification and mitigation of potential risks based on past performance and future projections.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Reporting:
Accurate year-end reporting is essential for compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements:
- Tax Returns: Accurate reporting of income and expenses for tax purposes.
- Audits: Preparation for external audits conducted by independent auditors to ensure financial statement accuracy.
- Regulatory Filings: Submission of required reports to relevant regulatory bodies.
- Investor Relations: Providing accurate and timely information to investors and other stakeholders.
The Year-End Reporting Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The year-end reporting process is complex and involves several key steps:
1. Data Collection and Verification:
This initial phase involves gathering all relevant financial and operational data from various sources. This data needs to be meticulously verified for accuracy and completeness.
2. Financial Statement Preparation:
Based on the collected and verified data, the core financial statements are prepared:
- Income Statement: Shows the company's revenue, expenses, and profit or loss for the year.
- Balance Sheet: Provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of the year.
- Cash Flow Statement: Illustrates the movement of cash within the business during the year.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: Shows changes in the company's equity during the year.
3. Performance Analysis and KPI Review:
This stage involves a detailed analysis of the financial statements and key performance indicators to identify trends, strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. Ratio analysis, trend analysis, and benchmarking are common techniques used.
4. Internal Review and Audit:
Before external reporting, the financial statements undergo a rigorous internal review process. This often involves an internal audit to ensure accuracy and compliance.
5. External Audit (If Required):
Many companies, particularly publicly traded ones, are required to undergo an independent external audit by a certified public accountant (CPA) firm.
6. Report Compilation and Distribution:
The final report, incorporating the financial statements, performance analysis, and other relevant information, is compiled and distributed to internal stakeholders, external stakeholders, and regulatory bodies.
Best Practices for Effective Year-End Reporting
To ensure the effectiveness and accuracy of year-end reporting, several best practices should be followed:
- Establish Clear Procedures: Implement clear and consistent procedures for data collection, verification, and reporting throughout the year.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage accounting software and other technology tools to streamline the reporting process and enhance accuracy.
- Maintain Strong Internal Controls: Implement robust internal controls to prevent errors, fraud, and other irregularities.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) throughout the year to identify potential issues early on.
- Invest in Training: Provide adequate training to employees involved in the reporting process to ensure they understand procedures and best practices.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Consider seeking professional assistance from accountants, auditors, or financial consultants, especially for complex situations.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Future Success
The calendar year-end reporting period is far more than just a deadline; it’s a pivotal moment for reflection, analysis, and planning. By understanding its definition, significance, and best practices, businesses can leverage this period to gain valuable insights into their performance, identify areas for improvement, and build a strong foundation for future success. The accuracy and completeness of this reporting are crucial not only for legal and regulatory compliance but also for making informed strategic decisions that drive growth and profitability. A well-executed year-end reporting process is a cornerstone of successful business management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Aluminum
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Customer Is Calling Her Insurance Company
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Device Consisting Of Four Heavy Balls
Apr 02, 2025
-
You Receive An Email Marked Important From Your Boss
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Bureau Of Transportation Statistics Collects Analyzes And Disseminates
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Calendar Year-end Reporting Period Is Defined As A . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
