111.3 With A Standard Deviation Of 62.9
Holbox
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
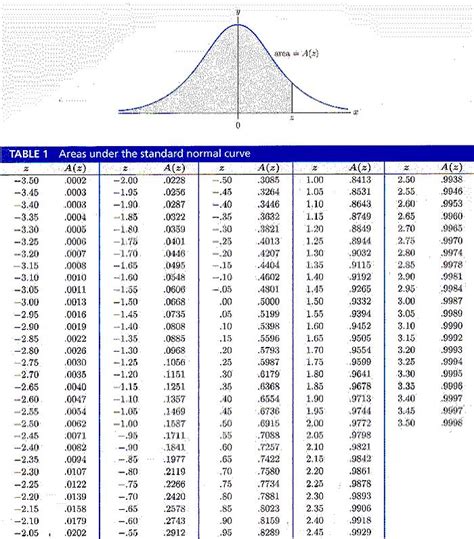
Table of Contents
- 111.3 With A Standard Deviation Of 62.9
- Table of Contents
- Unveiling the Secrets Behind a Dataset: Exploring a Mean of 111.3 and a Standard Deviation of 62.9
- Understanding Mean and Standard Deviation
- The Mean: A Measure of Central Tendency
- The Standard Deviation: A Measure of Dispersion
- Interpreting the Dataset: Mean = 111.3, Standard Deviation = 62.9
- Implications and Further Analysis
- 1. Data Visualization
- 2. Outlier Detection and Treatment
- 3. Exploring Underlying Factors
- 4. Confidence Intervals
- 5. Statistical Tests
- Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Further Analysis
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Unveiling the Secrets Behind a Dataset: Exploring a Mean of 111.3 and a Standard Deviation of 62.9
This article delves deep into the statistical significance of a dataset characterized by a mean of 111.3 and a standard deviation of 62.9. We will explore what these figures tell us about the data's distribution, variability, and potential underlying patterns. Understanding these parameters is crucial for data analysis, interpretation, and drawing meaningful conclusions. We'll cover various aspects, including:
Understanding Mean and Standard Deviation
Before we dive into the specifics of our dataset (mean = 111.3, standard deviation = 62.9), let's solidify our understanding of these fundamental statistical concepts.
The Mean: A Measure of Central Tendency
The mean, often referred to as the average, is the sum of all values in a dataset divided by the number of values. It provides a single number representing the central tendency or typical value of the data. In our case, a mean of 111.3 suggests that the "average" value within the dataset is 111.3.
The Standard Deviation: A Measure of Dispersion
The standard deviation measures the spread or dispersion of the data around the mean. It quantifies how much the individual data points deviate from the average. A high standard deviation indicates a wide spread of data, meaning the values are widely scattered around the mean. Conversely, a low standard deviation implies that the data points are clustered closely around the mean. Our standard deviation of 62.9 signifies a relatively large spread in the data.
Interpreting the Dataset: Mean = 111.3, Standard Deviation = 62.9
Having established the meaning of mean and standard deviation, let's analyze our specific dataset. The combination of a mean of 111.3 and a standard deviation of 62.9 reveals important characteristics:
-
Significant Variability: The standard deviation of 62.9 is considerably large relative to the mean of 111.3. This suggests substantial variability within the data. The data points are spread quite far from the average value.
-
Potential Outliers: The high standard deviation hints at the possibility of outliers – data points that are unusually high or low compared to the rest of the data. These outliers can significantly influence the mean and standard deviation. Further investigation is needed to identify and potentially address these outliers.
-
Skewness: The relationship between the mean and standard deviation doesn't directly indicate skewness (whether the data is more spread out on one side of the mean than the other). However, the large standard deviation relative to the mean suggests the possibility of significant skewness. Skewness can impact the interpretation of the mean as a representative value.
-
Data Distribution: Without knowing the specific dataset, we cannot definitively determine the underlying distribution (normal, skewed, uniform, etc.). However, the high standard deviation suggests that it is unlikely to be a tightly clustered, near-normal distribution. Histograms or other visual representations of the data would be highly beneficial in identifying the distribution.
Implications and Further Analysis
The high standard deviation (62.9) compared to the mean (111.3) demands a deeper investigation. Several crucial steps should be taken to better understand and interpret this dataset:
1. Data Visualization
Creating visual representations of the data, such as histograms, box plots, and scatter plots, is essential. These visuals will reveal the distribution's shape, identify potential outliers, and provide a clearer picture of the data's spread. For example, a histogram will visually confirm whether the data is skewed or close to a normal distribution. A box plot will effectively display the median, quartiles, and outliers.
2. Outlier Detection and Treatment
Identifying and dealing with outliers is crucial. Outliers can significantly distort statistical measures like the mean and standard deviation. Methods for detecting outliers include:
-
Z-score: Calculate the Z-score for each data point. Data points with Z-scores exceeding a certain threshold (e.g., |Z| > 3) are typically considered outliers.
-
IQR (Interquartile Range): Use the IQR method to identify data points that fall outside a specified range.
Once outliers are identified, decisions need to be made on how to handle them. Options include:
-
Removal: Removing outliers is sometimes appropriate if they're due to errors in data collection or represent truly exceptional circumstances outside the typical range of the dataset.
-
Transformation: Applying transformations (e.g., logarithmic transformation) can sometimes reduce the influence of outliers.
-
Winsorizing/Trimming: Replacing outliers with less extreme values (Winsorizing) or removing a certain percentage of extreme values (Trimming) are other options.
3. Exploring Underlying Factors
Understanding the context of the data is crucial. What does this dataset represent? Knowing the source and nature of the data can help explain the high standard deviation. Are there underlying factors contributing to the wide spread of values? Identifying these factors could lead to more insightful interpretations.
4. Confidence Intervals
Calculating confidence intervals around the mean will provide a range within which the true population mean likely lies. This helps account for the uncertainty inherent in using a sample to estimate the population parameter. The large standard deviation will result in a wider confidence interval, reflecting the higher uncertainty.
5. Statistical Tests
Depending on the research question, various statistical tests might be appropriate. For instance, if comparing this dataset to another, a t-test could be used. The large standard deviation needs to be considered when choosing and interpreting the results of any statistical test.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Further Analysis
A mean of 111.3 and a standard deviation of 62.9 reveal a dataset with substantial variability. The high standard deviation highlights the importance of further analysis to understand the data's underlying distribution, potential outliers, and influencing factors. Without additional information and further analysis, drawing definitive conclusions would be premature and potentially misleading. Visualizations, outlier detection, and exploring the data's context are crucial steps to gain a complete understanding of this dataset and its implications. Remember, statistical measures alone do not tell the whole story; a comprehensive approach incorporating data visualization, context understanding, and careful consideration of potential biases is paramount for robust data interpretation. The large standard deviation is not inherently "bad" or "good" - its significance depends entirely on the context of the data and the questions you're trying to answer.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 111.3 With A Standard Deviation Of 62.9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.